 PDF(3223 KB)
PDF(3223 KB)


 PDF(3223 KB)
PDF(3223 KB)
 PDF(3223 KB)
PDF(3223 KB)
GEDI与ICESat-2星载激光雷达数据反演树高研究
Inversion of tree height from GEDI and ICESat-2 spaceborne lidar
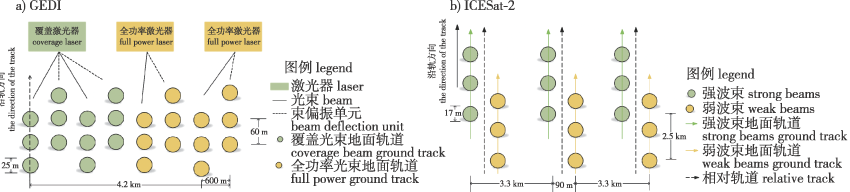
【目的】全球生态系统动力学调查(GEDI)多波束激光雷达与冰、云和陆地高程卫星二代(ICESat-2) 光子云使用不同激光雷达技术,导致两个任务之间的树高提取值存在差异。比较两种星载激光雷达数据在不同情况下有效反演树高的能力,为空间连续大区域高分辨率森林树高制图提供理论基础。【方法】通过对GEDI L2A字段信息进行定位和筛选,并进行地形高程精度验证,对比6种算法组反演树高;对ICESat-2数据去噪并提出基于坡度变化的光子云分类算法,建立地面光子线和冠层顶线反演树高,利用实测数据和机载激光雷达数据,验证并比较GEDI和ICESat-2在研究区内反演树高的精度。最后,定量分析GEDI和ICESat-2数据在不同地形坡度、植被覆盖度和森林类型情况下反演树高的差异。【结果】针对GEDI L2A产品数据,通过比较6组GEDI L2A算法中最优算法的反演精度为:R2=0.94,均方根误差(RMSE)为2.31 m,绝对平均误差(MAE)为1.27 m。针对ICESat-2 数据,通过使用50 m窗口计算,基于坡度变化的光子云分类算法提取树高与机载树高的R2=0.81,RMSE为3.68 m,MAE为2.45 m。植被覆盖度相对于地形坡度和森林类型对两种星载激光雷达反演树高产生更大的影响。【结论】对于较为平缓且森林类型以针叶林为主的较密集区域,其GEDI数据相比于ICESat-2数据表现出更优的评价精度。
【Objective】Global ecosystem dynamics investigation (GEDI) multibeam lidar and ice, cloud and land elevation satellite-2 (ICESat-2) photon clouds use different lidar technologies, resulting in differences in tree height extraction values between the two tasks. The purpose of this study is to compare the ability of two spaceborne lidar data to effectively invert forest height under different conditions. 【Method】By locating and filtering the GEDI L2A field information, and verifying the terrain elevation accuracy, the tree height of six algorithm groups was compared. The ICESat-2 data was denoised, a photonic cloud classification algorithm based on slope change was proposed, the ground photon line and the canopy top line inversion forest height were established, and the accuracy of GEDI and ICESat-2 in the study area was verified and compared by using the measured data and airborne lidar data. Finally, the differences of GEDI and ICESat-2 data in different terrain slopes, vegetation coverage and forest types were quantitatively analyzed. 【Result】According to the GEDI L2A product data, by comparing the optimal algorithms in GEDI L2A algorithm group from a1 to a6, the inversion accuracy of a4 was better: R2=0.94, root mean square error was 2.31 m, and mean absolute error was 1.27 m. For ICESat-2 data, R2=0.81, the root mean square error was 3.68 m, and the mean absolute error was 2.45 m, calculated using a 50 m window. Vegetation coverage had a greater impact on the tree height of the two spaceborne lidars compared to the terrain slope and forest type. 【Conclusion】Compared with ICESat-2 data, GEDI data showed a better evaluation accuracy standard for the more gentle and densely populated areas with coniferous forest types.
全球生态系统动力学调查(GEDI) / 冰、云和陆地高程卫星二代(ICESat-2) / 反演树高 / 地形坡度 / 植被覆盖度 / 森林类型 / 星载激光雷达
global ecosystem dynamics investigation(GEDI) / ice, cloud and land elevation satellite-2 (ICESat-2) / invert tree height / terrain slope / vegetation coverage / forest type / spaceborne LiDAR
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
胡艳, 王迪, 刘凌菲, 等. 利用大光斑激光雷达估测小兴安岭平均树高[J]. 安徽农业科学, 2014, 42(15):4707-4709.
|
| [8] |
董瀚元, 于颖, 范文义. 星载激光雷达GEDI数据林下地形反演性能验证[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2023, 47(2):141-149.
|
| [9] |
吴伟东. 联合卫星遥感影像与光子雷达数提取山林地区数字高程模型[D]. 广州: 广东工业大学, 2022.
|
| [10] |
黄佳鹏. 基于ICESat-2/ATLAS光子计数LiDAR数据反演森林冠层高度研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 东北林业大学, 2021.
|
| [11] |
覃志刚, 尤号田, 黄元威, 等. 不同植被覆盖区ICESat-2和GF-7卫星地表高程信息对比研究[J]. 航天返回与遥感, 2023, 44(5):91-104.
|
| [12] |
张少伟. 基于多源数据的内蒙古大兴安岭林区森林资源变化监测研究[D]. 北京: 中国林业科学研究院, 2019.
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
陆大进, 黎东, 朱笑笑, 等. 基于卷积神经网络的ICESat-2光子点云去噪分类[J]. 地球信息科学学报, 2021, 23(11):2086-2095.
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
陈雨莹, 王龑, 邹艳红, 等. 全球土地覆盖产品中森林类型数据在中国区域的质量评估[J]. 遥感技术与应用, 2023, 38(2):341-352.
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
韩明辉, 邢艳秋, 李国元, 等. GEDI不同算法组数据反演森林最大冠层高度和生物量精度比较[J]. 中南林业科技大学学报, 2022, 42(10):72-82.
|
| [22] |
秦磊. 基于ICESat-2星载激光雷达光子云数据反演森林冠层高度方法研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 东北林业大学, 2020.
|
| [23] |
王丽, 李毅, 朱建军, 等. ICESat-2 ATL08地形和冠层高度产品精度评估[J]. 遥感信息, 2023, 38(4): 144-152.
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |