 PDF(4192 KB)
PDF(4192 KB)


不同气候情景下照山白潜在适生区的预测
冯潇, 陈非非, 杨君利, 刘海龙, 唐玉红, 李金凤, 施晓灯, 贾忠奎, 尹群
南京林业大学学报(自然科学版) ›› 2025, Vol. 49 ›› Issue (4) : 161-169.
 PDF(4192 KB)
PDF(4192 KB)
 PDF(4192 KB)
PDF(4192 KB)
不同气候情景下照山白潜在适生区的预测
Prediction of potential suitable areas of Rhododendron micranthum under different climate scenarios
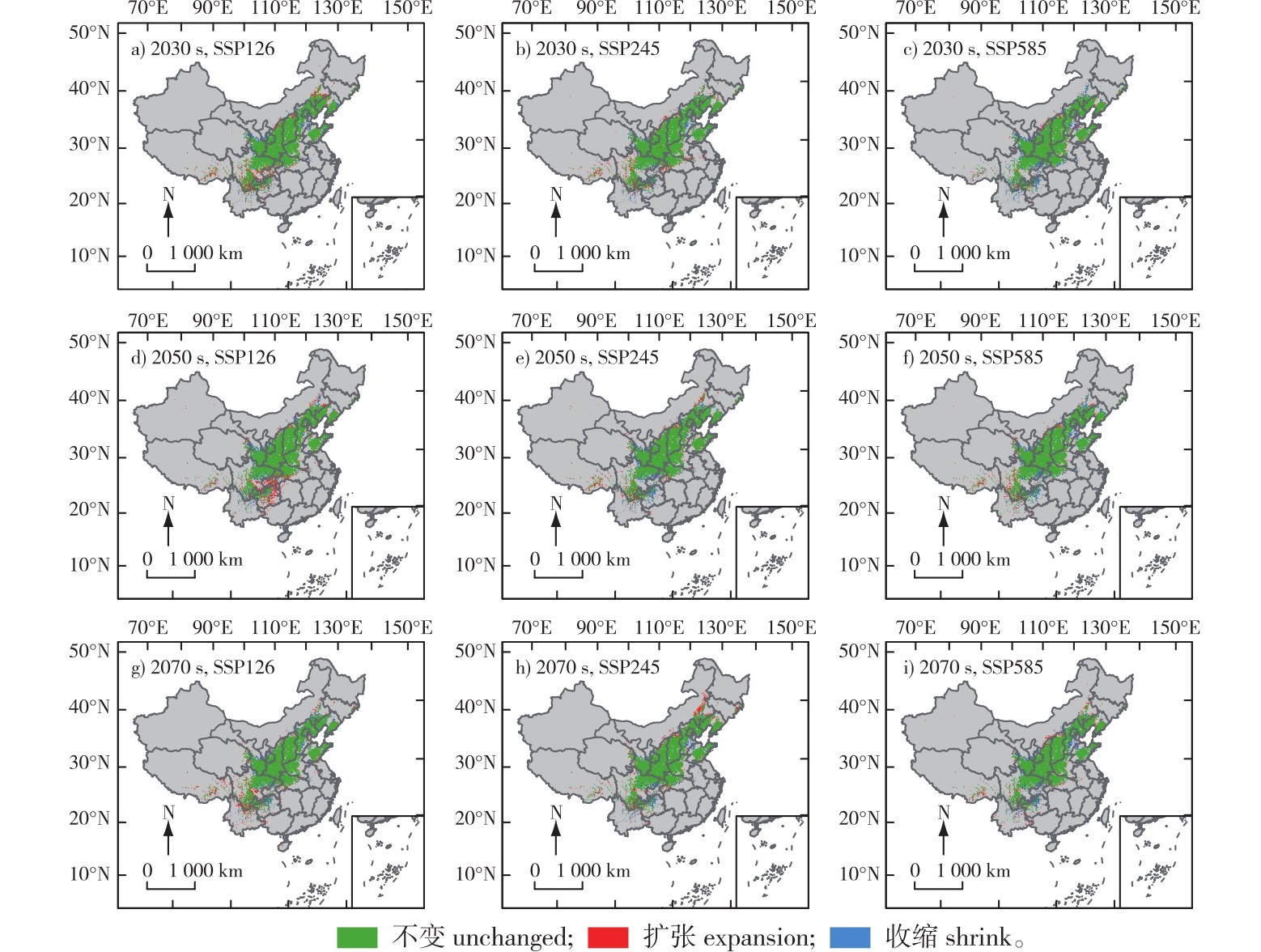
【目的】研究影响杜鹃花科植物照山白(Rhododendron micranthum)分布的主要环境变量及未来气候变化情景下照山白在中国的潜在地理分布,为冬季缺绿城市景观的提升提供资源,也为物种的保护和管理提供科学依据。【方法】以照山白为研究对象,运用R语言kuenm软件包优化的MaxEnt模型和ArcGIS软件,基于182条照山白分布点数据和18个环境变量进行潜在适生区预测,研究影响其地理分布的主要环境变量,同时预测其在3种温室气体排放路径下即2030s(2021—2040年)、2050s(2041—2060年)和2070s(2061—2080年)潜在适生区的空间分布格局和质心变化趋势。【结果】①最优模型参数正则化乘数调控倍频RM为2.9、特征组分FC为LQPTH时,模型预测AUC值最高(0.973 2±0.007 1);②影响照山白适生区分布主要环境变量及阈值为最冷月最低温(-13.48~1.02 ℃),最热季降水量(270.12~404.76 mm),环境变量在阈值范围内,照山白表现出一定的适生性;③当前气候条件下,照山白高、中、低适生区面积分别为43.83×104、43.79×104和62.01×104 km2,主要分布在北京、甘肃、陕西、河北、山东、山西、河南、辽宁和四川,其中,北京的平均适生指数最高(0.801 5);④未来气候条件下,温室气体排放强度越大,照山白总适生区越小,表明全球气候变暖不利于照山白的生长,同时,SSP126(低强迫情景)情景下,物种分布质心向低纬度迁移;SSP585(高强迫情景)情景下,质心向高纬度迁移。【结论】利用MaxEnt模型进行照山白不同时期潜在分布预测结果可靠,在未来气候情景下,照山白在中国适生区的破碎化程度均加重,低温室气体浓度排放下的气候条件有利于照山白植物的生长,高温室气体浓度排放下的气候条件使得照山白适生区面积减少。
【Objective】This study is dedicated to explore the key environmental variables affecting the distribution of Rhododendron micranthum and predicting its potential geographical distribution under future climate change scenarios in China. The findings aim to support urban greening strategies for winter vegetation-deficient cities and provide scientific guidance for species conservation and management of R. micranthum.【Method】R. micranthum was taken as the research object. Based on 182 distribution points and 34 environmental factors, the MaxEnt model and ArcGIS software, optimized by the R language kuenm software package, were utilized to predict the potential suitable areas. The main environmental variables influencing its geographical distribution were analyzed. Additionally, the spatial distribution patterns and centroid change trends of potential suitable areas in the 2030s (2021-2040), 2050s (2041-2060), and 2070s (2061-2080) under three different greenhouse gas emission scenarios were predicted.【Result】(1) When the optimal model parameters are set as RM = 2.9 and FC = LQPTH, the model achieves the highest prediction accuracy (AUC value is 0.973 2 ± 0.007 1).(2) The primary environmental variables and their corresponding thresholds that impact the distribution of suitable areas for R. micranthum are the lowest temperature of the coldest month, ranging from -13.48 ℃ to 1.02 ℃, and the rainfall during the hottest season, varying between 270.12 mm and 404.76 mm. Within the threshold ranges of these environmental variables, R. micranthum demonstrates a certain level of habitability.(3) Under the current climate conditions, the areas with high, medium, and low suitability for R. micranthum are 43.83×104, 43.79×104, and 62.01×104 km2, respectively. These areas are predominantly located in regions such as Beijing, Gansu, Shannxi, Hebei, Shandong, Henan, Liaoning, and Sichuan. Among them, Beijing has the highest average suitability index, which is 0.801 5.(4) Under future scenarios, higher emission intensities reduced total suitable areas, indicating global warming may hinder R. micranthum growth. Meanwhile, under the SSP126 (low-forcing scenario), the centroid of the suitable areas migrates towards lower latitudes, while under the SSP585 (high-forcing scenario), it migrates towards higher latitudes.【Conclusion】The analysis using the MaxEnt model yields reliable results for predicting the potential distribution of R. micranthum at different stages. In future climate scenarios, the fragmentation degree of suitable areas for R. micranthum in China is expected to increase. Climate conditions associated with low greenhouse gas concentration emissions are favorable for the growth of R. micranthum, whereas those under high greenhouse gas concentration emissions lead to a reduction in its suitable areas.
Rhododendron micranthum / potential suitable distribution / MaxEnt model / climate change
| [1] |
樊星, 秦圆圆, 高翔. IPCC第六次评估报告第一工作组报告主要结论解读及建议[J]. 环境保护, 2021, 49(增刊2):44-48.
|
| [2] |
张华, 赵浩翔, 王浩. 基于MaxEnt模型的未来气候变化情景下胡杨在中国的潜在地理分布[J]. 生态学报, 2020, 40(18):6552-6563.
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
杨宏, 董京京, 吴桐, 等. 基于MaxEnt模型的迎春樱桃潜在适生区预测[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2023, 47(4):131-138.
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
罗楚滢, 佘济云, 唐子朝. 基于SSPs气候场景的濒危植物银杉潜在分布区预测[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2024, 48(1):161-168.
|
| [15] |
谢登峰, 童芬, 杨丽娟, 等. MaxEnt模型下的外来入侵种香丝草在中国的潜在分布区预测[J]. 四川大学学报(自然科学版), 2017, 54(2):423-428.
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
孙娜. 照山白和耳叶杜鹃叶中的化学成分及其生物活性研究[D]. 武汉: 华中科技大学, 2019.
|
| [19] |
张艳红, 赵凤军, 王文平, 等. 辽宁耐寒杜鹃花资源调查[J]. 辽东学院学报(自然科学版), 2010, 17(2):98-102,132.
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
黄跃新, 王利宏. 照山白在园林绿化中应用的可行性研究[J]. 河北林果研究, 2012, 27(1):83-85.
|
| [22] |
柴冰. 照山白根化学成分及活性研究[D]. 北京: 北京协和医学院, 2020.
|
| [23] |
蒋淑磊, 白霄霞, 李国松, 等. 照山白杜鹃愈伤组织诱导及植株再生技术[J]. 分子植物育种, 2022, 20(5):1629-1634.
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
辛晓歌, 吴统文, 张洁, 等. BCC模式及其开展的CMIP6试验介绍[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2019, 15(5):533-539.
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
颜佳滢, 吴志峰, 申健, 等. 未来气候变化对粤港澳地区杜鹃花适生区的影响[J]. 生态学报, 2022, 42(13):5481-5492.
|
| [38] |
纪忠萍, 温晶, 方一川, 等. 近50年广东冬半年降水的变化及连旱成因[J]. 热带气象学报, 2009, 25(1):29-36.
|
| [39] |
云英英, 范秋云, 史佑海. 基于最大熵模型的海南杜鹃在中国的潜在地理分布[J]. 热带作物学报, 2024, 45(5):1031-1039.
|
| [40] |
高晓宁, 赵冰, 刘旭梅, 等. 4个杜鹃花品种对干旱胁迫的生理响应及抗旱性评价[J]. 浙江农林大学学报, 2017, 34(4):597-607.
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |