 PDF(2992 KB)
PDF(2992 KB)


接种丛枝菌根真菌(AMF)对夏雪片莲生长状况和光合特性的影响
王炜, 母洪娜, 杨慧敏, 孙陶泽
南京林业大学学报(自然科学版) ›› 2025, Vol. 49 ›› Issue (3) : 205-212.
 PDF(2992 KB)
PDF(2992 KB)
 PDF(2992 KB)
PDF(2992 KB)
接种丛枝菌根真菌(AMF)对夏雪片莲生长状况和光合特性的影响
The influence of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi (AMF) inoculation on the growth status and photosynthetic characteristics of Leucojum aestivum
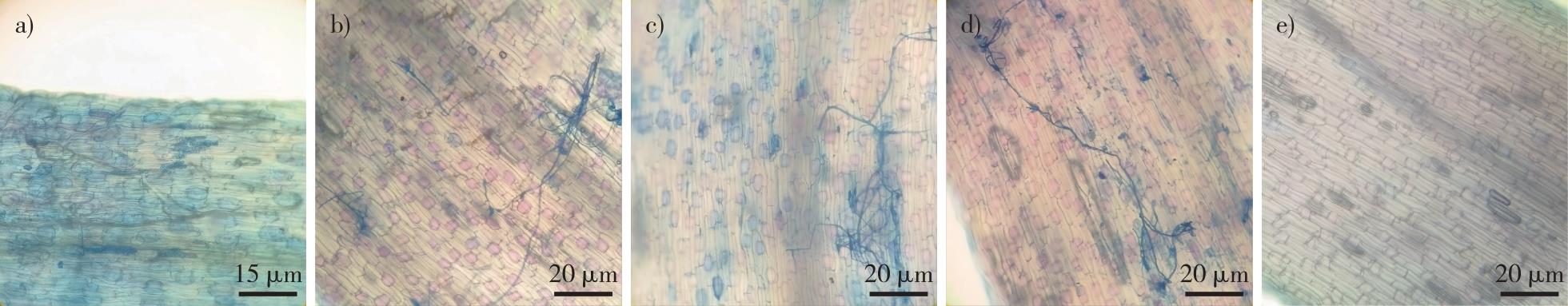
【目的】探究丛枝菌根真菌(arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi, AMF)定殖对夏雪片莲(Leucojum aestivum)生长和光合特性的影响,为培育高质量观赏及药用花卉提供相关依据。【方法】选择大小一致的夏雪片莲2年生球茎于温室中种植并接种AMF,试验组分别接种根内根孢囊霉(Rhizophagus intraradices, Ri)、摩西斗管囊霉(Funneliformis mosseae, Fm)和扭形多样孢囊霉(Diversispora tortuosa, Dt),以及混合接种3种AMF(以质量比1∶1∶1混合,Mi),对照组(CK)接种3类AMF混合(质量比1∶1∶1)的灭活菌剂;测定接种AMF后夏雪片莲的株高、干鲜质量及光合特性,并进行光合特性的相关性分析,同时采用隶属函数分析法综合评估所有指标。【结果】Fm组侵染率最高,为69.38%;Ri组最低,为36.93%,其中Ri组侵染率显著低于Fm、Dt和Mi组。在各处理组中,Fm组的株高最高(43.46 cm),且干质量也达到最大(39.94 g)。光合参数显示,Ri组表现出最高的气孔导度均值[Gs=0.30 mol/(m2·s)]、胞间CO2浓度均值(Ci=331 μmol/mol)和蒸腾速率均值[Tr=3.45 mmol/(m2·s)],其中Tr显著高于CK组。相关性分析揭示,净光合速率(Pn)与Gs在所有处理组中普遍呈显著正相关,气孔限制值(Ls)与Ci在菌根处理组中呈显著负相关;其余光合指标也存在一定的相关性,但不同处理间并未呈现规律性变化。隶属函数结果表明,Mi和Dt对夏雪片莲的光合能力和生物量综合影响较优。【结论】AMF的定殖能够有效促进夏雪片莲的生长,而且不同的AMF定殖对光合作用的影响效果不一;其中Dt和Mi对夏雪片莲的光合能力和生物量综合促进作用较好,Fm对夏雪片莲的株高具有促进作用,对光合能力影响不显著。
【Objective】This study investigated the effects of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi (AMF) colonization on the growth and photosynthetic characteristics of Leucojum aestivum. 【Method】Two-year-old bulbils of L. aestivum were selected as the experimental material. The experimental design consisted of five groups, three of which received single AMF inoculations [inoculated with Rhizophagus intraradices (Ri), Funneliformis mosseae (Fm), and Diversispora tortuosa (Dt)]. The fourth group was inoculated with a 1∶1∶1 mixture of the three AMF species (Mi), and the control group was inoculated with a sterilized 1∶1∶1 mixture of the AMFs. After two months, plant height, fresh and dry weight, and photosynthetic characteristics of L. aestivum were measured. 【Result】The Fm group exhibited the highest infection rate at 69.38%, while the Ri group had the lowest infection rate at 36.93%. The infection rate in the Ri group was significantly lower than those of the Fm, Dt, and Mi groups. Among the treatment groups, the Fm group showed the most plant height (43.46 cm) and the dry weight (39.94 g). Photosynthetic parameters indicated that the Ri group had the most average stomatal conductance [Gs = 0.30 mol/(m2·s), intercellular CO2 concentration (Ci = 331 μmol/mol), and transpiration rate (Tr = 3.45 mmol/(m2·s), with the transpiration rate significantly higher than in the control group (CK)]. Correlation analysis revealed a generally significant positive correlation between net photosynthetic rate (Pn) and Gs across all treatments, except for leaf stomatal conductance (Ls) and Ci. Although other photosynthetic indices exhibited correlations, no consistent pattern was observed across treatments. Membership function analysis indicated that the inoculation effect of the Mi group was the most beneficial, followed by Dt. 【Conclusion】AMF colonization effectively promotes the growth of L. aestivum. The effects on photosynthesis vary across different AMF species, with Dt and Mi significantly enhancing the photosynthetic capacity and biomass of L. aestivum. In contrast, Fm positively affected plant height but did not significantly influence photosynthetic capacity.
夏雪片莲 / 丛枝菌根真菌 / 生长状况 / 光合特性 / 相关性分析 / 隶属函数法
Leucojum aestivum. / arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi (AMF) / growth status / photosynthetic characteristics / correlation analysis / membership function method
| [1] |
殷小冬, 贾艳艳, 李其胜, 等. 丛枝菌根真菌和解磷细菌复合接种对水稻丛枝菌根真菌侵染率和肥料利用率的影响[J]. 江苏农业学报, 2023, 39(8):1680-1687.
|
| [2] |
吴亚胜, 王其传, 祁红英, 等. 育苗基质中添加丛枝菌根真菌菌剂对辣椒幼苗生长和光合参数的影响[J]. 蔬菜, 2018(7):12-16.
|
| [3] |
耿云芬, 邱琼, 卯吉华, 等. 铁力木幼苗接种丛枝菌根菌剂的效应[J]. 林业工程学报, 2015, 29(5):64-66.
|
| [4] |
袁洁, 吴晓晴, 石琨, 等. 丛枝菌根真菌对甘薯生物量、养分吸收和根系分泌物的影响[J]. 江苏农业学报, 2024, 40(11):2073-2082.
|
| [5] |
朱凌骏, 傅致远, 张金池, 等. 菌根真菌对榉树光合特性的影响[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 42(6):121-127.
|
| [6] |
崔令军, 刘瑜霞, 林健, 等. 丛枝菌根真菌对盐胁迫下桢楠光合生理的影响[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 45(1):101-106.
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
樊璐, 张莹, 李淑娟, 等. 夏雪片莲种子萌发特性的研究[J]. 西北林学院学报, 2011, 26(3):59-61.
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
张博, 石峰, 宋福强. AMF复合菌剂对寒地水稻光合作用和生长效应的影响[J]. 中国农学通报, 2022, 38(33):15-22.
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
叶子飘, 段世华, 康华靖. 不同CO2浓度下大豆叶片的水分利用效率比较[J]. 核农学报, 2019, 33(5):1006-1015.
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
温婷, 吴靖, 蔡军火, 等. 丛枝菌根真菌对红花石蒜植株及根际土壤养分影响[J]. 江西农业大学学报, 2023, 45(5):1196-1207.
|
| [18] |
王磊, 闫兴富, 唐占辉. 三种丛枝菌根真菌对浅裂剪秋萝生长的影响[J]. 北方园艺, 2021(20):77-83.
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
王玉娟, 高秀兵, 吴强盛, 等. 不同水分条件下AM真菌对福鼎大白茶生长和茶叶品质的影响[J]. 茶叶科学, 2020, 40(5):588-596.
|
| [21] |
彭思利, 王晓燕, 李剑, 等. 外生菌根真菌接种对干旱胁迫下构树幼苗生长及光合特性的影响[J]. 生态学杂志, 2021, 40(9):2719-2726.
|
| [22] |
吴维佳, 汪芳玲, 韩梦壮, 等. 根系内生真菌对田间油茶苗生长、气体交换和土壤特性的影响[J]. 经济林研究, 2023(4):163-169.
|
| [23] |
王紫瑄, 解甜甜, 王雅茹, 等. 丛枝菌根真菌(AMF)对蒙古沙冬青幼苗的促生特性及作用机制[J]. 干旱区研究, 2023, 40(1):78-89.
|
| [24] |
杨国, 卢可, 朱高樑, 等. 丛枝菌根真菌摩西斗管囊霉对铜胁迫下白术幼苗光合特性及抗氧化酶活性的影响[J]. 植物生理学报, 2018, 54(4):618-626.
|
| [25] |
刘选帅, 孙延亮, 安晓霞, 等. 施磷和接种解磷菌对紫花苜蓿光合特性及生物量的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(3):189-199.
|
| [26] |
余海霞, 汤行昊, 刘南, 等. 控水与补水条件下连续热浪对闽楠光合特性和生长速率的影响[J]. 生态学报, 2023, 43(8):3224-3235.
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
齐敏兴, 刘晓静, 张晓磊, 等. 不同磷水平对紫花苜蓿光合作用和根瘤固氮特性的影响[J]. 草地学报, 2013, 21(3):512-516.
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |