 PDF(2084 KB)
PDF(2084 KB)


土壤碱性改良剂处理下银红槭叶色变化及其与叶片矿质元素的关系
吴翼, 刘勇, 周晓杰, 王开勇, 王文霄
南京林业大学学报(自然科学版) ›› 2025, Vol. 49 ›› Issue (2) : 115-122.
 PDF(2084 KB)
PDF(2084 KB)
 PDF(2084 KB)
PDF(2084 KB)
土壤碱性改良剂处理下银红槭叶色变化及其与叶片矿质元素的关系
Changes in leaf color and their relationship with leaf mineral elements under soil alkaline conditioners of Acer×freemanii
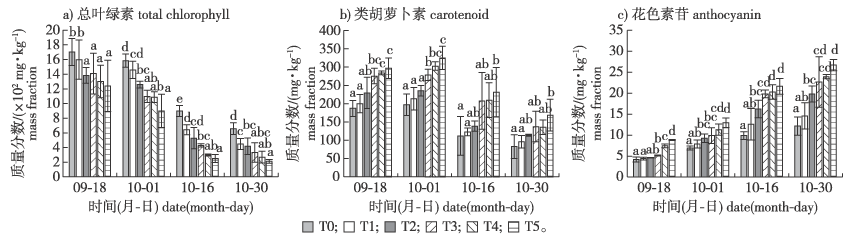
【目的】研究土壤改良剂对银红槭(Acer×freemanii)叶色变化的影响以及叶色变化与叶片矿质元素含量之间的关系,为解决银红槭叶色不红现象提供理论依据。【方法】以6年生银红槭为材料,设置了5个梯度的硫磺粉+脱硫石膏土壤碱性改良剂处理,并在秋季叶色转变的4个时间段测得叶片色素和10种矿质元素含量。【结果】土壤碱性改良剂处理能显著影响叶片叶绿素、类胡萝卜素和花色素苷含量,影响叶色参数L*、a*、b*值,而T5(1.94 kg/m3硫磺粉+2.33 kg/m3脱硫石膏)处理下呈色时间更长,叶色最为红艳;土壤碱性改良剂处理显著影响了叶片矿质元素含量以及变化趋势;叶片矿质元素与色素间相关性分析表明,N含量与叶绿素和类胡萝卜素含量呈极显著正相关(P<0.01),与花色素苷含量呈极显著负相关(P<0.01),K含量与类胡萝卜素含量呈显著负相关(P<0.05),Ca、Mg含量与叶绿素含量呈极显著负相关(P<0.01),与花色素苷含量呈显著正相关(P<0.05),Mn含量与类胡萝卜素含量呈极显著正相关(P<0.01)。【结论】在一定范围内,土壤pH降低能促进银红槭叶片呈色;施加土壤改良剂对银红槭叶片色素和矿质元素含量的影响是显著的,而叶片矿质元素,尤其是N、K、Ca、Mg、Mn与叶片显色具有较强相关性。
【Objective】 This study investigated the effects of soil amendments on the color changes in Acer×freemanii leaves and explored the relationship between leaf color changes and leaf mineral element content. The findings aim to provide a theoretical basis for addressing the issue of non-red coloration in Acer×freemanii leaves.【Method】Six-year-old Acer×freemanii trees were used as the experimental material. Five gradient treatments combining sulfur powder and desulfurization gypsum as soil alkaline amendments were applied. Leaf color changes were observed during four autumn time periods, with measurements of leaf pigments and the contents of ten mineral elements.【Result】Soil alkaline amendment treatments significantly influenced the contents of chlorophyll, carotenoids, and anthocyanins in leaves, as well as leaf color parameters (L*, a* and b* values). Among the treatments, T5 (1.94 kg/m3 sulfur powder and 2.33 kg/m3 desulfurized gypsum) resulted in the most vibrant leaf coloration and an extended period of color development. The treatments also significantly affected the content and variation trends of mineral elements in leaves. Correlation analysis revealed that nitrogen (N) showed a strong positive correlation with chlorophyll and carotenoids (P<0.01) and a strong negative correlation with anthocyanins (P < 0.01). Potassium (K) showed a significant negative correlation with carotenoids (P<0.05). Calcium (Ca) and Magnesium (Mg) showed a strong negative correlation with chlorophyll (P<0.01) and a significant positive correlation with anthocyanins (P<0.05). Manganese (Mn) showed a strong positive correlation with carotenoids (P<0.01).【Conclusion】Lowering soil pH within a certain range enhances the coloration of Acer×freemanii leaves. Soil amendments have a significant impact on pigment and mineral element contents in the leaves. Mineral elements, particularly N, K, Ca, Mg, and Mn, show strong correlations with leaf color changes, emphasizing their importance in managing leaf coloration.
Acer×freemanii / leaf mineral element / soil alkaline amendment / leaf color changes
| [1] |
梁杰. 北美彩色树种在北京地区的应用及其适应性评价[D]. 北京: 中国林业科学研究院, 2012.
|
| [2] |
何梅, 王华, 胡玉安, 等. 彩叶树种研究与开发利用现状[J]. 江西农业大学学报, 2018, 40(6):1134-1144.
|
| [3] |
李卫星, 杨舜博, 何智冲, 等. 植物叶色变化机制研究进展[J]. 园艺学报, 2017, 44(9):1811-1824.
|
| [4] |
付红岩, 李自强, 姚晶, 等. 金属离子和食品添加剂对紫甘薯花色苷稳定性的影响[J]. 食品工业科技, 2013, 34(15):273-276.
|
| [5] |
岳静, 潘远智, 鲜小林, 等. 光质和B9对杜鹃花观赏性状及生理特性的影响[J]. 林业科学, 2013, 49(1):77-84.
|
| [6] |
晁月文, 李竞芸, 张广辉. 彩叶植物呈色机理及其育种研究进展[J]. 江苏林业科技, 2008, 35(4):46-48,52.
|
| [7] |
崔舜, 邱国金, 吴茜, 等. 彩叶紫薇新品种红火球与仑山1号的叶色及生理变化特性[J]. 贵州农业科学, 2020, 48(9):16-21.
|
| [8] |
杨少瑕, 朱银玲. 红江橙叶片矿质元素含量的测定及元素分布状态分析[J]. 汕头大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 34(2):47-51.
|
| [9] |
于晓南, 张启翔. 观赏植物的花色素苷与花色[J]. 林业科学, 2002, 38(3):147-153.
|
| [10] |
王改萍, 张磊, 姚雪冰, 等. 金叶银杏叶色变化特性分析[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 44(5):41-48.
|
| [11] |
赵昶灵, 郭维明, 陈俊愉. 植物花色形成及其调控机理[J]. 植物学通报, 2005, 22(1):70-81.
|
| [12] |
曹槐, 张晓林, 刘世熙, 等. 烤烟矿质营养分布的因子分析[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2001, 7(3):318-324.
|
| [13] |
霍昭光, 孙志浩, 邢雪霞, 等. 不同施肥方式烤烟叶片矿质元素含量变化及其与干物质积累的关系[J]. 中国土壤与肥料, 2018(4):60-66.
|
| [14] |
金晓玲, 刘晓玲, 徐志毅, 等. 榉树秋季叶片呈色机理及化学物质的调控[J]. 湖南生态科学学报, 2019, 6(1):42-48.
|
| [15] |
胡静静, 沈向, 李雪飞, 等. 黄连木秋季叶色变化与可溶性糖和矿质元素的关系[J]. 林业科学, 2010, 46(2):80-86.
|
| [16] |
史宝胜. 紫叶李叶色生理变化及影响因素研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 东北林业大学, 2006.
|
| [17] |
朱书香, 杨建民, 王中华, 等. 4种李属彩叶植物色素含量与叶色参数的关系[J]. 西北植物学报, 2009, 29(8):1663-1669.
|
| [18] |
唐玲, 李倩中, 李淑顺, 等. 秋季模拟酸雨对鸡爪槭叶片呈色相关生理的影响[J]. 江苏农业学报, 2010, 26(6):1357-1361.
|
| [19] |
张珂, 孙冰, 廖绍波, 等. 岭南槭叶色表现与色叶性状研究[J]. 植物研究, 2017, 37(6):861-869.
|
| [20] |
袁洁, 俄胜哲, 姚嘉斌, 等. 脱硫石膏改良盐碱土技术的机理及研究进展[J]. 甘肃农业科技, 2014, 45(9):42-44.
|
| [21] |
陈义群, 董元华. 土壤改良剂的研究与应用进展[J]. 生态环境, 2008, 17(3):1282-1289.
|
| [22] |
李庆军, 林英, 李俊良, 等. 土壤pH和不同酸化土壤改良剂对苹果果实品质的影响[J]. 中国农学通报, 2010, 26(14):209-213.
|
| [23] |
魏永赞, 李伟才, 董晨, 等. 光照对植物花色素苷生物合成的调控及机制[J]. 植物生理学报, 2017, 53(9):1577-1585.
|
| [24] |
吴飞洋. 光照和土壤水分对乌桕秋季叶色及生理指标的影响[D]. 杭州: 浙江农林大学, 2019.
|
| [25] |
李性苑, 罗开源, 杨芩, 等. 施硫磺粉对土壤养分及蓝莓产量品质的影响[J]. 中国南方果树, 2015, 44(5):101-105.
|
| [26] |
中华人民共和国农业部.测土配方施肥技术规范:NY/T 1118—2006[S]. 北京: 中华人民共和国农业部, 2006.
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
唐前瑞, 陈德富, 陈友云, 等. 红檵木叶色变化的生理生化研究[J]. 林业科学, 2006, 42(2):111-115.
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
李梅洁, 刘玉民, 李力, 等. 叶面喷施蔗糖对北美红枫叶色表现的影响[J]. 西部林业科学, 2017, 46(4):93-100.
|
| [31] |
姜卫兵, 庄猛, 韩浩章, 等. 彩叶植物呈色机理及光合特性研究进展[J]. 园艺学报, 2005, 32(2):352-358.
|
| [32] |
崔祺, 吴昀, 李东泽, 等. 彩叶桂叶片发育过程中叶色表型与色素成分变化[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2023, 47(2):79-86.
|
| [33] |
陈芳. 金叶白蜡叶片呈色机理的研究[D]. 保定: 河北农业大学, 2013.
|
| [34] |
李力, 张盛楠, 刘亚敏, 等. 基于Lab模型的北美红枫呈色生理因素探究[J]. 西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2017, 45(9):87-94.
|
| [35] |
路买林, 陈梦娇, 张嘉嘉, 等. ‘红叶’杜仲叶色转变过程中叶片生理指标变化[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 45(1): 86-92.
|
| [36] |
赵东辉, 高玉福, 荣立苹, 等. 紫花槭秋季叶片呈色生理变化研究[J]. 经济林研究, 2019, 37(2):114-119.
|
| [37] |
靳慧琴, 梁俊林, 贾诗雨, 等. 土壤酸化对红枫叶片呈色生理的影响[J]. 四川农业大学学报, 2021, 39(5):590-595,625.
|
| [38] |
张恒, 陈锐帆, 林嘉蓓, 等. 微量元素在林木中的应用研究进展[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 46(5):229-239.
|
| [39] |
潘瑞炽. 植物生理学[M]. 5版. 北京: 高等教育出版社,2004:27-30.
|
| [40] |
林智, 吴洵, 俞永明. 土壤pH值对茶树生长及矿质元素吸收的影响[J]. 茶叶科学, 1990, 10(2):27-32.
|
| [41] |
王丹. 黄连木叶片矿质元素季节性变化规律研究[D]. 重庆: 西南大学, 2012.
|
| [42] |
李承秀, 张靖, 张义坤, 等. 元宝槭秋叶变色与土壤元素含量的关系分析[J]. 园艺与种苗, 2015, 35(9):47-50.
|
| [43] |
张敏, 黄利斌, 周鹏, 等. 榉树秋季转色期叶色变化的生理生化[J]. 林业科学, 2015, 51(8):44-51.
|
| [44] |
|
| [45] |
许志钊, 杨秀云, 王祎琛, 等. 黄连木变色期叶片色素变化规律及呈色机理[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2024, 48(2):97-104.
|
| [46] |
于伟, 潘远智, 任文, 等. 不同遮荫度对‘红叶’南天竹叶色变化及矿质营养积累的影响[J]. 热带亚热带植物学报, 2017, 25(4):339-347.
|
| [47] |
|
| [48] |
|
| [49] |
|
| [50] |
付尧, 许言, 万宗喆, 等. 北陵鸢尾花色素的提取及稳定性研究[J]. 江西农业大学学报, 2015, 37(4):719-724.
|
| [51] |
赵大球, 郝召君, 陶俊. 理化因子对芍药花色苷呈色的影响[J]. 吉林农业大学学报, 2015, 37(6):687-693.
|
| [52] |
李富香. 影响钝裂银莲花(Anemone obtusiloba)花色的生态因素研究[D]. 兰州: 兰州理工大学, 2014.
|
| [53] |
王露, 孙双勋, 邵烨丹, 等. 红肉桃花色苷的提取纯化及稳定性研究[J]. 食品工业科技, 2014, 35(24):113-117,122.
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |