 PDF(12992 KB)
PDF(12992 KB)


浙江玉环漩门湾湿地越冬期黑脸琵鹭的种群动态及生境特征
陈严雪, 吴丞昊, 章旭日, 李元春, 郭传良
南京林业大学学报(自然科学版) ›› 2025, Vol. 49 ›› Issue (4) : 179-185.
 PDF(12992 KB)
PDF(12992 KB)
 PDF(12992 KB)
PDF(12992 KB)
浙江玉环漩门湾湿地越冬期黑脸琵鹭的种群动态及生境特征
Population dynamics and habitat characteristics of black-faced spoonbill (Platalea minor) during the wintering periods in Yuhuan Xuanmen Bay Wetland, Zhejiang Province
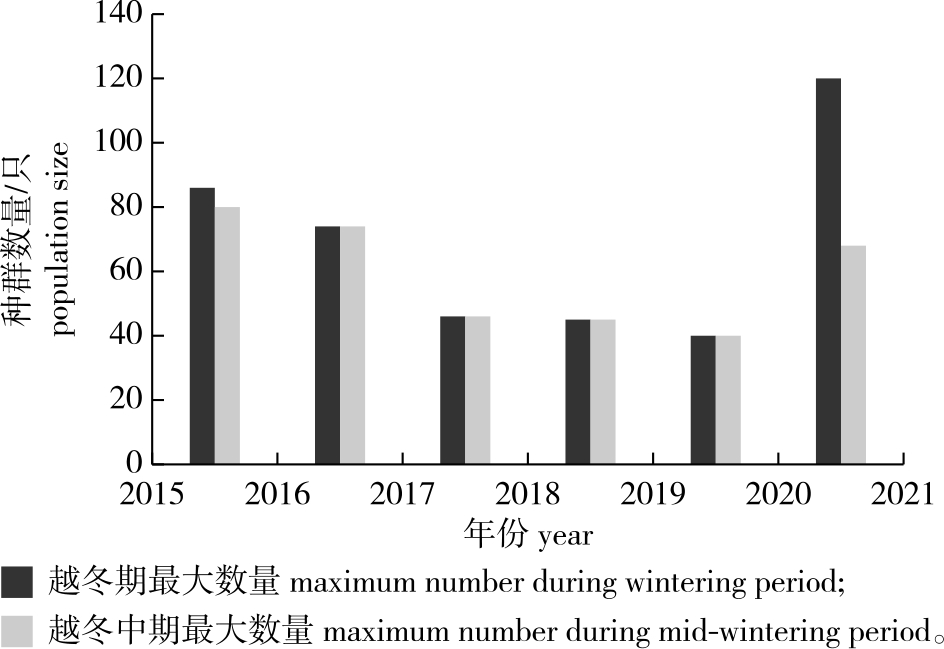
【目的】了解浙江玉环漩门湾湿地越冬期黑脸琵鹭(Platalea minor)的种群动态和栖息地特征,为黑脸琵鹭的保护和栖息地管理提供科学依据。【方法】在2015—2021年的6个越冬期,采用样线法和样点法对浙江玉环漩门湾湿地黑脸琵鹭种群进行调查统计,通过比较不同越冬期的数量和分布分析黑脸琵鹭的种群动态及影响因素,应用Pearson相关分析检验黑脸琵鹭越冬时长与气候因子的关系。在黑脸琵鹭栖息地设置样方,对样方内的12个生境因子进行调查,通过主成分分析确定影响其生境选择的主要因子。【结果】黑脸琵鹭一般每年10月中下旬到达漩门湾湿地,次年4月中下旬离开,越冬时长为(176.83±13.48)d。黑脸琵鹭的越冬天数仅与2月和3月的降水天数呈显著正相关(P<0.05)。2015—2017年黑脸琵鹭越冬个体数量为(77.00±3.00)只,2017—2020年越冬个体数量为(43.67±2.62)只,2020—2021年越冬个体数量为68只。黑脸琵鹭种群数量动态多数年份呈“钟”形,少数年份呈“M”形。整个漩门湾湿地共记录黑脸琵鹭分布点19处,其中湿地公园10处,三期建设区9处。黑脸琵鹭主要分布在湿地公园,三期建设区较少。主成分分析显示,植被盖度[(15.91±15.79)%]、裸露泥地面积占比[(66.36±28.45)%]、离大道最近距离[(1 166.46±627.89)m]、植被高度[(0.80±0.93)m]、离居民点最近距离[(1 616.18±490.08)m]是影响黑脸琵鹭生境选择的主要因子。【结论】浙江玉环漩门湾湿地是黑脸琵鹭的重要越冬地和迁徙停歇地。黑脸琵鹭在漩门湾湿地的越冬时长随着2、3月降水天数的增加而延长,其种群数量和分布受到栖息地改造和工程建设的干扰而有所波动。黑脸琵鹭偏好植被分布稀疏、有较大裸露泥地面积以及人为干扰和噪音小的环境栖息。避开越冬期施工、减少人为干扰、保留原始滩地和养殖塘、控制水位等,有助于对黑脸琵鹭的保护。
【Objective】This study aims to investigate the population dynamics and habitat characteristics of the endangered black-faced spoonbill (Platalea minor) during the wintering periods in Yuhuan Xuanmen Bay Wetland of Zhejiang Province, so as to provide a theoretical basis for the protection of this species and habitat management.【Method】During six consecutive wintering periods from 2015 to 2021, the population dynamics and influencing factors of P. minor were analyzed by comparing the individual numbers and distribution patterns of different wintering periods using the line transect and point count methods. Pearson correlation analysis was employed to examine the relationship between the wintering duration and climate factors. 12 habitat factors were investigated using the quadrat method, and the main factors affecting habitat selection were determined through principal component analysis.【Result】The P. minor usually arrives at the Xuanmen Bay Wetland in mid to late October and leaves in mid to late April. The wintering duration is (176.83±3.48) days, and it is only significantly positive correlation with the rain days in February and March (P<0.05). The individual numbers of wintering P. minor are (77.00±3.00) individuals from 2015 to 2017, (43.67±2.62) individuals from 2017 to 2020, and 68 from 2020 to 2021. The population dynamics of P. minor follows a “bell-shaped” pattern in most years, with some years showing an “M-shaped” pattern. A total of 19 distribution points of P. minor are recorded in the Xuanmen Bay Wetland, including 10 points in the wetland park and 9 points in the phase Ⅲ construction area. The P. minor is mainly distributed in the wetland park, with fewer in the phase Ⅲ construction area. Principal component analysis shows that vegetation coverage [(15.91±15.79)%], bare mud proportion [(66.36±28.45)%], closest distance to road [(1 166.46±627.89) m], vegetation height [(0.80±0.93) m], and closest distance to residential location [(1 616.18±490.08) m] are the main factors affecting habitat selection for the P. minor.【Conclusion】The Xuanmen Bay Wetland in Yuhuan, Zhejiang, is an important wintering ground and stopover for the P. minor. The wintering duration of this species extends with the increase of rain days in February and March. The population dynamics of this species is fluctuated by habitat modification and engineering construction. The P. minor prefers to inhabit the environment with sparse vegetation distribution, large bare mud area, and low human interference and noise. Reducing human interference, avoiding construction during the wintering periods, preserving the shallows and aquaculture ponds, and controlling water levels may help to protect this species.
黑脸琵鹭 / 种群动态 / 生境特征 / 降水日 / 植被 / 水位 / 工程建设 / 浙江玉环漩门湾湿地
black-faced spoonbill (Platalea minor) / population dynamic / habitat characteristic / rain day / vegetation / water level / engineering construction / Yuhuan Xuanmen Bay Wetland, Zhejiang Province
| [1] |
刘阳, 陈水华. 中国鸟类观察手册[M]. 长沙: 湖南科学技术出版社, 2021.
|
| [2] |
香港观鸟会. 黑脸琵鹭全球数量再创新高后海湾数量下降呼吁关注栖息地状况[EB/OL].[2023-08-30]. http://www.hkbws.org.hk/.
Hong Kong Bird Watching Society. The global population of black-faced spoonbills has reached a new high, but decreased in Houhai Bay, and call for attention to habitat status[EB/OL].[2023-08-30]. http://www.hkbws.org.hk/.
|
| [3] |
IUCN. The IUCN red list of threatened species.version 2022-2[DB/OL].[2023-08-30]. https://www.iucnredlist.org.
|
| [4] |
张雁云, 郑光美. 中国生物多样性红色名录:脊椎动物:第二卷鸟类[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2021.
|
| [5] |
国家林业和草原局, 农业农村部. 《国家重点保护野生动物名录》(2021年2月1日修订)[J]. 野生动物学报, 2021, 42(2):605-640.
National Forestry and Grassland Administration, Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs. List of national key protected wild animals (revised in 2021-2-1)[J]. Chinese Journal of Wildlife, 2021, 42(2):605-640.DOI:10.19711/j.cnki.issn2310-1490.2021.02.045.
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
张国钢, 梁伟, 楚国忠. 海南黑脸琵鹭的越冬行为分析[J]. 生物多样性, 2006, 14(4):352-358.
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
金杰锋, 刘伯锋, 余希, 等. 福建兴化湾黑脸琵鹭觅食生境的鱼类和虾类组成[J]. 动物学杂志, 2010, 45(2):69-74.
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
金杰锋. 福建省兴化湾黑脸琵鹭越冬生态学研究[D]. 南京: 南京林业大学, 2009.
|
| [14] |
张敏, 邹发生, 张桂达, 等. 黑脸琵鹭在澳门的越冬分布和人为干扰影响[J]. 动物学杂志, 2010, 45(2):75-81.
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
袁晓, 章克家. 崇明东滩黑脸琵鹭迁徙种群的初步研究[J]. 华东师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2006(6):131-136.
|
| [17] |
金杰锋, 刘伯锋, 余希, 等. 福建省兴化湾黑脸琵鹭的越冬及迁徙[J]. 动物学杂志, 2009, 44(1):47-53.
|
| [18] |
李飞, 卢刚, 冯尔辉, 等. 海南岛黑脸琵鹭越冬种群的变化与保护策略[J]. 湿地科学, 2021, 19(6):667-672.
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
金伟, 刘宝权, 吴丞昊, 等. 浙江省黑脸琵鹭种群数量调查研究[C]// 浙江省科学技术学会.第七届浙江省生物多样性保护研讨会摘要集. 丽水: 庆元百山祖国家级自然保护区管理处, 2017:18-19.
|
| [22] |
孙海平, 陈严雪, 赵洪, 等. 浙江玉环漩门湾国家湿地公园鸟类多样性研究[J]. 湿地科学, 2021, 19(4):423-434.
|
| [23] |
孙海平, 赵洪, 岳春雷, 等. 浙江玉环漩门湾国家湿地公园湿地资源现状和保护对策探讨[J]. 台州学院学报, 2023, 45(3):65-71.
|
| [24] |
杨璐璐. 仰天岗国家森林公园康复性景观综合评价研究[J]. 森林工程, 2023, 39 (2): 63-71, 81.
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
王强, 吕宪国. 鸟类在湿地生态系统监测与评价中的应用[J]. 湿地科学, 2007, 5(3):274-281.
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
孙儒泳, 王德华, 牛翠娟, 等. 动物生态学原理[M]. 4版. 北京: 北京师范大学出版社, 2019.
|
| [31] |
赵正阶. 中国鸟类志[M]. 长春: 吉林科学技术出版社, 2001.
|
| [32] |
国家林业局《湿地公约》履约办公室. 湿地公约履约指南[M]. 北京: 中国林业出版社, 2001.
Performance Office of the State Forestry Administration Convention on International Wetlands. Guide on implementing Ramsar Convention in China[M]. Beijing: China Forestry Publishing House, 2001.
|
| [33] |
邵明勤, 植毅进. 江西水鸟多样性与越冬生态研究[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2019.
|
| [34] |
席珍华, 刘彦东, 张婵. 微塑料和抗生素对水生生物联合毒性效应研究进展[J]. 江苏农业学报, 2024, 40(8):1561-1568.
|
| [35] |
杨福成, 雷小勇, 曾健辉, 等. 鄱阳湖越冬期东方白鹳取食行为及其在2个区域的种群动态[J]. 林业科学, 2023, 59(5):128-135.
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |