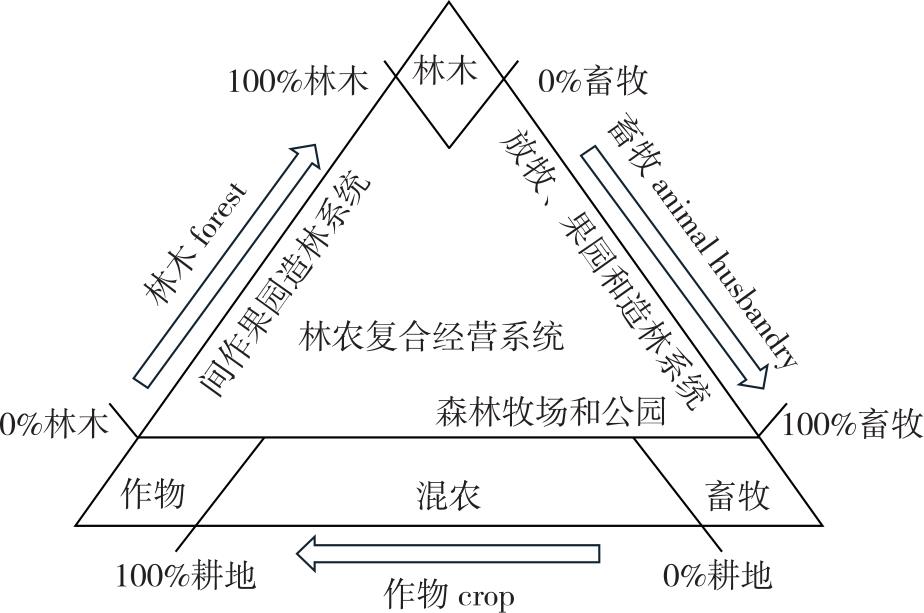
【目的】林农复合经营被认为是维持未来农业可持续生产比较有前途的一种方式。本研究旨在探索和优化中国特色的林农复合经营系统,通过厘清其复杂机制并总结经验模式,以维持未来林业和农业的可持续生产。【方法】在梳理林农复合经营实践的基础之上,重点构建林农复合经营机制并识别作用因子,归纳林农复合经营经验模式以适应不同环境条件。【结果】①林农复合经营机制受到生物物理因素、社会经济因素、农户禀赋、生产企业以及保障性措施等条件的显著影响。②林农复合经营系统可根据生态系统类型的利用程度划分为农林系统、林牧系统、农林牧系统及其他特殊系统。③欧洲和美洲通过农场和科研院所分别构建了林农牧复合经营实践系统和科研系统,实现了农林业生产的精细化管理,而亚洲多数地区仍以传统的林农复合经营系统为主。④中国的林农复合经营具有悠久历史和多样化模式,在空间上呈现差异化的特点,但在技术应用方面与国际先进水平存在差距。【结论】必须通过因地制宜地建立林农复合经营机制、积极改善农户生产理念和技术水平、构建风险防御机制和政策保障体系等措施来推动中国林农复合经营系统的可持续发展。
【Objective】Agroforestry compound management is widely acknowledged as a promising strategy for guaranteeing the sustainability of future agricultural production. This research is dedicated to exploring and optimizing the agroforestry management system with Chinese characteristics. By elucidating its complex mechanisms and summarizing empirical models, the study aims to maintain the sustainable production of both forestry and agriculture in the future. 【Method】Based on an all-round review of agroforestry management practices, this paper focuses on constructing the agroforestry management mechanism to identify the roles of various factors. It also aims to summarize experience-based models suitable for different environmental conditions. Specifically, a detailed analysis of biophysical factors, socio-economic factors, farmers’ endowments, production enterprises, and safeguard measures has been carried out. 【Result】(1) The agroforestry management mechanism is significantly influenced by multiple factors. These encompass biophysical conditions such as soil quality, climate, and topography; socio-economic factors like market demand, economic policies, and the rural labor force; farmers’ endowments in terms of land resources, farming skills, and financial capabilities; production enterprises with their production scale, technological innovation, and market-orientation; and safeguard measures including agricultural policies, forest protection regulations, and rural infrastructure construction. (2) According to the degree of utilization of ecosystem types, agroforestry management systems can be classified into four main categories: agroforestry systems, mainly centering on the combination of agricultural crops and forest trees; forest-pastoral systems, emphasizing the integration of forestry and livestock grazing; agroforestry-pastoral systems, integrating agriculture, forestry, and animal husbandry; and other special systems customized to specific local ecological and socio-economic conditions. (3) In Europe and the Americas, through the efforts of farms and research institutes, forest-farm-livestock composite management practice systems and scientific research systems have been established respectively. These systems enable the meticulous management of agricultural production, covering aspects such as precise resource allocation, scientific breeding, and the efficient utilization of agricultural land. In contrast, most regions in Asia still primarily rely on traditional agroforestry management systems, which are characterized by relatively simple production models and less advanced technologies. (4) China has a long-standing history of agroforestry management with diverse modes. These modes show obvious spatial differentiation due to differences in the natural environment, economic development level, and cultural traditions in different regions. However, there is still a gap between the technological application in China’s agroforestry management and the international advanced level, especially in areas such as modern agricultural machinery, information technology, and ecological management. 【Conclusion】In light of the above-mentioned findings, it is of great significance to promote the sustainable development of China’s agroforestry management system. This can be achieved by establishing an agroforestry management mechanism tailored to local conditions, actively enhancing farmers’ production concepts and technical capabilities through training and extension services, and constructing a comprehensive risk-defense mechanism and a sound policy-guarantee system. The risk-defense mechanism should cover aspects such as natural disaster prevention, market risk mitigation, and technological innovation risks, while the policy-guarantee system should include preferential policies for agroforestry development, financial support, and land-use policies.
 PDF(1467 KB)
PDF(1467 KB)


 PDF(1467 KB)
PDF(1467 KB)
 PDF(1467 KB)
PDF(1467 KB)