 PDF(1750 KB)
PDF(1750 KB)


栗子坪自然保护区不同海拔梯度土壤入渗特性研究
陆其伟, 脱云飞, 郑阳, 骆伟, 代勤龙, 何霞红
南京林业大学学报(自然科学版) ›› 2025, Vol. 49 ›› Issue (2) : 143-152.
 PDF(1750 KB)
PDF(1750 KB)
 PDF(1750 KB)
PDF(1750 KB)
栗子坪自然保护区不同海拔梯度土壤入渗特性研究
Research on characteristics of soil infiltration at different altitude gradients in Liziping Nature Reserve
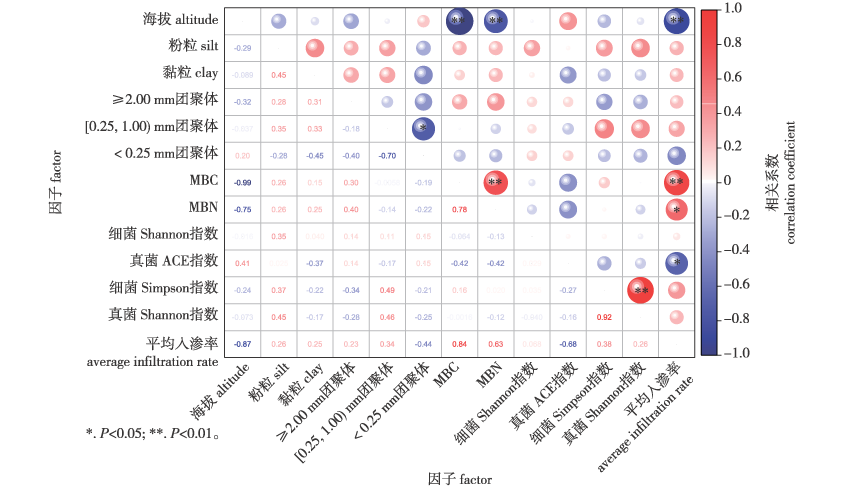
【目的】探究四川栗子坪国家级自然保护区土壤入渗对不同海拔梯度土壤类型响应特征。【方法】以自然保护区4个海拔梯度(1 900、2 100、2 300和2 500 m)土壤为采样对象,通过环刀法测定不同海拔梯度土壤入渗特征,采用通径及相关性分析法明确影响土壤入渗特征的关键因子,并用Kostiakov、Philip、Horton等入渗模型进行拟合,分析其适宜性。【结果】土壤入渗速率与海拔呈极显著负相关关系(P<0.01),而土壤微生物生物量与入渗速率呈显著正相关关系(P<0.05),促进了土壤水分入渗;在入渗前20 min,海拔1 900、2 100 m土壤入渗率降低了50%左右,海拔2 300、2 500 m降低了72%~85%,海拔2 300、2 500 m入渗衰弱速率明显快于海拔1 900、2 100 m,这主要是受到土壤有机质含量、团聚体粒级结构及微生物生物量影响;模型拟合发现,Kostiakov模型R2为0.896~0.959,Philip模型R2为0.874~0.965,Horton模型R2为0.945~0.984,综合考虑土壤入渗模型决定系数R2大小以及拟合值与实测值精确度的一致性,Kostiakov模型更适合对研究区域土壤入渗进行拟合。【结论】海拔梯度对土壤入渗特征影响显著,主要是受到土壤有机质含量、团聚体粒级结构及微生物生物量等因素影响。
【Objective】The purpose of this study was to explore how soil infiltration responds to different elevation gradients in Liziping National Nature Reserve, Sichuan. 【Method】Soil samples were collected from four elevation gradients (1 900, 2 100, 2 300, and 2 500 m) within the nature reserve. Soil infiltration characteristics at these gradients were measured using the ring knife method. Key factors affecting soil infiltration were identified through path and correlation analyses. Additionally, the suitability of infiltration models, including Kostiakov, Philip and Horton, was evaluated by fitting and analyzing the data. 【Result】Soil infiltration rates showed a highly significantly negative correlation with elevation (P < 0.01). Soil microbial biomass had a significant positive correlation with infiltration rates (P < 0.05), promoting water infiltration. In the first 20 min, soil infiltration rates decreased by about 50% at elevations of 1 900 and 2 100 m, and by 72% to 85% at elevations of 2 300 and 2 500 m. The rate of infiltration decreased at 2 300 and 2 500 m was significantly faster that than at 1 900 and 2 100 m, primarily due to differences in soil organic matter, aggregate grain structure, and microbial biomass. The model fitting showed that the R2 values were 0.896-0.959 for the Kostiakov model, 0.874-0.965 for the Philip model, and 0.945-0.965 for the Horton model. Based on the R2 values and the alignment between fitted and measured values, the Kostiakov model was found to be the most suitable for the study area. 【Conclusion】Elevation gradients significantly affect soil infiltration characteristics, primarily influenced by soil organic matter, aggregate grain structure, and microbial biomass.
海拔梯度 / 土壤理化性质 / 入渗特征 / 模型拟合 / 栗子坪自然保护区 / 微生物生物量
elevation gradient / soil physical and chemical property / infiltration characteristic / model fitting / Liziping Nature Reserve / microbial biomass
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
刘目兴, 杜文正, 张海林. 三峡库区不同林型土壤的入渗能力研究[J]. 长江流域资源与环境, 2013, 22(3):299-306.
|
| [3] |
陈娟, 陈林, 宋乃平, 等. 荒漠草原不同土壤类型水分入渗特征[J]. 水土保持学报, 2018, 32(4):18-23.
|
| [4] |
周维, 张建辉. 金沙江支流冲沟侵蚀区四种土地利用方式下土壤入渗特性研究[J]. 土壤, 2006, 38(3):333-337.
|
| [5] |
刘茜茹, 冯天骄, 王平, 等. 晋西黄土区长期植被恢复对土壤表层入渗与水分储量差异的影响[J]. 水土保持通报, 2023, 43(2):50-59.
|
| [6] |
赵洋毅, 王玉杰, 王云琦, 等. 渝北水源区水源涵养林构建模式对土壤渗透性的影响[J]. 生态学报, 2010, 30(15):4162-4172.
|
| [7] |
舒锟, 张家春, 张珍明, 等. 不同海拔梯度下梵净山土壤机械组成及养分特征[J]. 四川农业大学学报, 2017, 35(1):52-59.
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
卢振启, 黄秋娴, 杨新兵. 河北雾灵山不同海拔油松人工林枯落物及土壤水文效应研究[J]. 水土保持学报, 2014, 28(1):112-116.
|
| [11] |
胡晓聪, 黄乾亮, 金亮. 西双版纳热带山地雨林枯落物及其土壤水文功能[J]. 应用生态学报, 2017, 28(1):55-63.
|
| [12] |
亢晨波, 郭汉清, 张垚, 等. 关帝山不同海拔和坡向土壤水分入渗特征[J]. 东北林业大学学报, 2022, 50(6):76-82.
|
| [13] |
刘瑞, 夏卫生, 梁羽石, 等. 湖南省衡山不同海拔高度土壤的入渗特征[J]. 水土保持通报, 2019, 39(4):82-88.
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
印家旺, 阿拉木萨, 苏宇航, 等. 科尔沁沙地不同土地利用类型土壤入渗特征比较研究[J]. 水土保持通报, 2022, 42(4):90-98.
|
| [16] |
云慧雅, 毕华兴, 王珊珊, 等. 不同林分类型土壤理化特征及其对土壤入渗过程的影响[J]. 水土保持学报, 2021, 35(6):183-189.
|
| [17] |
张利荣, 李惠通, 郑立津, 等. 不同林龄杉木人工林的林下植被与土壤理化特性[J]. 亚热带农业研究, 2021, 17(3):165-172.
|
| [18] |
李新星, 刘桂民, 吴小丽, 等. 马衔山不同海拔土壤碳、氮、磷含量及生态化学计量特征[J]. 生态学杂志, 2020, 39(3):758-765.
|
| [19] |
韦慧, 邓羽松, 林立文, 等. 喀斯特生态脆弱区典型小生境土壤团聚体稳定性比较研究[J]. 生态学报, 2022, 42(7):2751-2762.
|
| [20] |
刘光崧. 土壤理化分析与剖面描述[M]. 北京: 中国标准出版社,1996.
|
| [21] |
鲍士旦. 土壤农化分析[M]. 3版. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2000.
|
| [22] |
刘艳娇, 刘庆, 贺合亮, 等. 亚高山粗枝云杉人工林土壤原核微生物群落结构与功能变化[J]. 应用生态学报, 2023, 34(12):3279-3290.
|
| [23] |
阿茹·苏里坦, 常顺利, 张毓涛. 天山林区不同群落土壤水分入渗特性的对比分析与模拟[J]. 生态学报, 2019, 39(24):9111-9118.
|
| [24] |
牛文全, 邹小阳, 刘晶晶, 等. 残膜对土壤水分入渗和蒸发的影响及不确定性分析[J]. 农业工程学报, 2016, 32(14):110-119.
|
| [25] |
郑健, 张彦宁, 王燕, 等. 沼液穴灌入渗特征及Philip入渗模型拟合[J]. 干旱地区农业研究, 2019, 37(1):144-150.
|
| [26] |
曾江敏, 何丙辉, 李天阳, 等. 喀斯特槽谷区不同林草恢复模式下土壤入渗特征[J]. 水土保持学报, 2019, 33(4):58-64.
|
| [27] |
陆其伟, 脱云飞, 冯永钰, 等. 栗子坪自然保护区林分类型对土壤化学计量特征、微生物及其季节动态响应[J]. 水土保持学报, 2024, 38(5):285-295.
|
| [28] |
李志, 袁颖丹, 胡耀文, 等. 海拔及旅游干扰对武功山山地草甸土壤渗透性的影响[J]. 生态学报, 2018, 38(2):635-645.
|
| [29] |
石玉龙, 周晨霓, 王建峰, 等. 西藏色季拉山不同海拔梯度急尖长苞冷杉林土壤入渗特征研究[J]. 林业资源管理, 2015(4):98-103.
|
| [30] |
曹瑞, 吴福忠, 杨万勤, 等. 海拔对高山峡谷区土壤微生物生物量和酶活性的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 2016, 27(4):1257-1264.
|
| [31] |
丛静, 刘晓, 卢慧, 等. 神农架自然保护区土壤微生物生物量碳、氮沿海拔梯度的变化及其影响因素[J]. 生态学杂志, 2014, 33(12):3381-3387.
|
| [32] |
胡璟, 刘兴良, 胡宗达, 等. 川西亚高山典型灌丛土壤微生物量及其碳氮磷化学计量特征[J]. 应用与环境生物学报, 2024, 30(2):220-228.
|
| [33] |
胡嵩, 张颖, 史荣久, 等. 长白山原始红松林次生演替过程中土壤微生物生物量和酶活性变化[J]. 应用生态学报, 2013, 24(2):366-372.
|
| [34] |
王彦武, 罗玲, 张峰, 等. 河西绿洲荒漠过渡带梭梭林土壤保育效应[J]. 土壤学报, 2019, 56(3):749-762.
|
| [35] |
李秋嘉, 薛志婧, 周正朝. 宁南山区植被恢复对土壤团聚体养分特征及微生物特性的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 2019, 30(1):137-145.
|
| [36] |
翟辉, 张海, 张超, 等. 黄土峁状丘陵区不同类型林分土壤微生物功能多样性[J]. 林业科学, 2016, 52(12):84-91.
|
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
冯娜, 刘冬冬, 赵荣存, 等. 岩溶山地植被恢复中碳酸盐岩红土入渗特征及其影响因素[J]. 水土保持学报, 2019, 33(6):162-169,175.
|
| [39] |
郭海云, 王根绪, 孙守琴. 氮添加对亚高山针叶林土壤结构及水分入渗性能的影响[J]. 水土保持学报, 2023, 37(1):238-245.
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |