 PDF(4509 KB)
PDF(4509 KB)


 PDF(4509 KB)
PDF(4509 KB)
 PDF(4509 KB)
PDF(4509 KB)
我国寒竹属空间分布特征及影响因素
Spatial distribution characteristics and influencing factors of Chimonobambusa in China
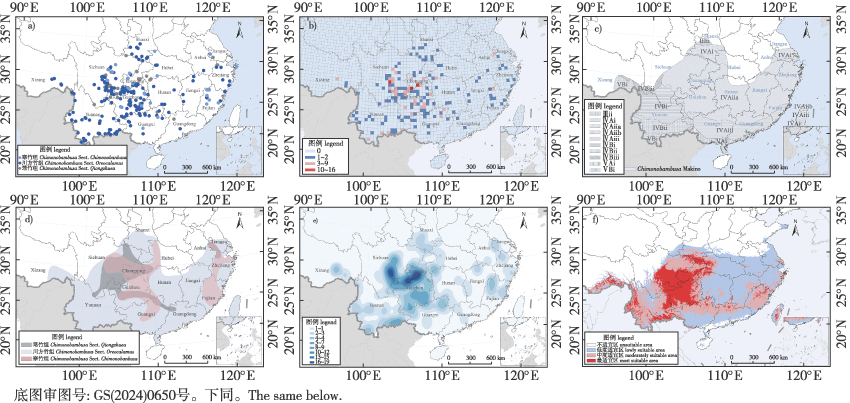
【目的】明确我国寒竹属(Chimonobambusa)植物水平分布和垂直分布状况,利用模型模拟方法分析影响我国寒竹属植物分布的主要因素,为寒竹属种质资源的开发、利用和保护提供科学参考。【方法】借助ArcGIS空间分析工具和MaxEnt模型,综合8个环境变量及340个物种分布记录,分析寒竹属物种的空间分布范围及类型、空间分布密度、物种丰富度及相关影响因素。【结果】寒竹属植物在我国分布广泛,主要分布于中亚热带常绿阔叶林北部亚地带,云南、贵州、四川和重庆4个行政区划为分布中心;海拔1 000~2 000 m为寒竹属植物多样性最高的区域;在空间分布上,寒竹属各组之间存在较大差异。模型模拟结果表明,降水量和温度限定了寒竹属植物现代最适宜分布区,潜在分布区与实际分布区具有很好的一致性。【结论】我国寒竹属植物资源丰富,其地理分布与我国植被区划、气候区划等相关,最适宜生存在温度相对较低、气候较湿润、降雨量较为充沛的环境。研究结果对深入挖掘中国竹类资源和物种多样性保护具有重要意义。
【Objective】 This study elucidated the horizontal and vertical distribution patterns of Chimonobambusa in China. Using model simulation methods, we analyzes the key factors influencing its distribution, providing a scientific basis for the development, utilization, and conservation of Chimonobambusa germplasm resources.【Method】 The study employed the ArcGIS spatial analyst tools and the MaxEnt model, integrating eight environmental variables and 340 distribution records. We examined the spatial distribution, distribution types, density, species richness, and influencing factors of Chimonobambusa. 【Result】Chimonobambusa species are widely distributed, with their primary centers located in Yunnan, Guizhou, Sichuan, and Chongqing. They are predominantly found in the middle subtropical broadleaf evergreen forest northern subzone, with altitudes between 1 000 and 2 000 meters exhibiting the highest species diversity. Intrageneric differences in spatial distribution are significant. Model simulations reveal that precipitation and temperature are the primary factors limiting the distribution of Chimonobambusa. Furthermore, the potential distribution areas predicted by the model closely align with the actual observed distributions. 【Conclusion】 China possesses abundant Chimonobambusa resources, with their distribution strongly correlated with the country’s vegetation and climatic regionalization. These plants thrive in environments characterized by relatively low temperatures, humid climates, and high rainfall. The findings hold significant value for the sustainable development and conservation of local bamboo resources and the preservation of species diversity in China.
寒竹属 / ArcGIS / MaxEnt模型 / 地理分布
Chimonobambusa / ArcGIS / MaxEnt model / geographical distribution
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
薛纪如, 章伟平. 寒竹属[M]// 耿伯介, 王正平. 中国植物志: 第9卷第1分册. 北京: 科学出版社, 1996: 324-344.
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
冯鹏飞, 李玉敏. 2021年中国竹资源报告[J]. 世界竹藤通讯, 2023, 21(2); 100-103.
|
| [10] |
易同培, 史军义, 马丽莎. 中国竹类图志[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2008.
|
| [11] |
梁泰然. 中国竹林区划[J]. 河南农学院科技通讯, 1978, 12(1):96-123.
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
许祖昌, 罗亚皇, 秦声远, 等. 中国竹类植物馆藏标本现状与地理分布[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(7): 897-909.
|
| [16] |
董苏君, 马松梅, 张丹, 等. 新疆猪毛菜属植物多样性地理分布格局及其环境解释[J]. 生态学报, 2023, 43(19): 8025-8034.
|
| [17] |
杨宏, 董京京, 吴桐, 等. 基于MaxEnt模型的迎春樱桃潜在适生区预测[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2023, 47(4):131-138.
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
易同培. 中国竹类图志( 续-ⅡM]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2017.
|
| [20] |
王海涛, 史军义, 易同培, 等. 台湾的竹类植物及其特点[J]. 四川林业科技, 2007, 28(6):44-47.
|
| [21] |
中国植被编辑委员会. 中国植被[M]. 北京: 科学出版社,1980.
Editorial Committee of China Vegetation Editorial Committee. Chinese vegetation[M]. Beijing: Science Press,1980.
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
崔相艳, 王文娟, 杨小强, 等. 基于生态位模型预测野生油茶的潜在分布[J]. 生物多样性, 2016, 24(10):1117-1128.
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
张新时. 中华人民共和国植被图[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2007.
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |