 PDF(25094 KB)
PDF(25094 KB)


跨区域生态安全格局时空演变特征与优化路径研究——以南京-合肥双都市圈为例
余瑞, 郑志元, 郑杰, 鲁珊
南京林业大学学报(自然科学版) ›› 2025, Vol. 49 ›› Issue (4) : 241-252.
 PDF(25094 KB)
PDF(25094 KB)
 PDF(25094 KB)
PDF(25094 KB)
跨区域生态安全格局时空演变特征与优化路径研究——以南京-合肥双都市圈为例
Study on the spatial and temporal evolution characteristics and optimization path of cross-regional ecological security pattern—taking Nanjing-Hefei metropolitan area as an example
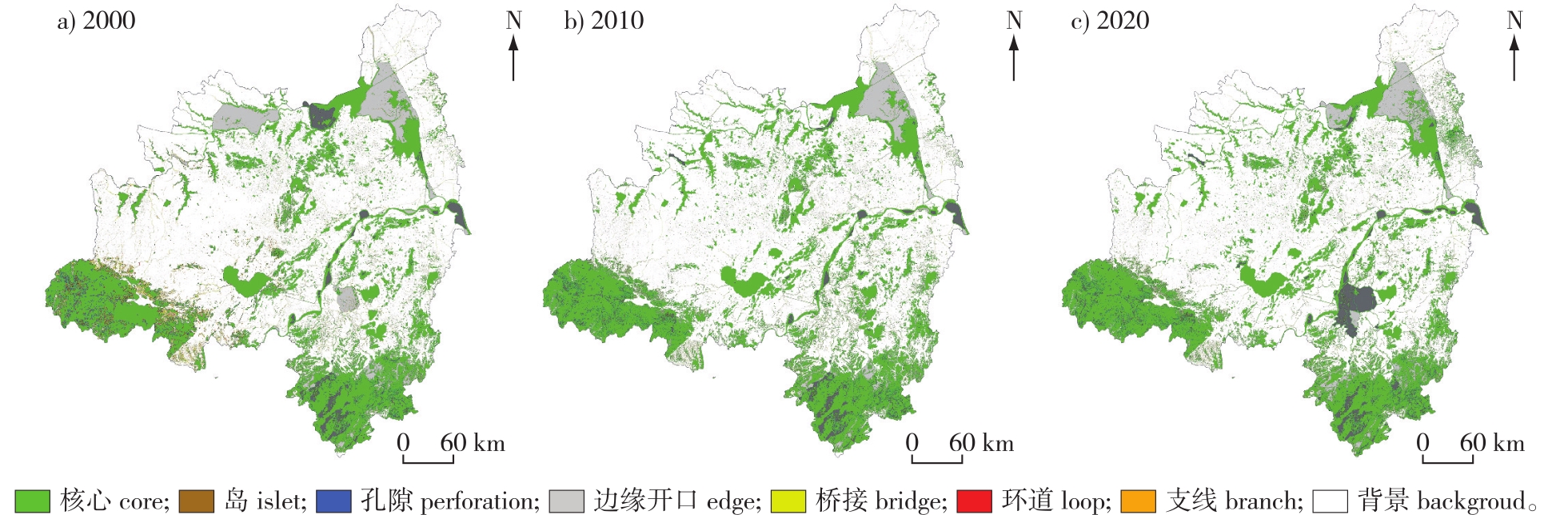
【目的】跨界地区生态安全格局的构建是保障区域生态安全以及高质量发展的关键,通过构建跨区域的生态网络,揭示快速城市化进程中生态屏障功能退化与空间异质性特征,促进生态源地间的完整性、连通性、稳定性,为跨省域城市群生态安全格局的保护与优化提供科学依据。【方法】以南京-合肥双都市圈为研究区域,对比分析了2000、2010、2020年3个时期生态安全格局的时空格局变化特征,根据生态源地具有可逆性的特点选择恢复和新增的生态源地,对区域的生态安全格局进行优化,结合区域生态本底提出国土空间保护修复格局,探究跨界地区生态网络协同治理路径。【结果】①2000—2020年研究区生态源地数量逐年减少,总面积稳定上升;②2000—2020年研究区生境质量整体处于中等水平且呈现衰退的趋势,而生态综合阻力逐渐升高;③3个时期生态廊道数量先增加后减少,生态节点逐年增加,研究区东部生态廊道匮乏;④2000—2020年研究区域高优先级生态廊道数量先增后减,总体呈现倒“T”形空间分布格局,生态网络结构也愈发脆弱;⑤结合研究区域自然生态本底的空间分布与优化后生态安全格局,提出“多核四廊三屏两带一心”的国土空间保护修复格局,并探索跨界地区的生态环境协同治理的建设路径。【结论】本研究从时空变化的角度,考虑南京-合肥双都市圈生态网络的整体性,结合区域生态本底的实际情况进行生态安全格局的优化并提出国土空间保护修复对策,可为南京-合肥双都市圈生态安全和国土空间跨区域保护修复提供理论依据和技术参考。
【Objective】The construction of an ecological security pattern in cross-border areas is the key to ensuring regional ecological security and high-quality development. By building an ecological network across regions, this study reveals the degradation and spatial heterogeneity characteristics of ecological barriers in the process of rapid urbanization, promotes the integrity, connectivity and stability among ecological sources, and provides a scientific basis for the protection and optimization of the ecological security pattern of cross-provincial urban agglomerations.【Method】Taking the Nanjing-Hefei metropolitan area as the research area, the spatio-temporal pattern changes of the ecological security pattern in 2000, 2010 and 2020 were compared and analyzed. Based on the reversible nature of ecological sources, the restored and newly added ecological sources were selected to optimize the regional ecological security pattern. Combined with the regional ecological background, the protection and restoration pattern of territorial space was proposed, and the collaborative governance path of the ecological network in the cross-border area was explored.【Result】(1)The number of ecological sources in the study area decreased year by year from 2000 to 2020, while the total area remained stable and increased. (2)The overall habitat quality in the study area was at a medium level from 2000 to 2020 and showed a declining trend, while the ecological resistance gradually increased.(3)The number of ecological corridors increased first and then decreased in the three periods, and the number of ecological nodes increased year by year. The eastern part of the study area was lacking in ecological corridors.(4)The number of high-priority ecological corridors in the study area increased first and then decreased from 2000 to 2020, and the overall spatial distribution pattern was an inverted “T” shape. The ecological network structure became increasingly fragile.(5)Combining the spatial distribution of the natural ecological background of the study area and the optimized ecological security pattern, the protection and restoration pattern of territorial space was proposed as “multiple cores, four corridors, three screens, two belts and one center”, and the construction path of collaborative governance of the ecological environment in the cross-border area was explored.【Conclusion】This study considers the integrity of the ecological network of the Nanjing-Hefei metropolitan area from the perspective of spatiotemporal changes, and optimizes the ecological security pattern based on the actual situation of the regional ecological background. It also proposes measures for the protection and restoration of national land space, which can provide theoretical basis and technical reference for the ecological security and cross regional protection and restoration of national land space in the Nanjing-Hefei metropolitan area.
生态安全格局 / 时空演化 / 布局优化 / 南京-合肥都市圈
ecological security pattern / spatial and temporal evolution / layout optimization / Nanjing-Hefei metropolitan area
| [1] |
党秀云, 郭钰. 跨区域生态环境合作治理:现实困境与创新路径[J]. 人文杂志, 2020(3):105-111.
|
| [2] |
方创琳. 新发展格局下的中国城市群与都市圈建设[J]. 经济地理, 2021, 41(4):1-7.
|
| [3] |
刘迪, 赵宪峰. 制度经济学视角下跨界地区生态治理实践反思:以长三角一体化示范区生态治理规划为例[J]. 上海城市规划, 2022(2):126-132.
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
张琦. 都市圈发展过程中的府际协作发生机制[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2023.
|
| [6] |
张京祥, 胡航军. 新发展环境下的都市圈发展、规划与治理创新[J]. 经济地理, 2023, 43(1):17-25.
|
| [7] |
陈利顶, 孙然好, 孙涛, 等. 城市群生态安全格局构建:概念辨析与理论思考[J]. 生态学报, 2021, 41(11):4251-4258.
|
| [8] |
俞孔坚, 王思思, 李迪华, 等. 北京市生态安全格局及城市增长预景[J]. 生态学报, 2009, 29(3):1189-1204.
|
| [9] |
陈月娇, 李祥, 王月健, 等. 尺度整合视角下伊犁河谷地区生态安全格局构建:以昭苏县为例[J]. 生态学报, 2023, 43(19):8181-8192.
|
| [10] |
方莹, 王静, 黄隆杨, 等. 基于生态安全格局的国土空间生态保护修复关键区域诊断与识别:以烟台市为例[J]. 自然资源学报, 2020, 35(1):190-203.
|
| [11] |
申世广, 刘小钊, 范晨璟. 基于生态安全格局的苏锡常都市圈绿化系统空间布局研究[J]. 现代城市研究, 2018, 33(11):20-25.
|
| [12] |
王国玉, 白伟岚, 熊筱, 等. 京津冀城市群生态空间受损识别研究[J]. 城市规划, 2021, 45(8):9-19,41.
|
| [13] |
高星, 宋昭颖, 李晨曦, 等. 基于景观生态风险评价的白洋淀流域景观格局优化研究[J]. 生态与农村环境学报, 2023, 39(2):174-183.
|
| [14] |
曲艺, 陆明. 生态网络规划研究进展与发展趋势[J]. 城市发展研究, 2016, 23(8):29-36.
|
| [15] |
缪鑫辉, 梁勤欧. 基于遥感生态指数的甬江流域生态环境变化分析[J]. 长江流域资源与环境, 2021, 30(2):427-438.
|
| [16] |
胡丰, 张艳, 郭宇, 等. 基于PLUS和InVEST模型的渭河流域土地利用与生境质量时空变化及预测[J]. 干旱区地理, 2022, 45(4):1125-1136.
|
| [17] |
赵燕如, 邹自力, 张晓平, 等. 基于LEI和MSPA的南昌市城市扩张类型与生态景观类型变化关联分析[J]. 自然资源学报, 2019, 34(4):732-744.
|
| [18] |
甘琳, 陈颖彪, 吴志峰, 等. 近20年粤港澳大湾区生态敏感性变化[J]. 生态学杂志, 2018, 37(8):2453-2462.
|
| [19] |
郑好, 高吉喜, 谢高地, 等. 生态廊道[J]. 生态与农村环境学报, 2019, 35(2):137-144.
|
| [20] |
韦宝婧, 苏杰, 胡希军, 等. 基于“HY-LM”的生态廊道与生态节点综合识别研究[J]. 生态学报, 2022, 42(7):2995-3009.
|
| [21] |
黄木易, 岳文泽, 冯少茹, 等. 基于MCR模型的大别山核心区生态安全格局异质性及优化[J]. 自然资源学报, 2019, 34(4):771-784.
|
| [22] |
杜雨阳, 王征强, 于庆和, 等. 基于生境质量模型和电路理论的区域生态安全格局构建:以秦岭(陕西段)为例[J]. 农业资源与环境学报, 2022, 39(5):1069-1078.
|
| [23] |
张美丽, 齐跃普, 张利, 等. 基于Linkage Mapper与粒度反推法的太行山中北段生态节点识别与分析:以河北省阜平县为例[J]. 生态与农村环境学报, 2020, 36(12):1569-1578.
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
彭建, 赵会娟, 刘焱序, 等. 区域生态安全格局构建研究进展与展望[J]. 地理研究, 2017, 36(3):407-419.
|
| [26] |
金爱博, 张诗阳, 王向荣. 宁绍平原绿地生态网络时空格局与优化研究[J]. 生态与农村环境学报, 2022, 38(11):1415-1426.
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
王倩娜, 谢梦晴, 张文萍, 等. 成渝城市群区域生态与城镇发展双网络格局分析及时空演变[J]. 生态学报, 2023, 43(4):1380-1398.
|
| [29] |
杨志广, 蒋志云, 郭程轩, 等. 基于形态空间格局分析和最小累积阻力模型的广州市生态网络构建[J]. 应用生态学报, 2018, 29(10):3367-3376.
|
| [30] |
刘学, 杨春艳, 高艳妮, 等. 厦门市生态安全格局识别与生态管控区分级管控[J]. 生态学报, 2023, 43(13):5357-5369.
|
| [31] |
黄浦江. 城市绿道网络识别、评价与优化[D]. 武汉: 武汉大学, 2014.
|
| [32] |
陆禹, 佘济云, 陈彩虹, 等. 基于粒度反推法的景观生态安全格局优化:以海口市秀英区为例[J]. 生态学报, 2015, 35(19):6384-6393.
|
| [33] |
马晓武, 徐昔保. 区域尺度生态保护红线连通性优化与管控:以长三角为例[J]. 自然资源学报, 2022, 37(12):3088-3101.
|
| [34] |
余瑞, 鲁珊, 郑志元, 等. 城市扩张对区域生态安全格局影响研究:以合肥市为例[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2023, 23(26):11327-11337.
|
| [35] |
张远景, 俞滨洋. 城市生态网络空间评价及其格局优化[J]. 生态学报, 2016, 36(21):6969-6984.
|
| [36] |
卫新东, 林良国, 冯小龙, 等. 神木市生态安全格局构建与生态问题定量诊断[J]. 生态学报, 2023, 43(1):82-94.
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |