 PDF(1552 KB)
PDF(1552 KB)


干旱对杨树人工林土壤微生物生物量碳氮磷生态化学计量特征的影响
赵紫薇, 阮宏华, 杨艳, 谢友超, 沈彩芹, 徐亚明, 曹国华
南京林业大学学报(自然科学版) ›› 2025, Vol. 49 ›› Issue (3) : 33-40.
 PDF(1552 KB)
PDF(1552 KB)
 PDF(1552 KB)
PDF(1552 KB)
干旱对杨树人工林土壤微生物生物量碳氮磷生态化学计量特征的影响
Effects of drought on the soil microbial biomass C, N, P ecological stoichiometric characteristics of poplar plantation
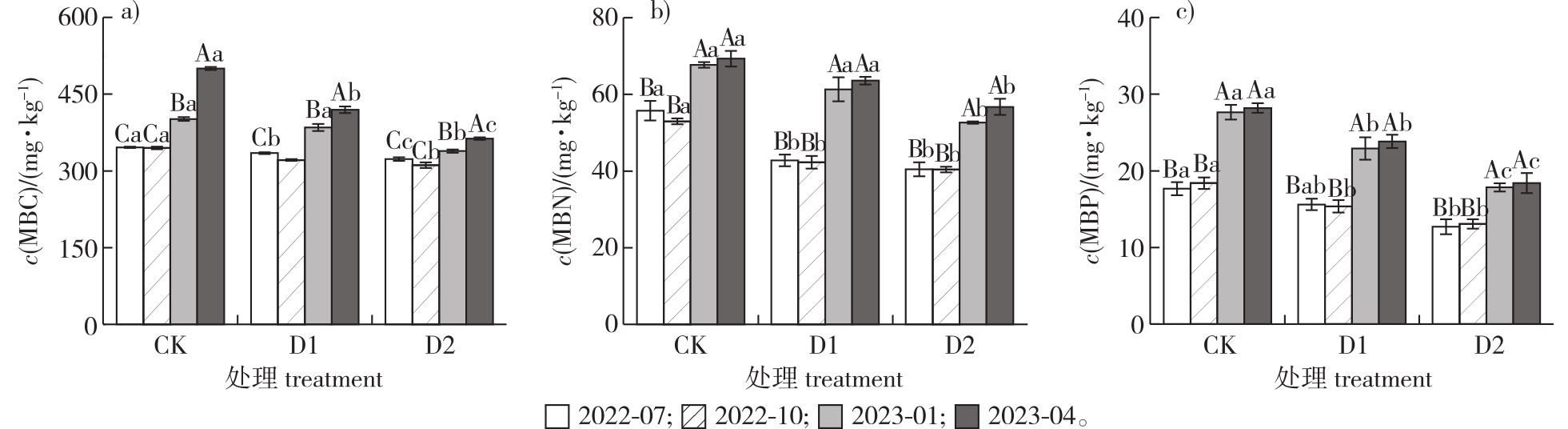
【目的】揭示干旱对杨树人工林土壤微生物生物碳量(C)、氮(N)、磷(P)及其生态化学计量特征的影响。为深入了解未来全球干旱背景下杨树人工林土壤C、N、P生物地球化学循环,以及人工林的合理经营提供理论依据。【方法】以江苏省东台林场美洲黑杨(Populus deltoides)人工林为对象,设置自然降水(CK)、穿透雨减少30%(D1)和穿透雨减少50%(D2)3种处理,探讨土壤微生物生物量碳(MBC)、氮(MBN)、磷(MBP)及其生态化学计量特征(记为MBC/MBN、MBC/MBP、MBN/MBP)对干旱处理的响应,分析其与土壤理化性质之间的关系。【结果】①干旱处理显著降低了土壤MBC、MBN、MBP含量,D2处理较对照MBC、MBN、MBP分别降低了16.09%、22.60%、32.49%;干旱处理显著增加了MBC/MBN和MBC/MBP,与CK相比,D2处理两个比值分别提高了10.33%、25.15%,但干旱处理对MBN/MBP的影响不显著。②土壤MBC、MBN、MBP含量均有季节性差异,变化范围分别为344.67~500.12、45.21~63.22和15.33~23.48 mg/kg,在夏、秋两季,其含量均较低,而冬、春两季,其含量上升到较高水平,而土壤MBC/MBN和MBC/MBP的季节变化与之完全相反,MBN/MBP没有明显的季节变化。③与对照相比,干旱处理显著降低了土壤铵态氮($\mathrm{NH}_{4}^{+}-\mathrm{N}$)、可溶性有机碳(DOC)、有效磷(AP)含量和含水率(SWC),分别降低了68.81%、32.77%、29.87%和11.05%;而干旱处理后,土壤pH升高、硝态氮($\mathrm{NO}_{3}^{-}-\mathrm{N}$)含量增加,分别增加了1.51%和194.34%。相关性分析表明,土壤MBC、MBN、MBP与SWC和全氮(TN)含量呈极显著正相关,与土壤有机碳(SOC)、$\mathrm{NO}_{3}^{-}-\mathrm{N}$含量和碳氮比(C/N)呈显著或极显著负相关。土壤MBC/MBN、MBC/MBP、MBN/MBP与$\mathrm{NO}_{3}^{-}-\mathrm{N}$含量和C/N呈显著或极显著正相关,与SWC和TN含量呈显著或极显著负相关。【结论】干旱显著影响了杨树人工林土壤微生物生物量C、N、P含量及其生态化学计量特征,进而对土壤养分平衡和循环过程产生影响。
【Objective】This study aimed to reveal the effects of drought on soil microbial biomass carbon (C), nitrogen (N), and phosphorus (P), as well as their ecological stoichiometric characteristics in poplar plantations. We also aimed to understand the soil C, N, and P biogeochemical cycles in poplar plantations under a future global drought scenario and provide a theoretical basis for the rational management of these plantations.【Method】Soil microbial biomass C (MBC), N (MBN) and P (MBP), along with their ecological stoichiometric characteristics (i.e., MBC/MBN, MBC/MBP, and MBN/MBP), and soil physicochemical properties, were examined in a poplar plantation (Populus deltoides) at Dongtai Forest Farm, Jiangsu Province, China. Three treatments were established in this study, control (CK), 30% throughfall reduction (D1), and 50% throughfall reduction (D2).【Result】(1) Soil MBC, MBN, and MBP were significantly reduced under drought conditions compared to the control, with reductions of 16.09%, 22.60%, and 32.49%, respectively, for the D2 treatment. Both MBC/MBN and MBC/MBP were significantly increased under drought conditions, with increases of 10.33% and 25.15%, respectively, in the D2 treatment, while soil MBN/MBP ratios did not change significantly. (2) Soil MBC, MBN and MBP showed significant seasonal variations, ranging from 344.67 to 500.12 mg/kg, 45.21 to 63.22 mg/kg, and 15.33 to 23.48 mg/kg, respectively. MBC, MBN, and MBP contents were lower in summer and fall than in winter and spring. In contrast, seasonal variations in MBC/MBN and MBC/MBP showed opposite trends to those of MBC, MBN, and MBP, while seasonal variations in MBN/MBP were not significant. (3) Compared with the control, drought treatments significantly reduced $\mathrm{NH}_{4}^{+}-\mathrm{N}$, dissolved organic carbon (DOC), available phosphorus (AP), and soil water content (SWC) by 68.81%, 32.77%, 29.87%, and 11.05%, respectively. Drought treatments increased soil pH and $\mathrm{NO}_{3}^{-}-\mathrm{N}$ content by 1.51% and 194.34%, respectively. Correlation analyses showed that soil MBC, MBN, and MBP had highly significant positive correlations with SWC and total nitrogen (TN) and significant or highly significant negative correlations with SOC, $\mathrm{NO}_{3}^{-}-\mathrm{N}$ content, and the total carbon to nitrogen ratio (C/N). Soil MBC/MBN, MBC/MBP, and MBN/MBP showed significantly or highly significant positive correlations with $\mathrm{NO}_{3}^{-}-\mathrm{N}$ and C/N and significant or highly significant negative correlations with SWC and TN content.【Conclusion】Drought significantly affected soil microbial C, N, and P and their ecological stoichiometric characteristics in poplar plantations, potentially altering the soil nutrient balance and cycling in these plantations.
杨树人工林 / 土壤微生物 / 干旱 / 生态化学计量特征 / 季节变化
soil microbes / drought / ecological stoichiometric characteristics / popular plantation / seasonal variation
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
朴世龙, 张新平, 陈安平, 等. 极端气候事件对陆地生态系统碳循环的影响[J]. 中国科学:地球科学, 2019, 49(9):1321-1334.
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
姚庭玉, 陈小梅, 何俊杰, 等. 模拟干旱对鼎湖山季风常绿阔叶林土壤碳氮磷化学计量特征的影响[J]. 西南林业大学学报, 2017, 37(1):104-109.
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
许华, 何明珠, 唐亮, 等. 荒漠土壤微生物量碳、氮变化对降水的响应[J]. 生态学报, 2020, 40(4):1295-1304.
|
| [9] |
许淼平, 任成杰, 张伟, 等. 土壤微生物生物量碳氮磷与土壤酶化学计量对气候变化的响应机制[J]. 应用生态学报, 2018, 29(7):2445-2454.
|
| [10] |
李品, 木勒德尔·吐尔汗拜, 田地, 等. 全球森林土壤微生物生物量碳氮磷化学计量的季节动态[J]. 植物生态学报, 2019, 43(6):532-542.
|
| [11] |
李帅军, 郭剑芬, 吴东梅, 等. 隔离降雨对米槠天然林土壤微生物生物量和酶活性的影响[J]. 亚热带资源与环境学报, 2018, 13(1):17-25.
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
王绍强, 于贵瑞. 生态系统碳氮磷元素的生态化学计量学特征[J]. 生态学报, 2008, 28(8):3937-3947.
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
哈斯其美格, 杨嘉琪, 汪珊珊, 等. 土壤微生物生物量的生态化学计量特征[J]. 甘肃科技纵横, 2022, 51(1):12-14,19.
Haschinegger,
|
| [17] |
朱湾湾, 许艺馨, 王攀, 等. 降水量及N添加对荒漠草原植物和土壤微生物C∶N∶P生态化学计量特征的影响[J]. 西北植物学报, 2020, 40(4):676-687.
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
王凯, 邢仕奇, 张日升, 等. 科尔沁沙地杨树人工林植物-土壤C、N、P化学计量变化[J]. 生态学杂志, 2024, 43(1):162-169.
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
鲍士旦. 土壤农化分析[M]. 3版. 北京: 中国农业出版社,2000:1-51.
|
| [22] |
王国兵, 王瑞, 徐瑾, 等. 生物炭对杨树人工林土壤微生物生物量碳、氮、磷及其化学计量特征的影响[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 43(2):1-6.
|
| [23] |
吴金水, 林启美, 黄巧云, 等. 土壤微生物生物量测定方法及其应用[M]. 北京: 气象出版社,2006:79-84.
|
| [24] |
黄菊莹, 余海龙, 刘吉利, 等. 控雨对荒漠草原植物、微生物和土壤C、N、P化学计量特征的影响[J]. 生态学报, 2018, 38(15):5362-5373.
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
许艺馨, 余海龙, 李春环, 等. 模拟降水量变化对荒漠草原土壤酶活性的影响及其相关因素分析[J]. 西北植物学报, 2021, 41(11):1912-1923.
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
王国兵, 阮宏华, 唐燕飞, 等. 森林土壤微生物生物量动态变化研究进展[J]. 安徽农业大学学报, 2009, 36(1):100-104.
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |