 PDF(1896 KB)
PDF(1896 KB)


 PDF(1896 KB)
PDF(1896 KB)
 PDF(1896 KB)
PDF(1896 KB)
基于最小数据集的喀斯特不同类型人工林土壤质量评价
Assessment of different Karst plantation types on soil quality based on a minimum data set
【目的】评价喀斯特山地不同类型人工林植被恢复对土壤质量的影响,为该地区选择适宜的造林树种和改善林地土壤质量提供参考依据。【方法】以贵州省喀斯特山地营造的干香柏 (Cupressus duclouxiana,下称滇柏)纯林、刺槐(Robinia pseudoacacia)纯林和滇柏-刺槐混交林这3种类型人工林及未造林地(CK)为研究对象,对喀斯特山地不同类型人工林土壤理化性质和酶活性变化进行了研究,采用冗余分析、主成分分析(PCA)、全体数据集(TDS)、最小数据集(MDS)和灰色关联度(GRA)等方法评估土壤质量。【结果】①3种人工林地土壤含水率、孔隙度、有机质、全氮、碱解氮、全磷、速效磷质量分数均显著高于未造林地,容重、pH、全钾、速效钾质量分数均显著低于未造林地。②土壤脲酶、多酚氧化酶、蔗糖酶、碱性磷酸酶、过氧化氢酶这5种酶中,除碱性磷酸酶活性外,其余4种土壤酶活性均在滇柏-刺槐混交林土壤中最高。3种类型人工林土壤脲酶、碱性磷酸酶、过氧化氢酶活性均高于未造林地。③基于主成分分析法的最小数据集适合作为喀斯特山地人工林土壤质量评价的最小数据集提取方法,本研究选择的最小数据集包括土壤全氮、全钾、速效钾质量分数、非毛管孔隙度、碱性磷酸酶、多酚氧化酶活性。④基于MDS 建立的土壤质量评价结果与基于TDS和灰色关联度的评价结果相一致,土壤质量评价得分从大到小顺序均为滇柏-刺槐混交林>刺槐林>滇柏林>未造林地。总体上看,混交林土壤质量明显优于纯林。【结论】在喀斯特山地植被恢复和人工林营造中,可遵循适树适地的原则,以营造混合林为主,从而达到改善土壤综合质量,提高人工植被修复生态效益的目的。
【Objective】This study evaluated soil quality under different types of plantation vegetation restoration in Karst areas, aiming to provide guidance on selecting suitable tree species and improving soil quality. 【Method】Three types of plantation forests—Cupressus duclouxiana forest, Robinia pseudoacacia forest, and C. duclouxiana-R. pseudoacacia mixed forest—along with unplanted land (control) in Guizhou Province, were selected for the study. The soil physical, chemical, and enzymatic characteristics were analyzed. Redundancy analysis and principal component analysis (PCA) were used to assess soil fertility quality, while total data set (TDS), minimum data set (MDS), and gray correlation degree method (GRA) were employed to evaluate soil fertility. 【Result】(1) Compared with unplanted land, soil water content, porosity, organic matter, total nitrogen, alkali-hydrolyzed nitrogen, total phosphorus, and available phosphorus content were significantly higher in plantation forests. Conversely, soil bulk density, pH, total potassium, and available potassium were significantly lower. (2) Except for alkaline phosphatase, the activities of urease, polyphenol oxidase, sucrase, and catalase were the highest in the C. duclouxiana-R. pseudoacacia mixed forest. Urease, alkaline phosphatase, and catalase activities were higher in plantations than those in unplanted land. (3) The minimum data set derived from PCA was suitable for soil quality evaluation in Karst plantations. This data set included soil total nitrogen, total potassium, available potassium content, non-capillary porosity, alkaline phosphatase, and polyphenol oxidase activities. (4) Soil quality evaluations based on MDS align with those based on TDS and grey correlation degree. The soil quality order was as follows: C. duclouxiana-R. pseudoacacia mixed forest > R. pseudoacacia forest > C. duclouxiana forest > unplanted land. The mixed forest demonstrated significantly better soil quality than the pure forests. 【Conclusion】 During vegetation restoration and plantation development in Karst areas, following the principles of tree adaptation and site suitability, and focusing on constructing mixed forests, can enhance overall soil quality and improve the ecological benefits of artificial vegetation restoration.
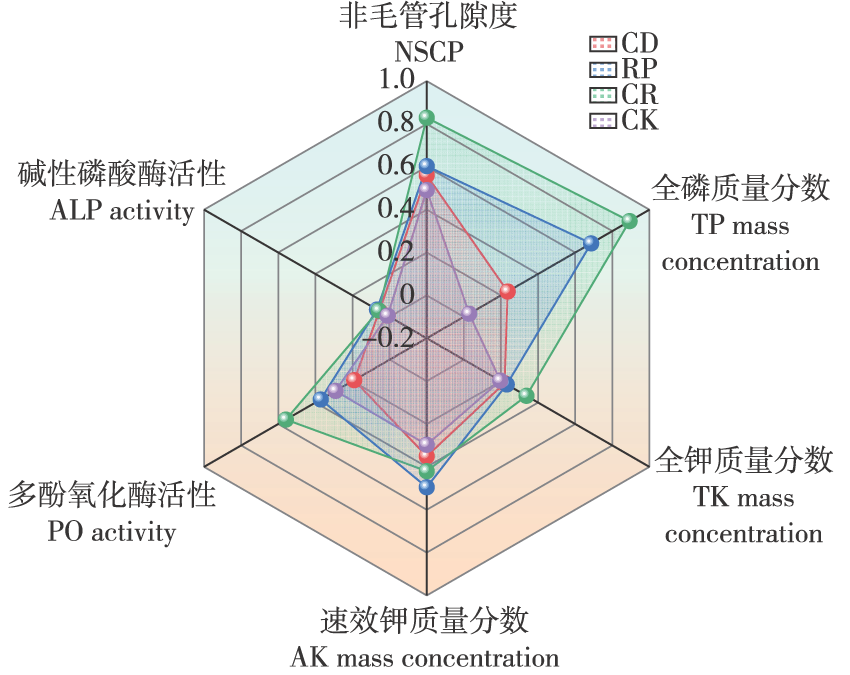
喀斯特山地 / 土壤质量综合评价 / 主成分分析法(PCA) / 最小数据集(MDS)
Karst area / evaluation of soil quality / principal component analysis(PCA) / minimum data set(MDS)
| [1] |
戎宇, 刘成刚, 薛建辉. 喀斯特山地不同人工林土壤特性差异与综合评价[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2011, 35(2): 108-112.
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
刘占锋, 傅伯杰, 刘国华, 等. 土壤质量与土壤质量指标及其评价[J]. 生态学报, 2006(3): 901-913.
|
| [5] |
张连金, 赖光辉, 孙长忠, 等. 北京九龙山土壤质量综合评价[J]. 森林与环境学报, 2016, 36(1): 22-29.
|
| [6] |
梅楠, 谷岩, 李德忠, 等. 基于最小数据集的吉林省黑土耕层土壤质量评价[J]. 农业工程学报, 2021, 37(12): 91-98.
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
杨文娜, 任嘉欣, 李忠意, 等. 主成分分析法和模糊综合评价法判断喀斯特土壤的肥力水平[J]. 西南农业学报, 2019, 32(6): 1307-1313.
|
| [12] |
刘成刚, 薛建辉. 喀斯特石漠化山地不同类型人工林土壤的基本性质和综合评价[J]. 植物生态学报, 2011, 35(10): 1050-1060.
|
| [13] |
马洁, 薛建辉, 吴永波, 等. 贵州省喀斯特山地3种人工林林下植物多样性和地上部生物量及其相关性[J]. 植物资源与环境学报, 2021, 30(1): 17-26.
|
| [14] |
鲁如坤. 土壤农业化学分析方法[M]. 北京: 中国农业科技出版社, 2000.
|
| [15] |
关松荫, 张德生, 张志明. 土壤酶及其研究法[M]. 北京: 农业出版社, 1986, 14-339.
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
冯瑞琦, 潘萍, 欧阳勋志, 等. 基于最小数据集的闽楠天然次生林土壤质量评价[J]. 江西农业大学学报, 2021, 43(3): 585-597.
|
| [18] |
王建国, 杨林章, 单艳红. 模糊数学在土壤质量评价中的应用研究[J]. 土壤学报, 2001, 38(2): 176-183.
|
| [19] |
金晶炜, 许岳飞, 熊俊芬, 等. 应用灰色关联度法评价砷污染土壤修复效果[J]. 水土保持通报, 2009, 29(6): 213-216.
|
| [20] |
刘可意, 杨佳, 姜淑娜, 等. 基于最小数据集的典型黑土区不同林龄小黑杨土壤质量差异[J]. 生态学报, 2024, 44(9).
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
贡璐, 张雪妮, 冉启洋. 基于最小数据集的塔里木河上游绿洲土壤质量评价[J]. 土壤学报, 2015, 52(3): 682-689.
|
| [23] |
金慧芳, 史东梅, 陈正发, 等. 基于聚类及PCA分析的红壤坡耕地耕层土壤质量评价指标[J]. 农业工程学报, 2018, 34(7): 155-164.
|
| [24] |
邓绍欢, 曾令涛, 关强, 等. 基于最小数据集的南方地区冷浸田土壤质量评价[J]. 土壤学报, 2016, 53(5): 1326-1333.
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
魏树伟, 王少敏, 张勇, 等. 不同土壤管理方式对梨园土壤养分、酶活性及果实风味品质的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2015, 24(12): 46-55.
|
| [28] |
唐祎欣, 张伟, 吴汉卿, 等. 植被恢复对西南喀斯特地区土壤气候韧性的提升作用[J]. 生态学报, 2023, 43(20): 8430-8441.
|
| [29] |
石海龙, 张林星, 甘凤玲, 等. 喀斯特槽谷区侵蚀坡面的土壤质量评价及障碍因子[J]. 水土保持学报, 2024, 38(2).
|
| [30] |
田英, 许喆, 王娅丽, 等. 宁夏银川平原沙化土地不同人工林土壤质量评价[J]. 生态学报, 2023(4): 1-11.
|
| [31] |
董茜, 王根柱, 庞丹波, 等. 喀斯特区不同植被恢复措施土壤质量评价[J]. 林业科学研究, 2022, 35(3): 169-178.
|
| [32] |
黄宇, 汪思龙, 冯宗炜, 等. 不同人工林生态系统林地土壤质量评价[J]. 应用生态学报, 2004(12): 2199-2205.
|
| [33] |
戴凌, 黄志宏, 文丽. 长沙市不同森林类型土壤养分含量与土壤酶活性[J]. 中南林业科技大学学报, 2014, 34(6): 100-105.
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
李静鹏, 徐明锋, 苏志尧, 等. 不同植被恢复类型的土壤肥力质量评价[J]. 生态学报, 2014, 34(9): 2297-2307.
|
| [36] |
钟琪. 混交林营造技术分析[J]. 绿色科技, 2016(9): 81-83.
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |