 PDF(1598 KB)
PDF(1598 KB)


 PDF(1598 KB)
PDF(1598 KB)
 PDF(1598 KB)
PDF(1598 KB)
基于MSOR理论模型的世界地质公园边缘旅游地扰动机制分析
An analysis of the disturbance mechanism of tourist destinations at the edge of world geological parks based on the MSOR theoretical model
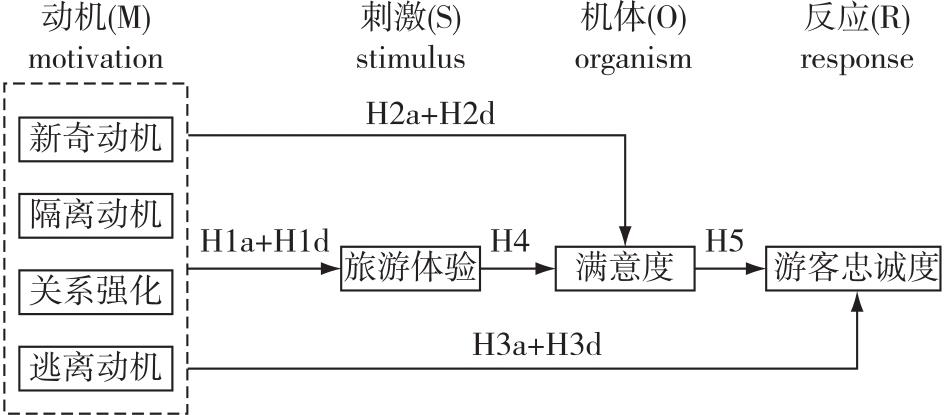
【目的】探讨雁荡山世界地质公园边缘旅游地游客不同旅游动机(M)对公园景观旅游体验(S)、满意度(O)和忠诚度(R)的影响机制,为边缘旅游地扰动机制研究提供理论支持和实践指导。【方法】以雁荡山世界地质公园非核心景区——南雁荡山为研究区,使用Amos和Mplus软件,结合调查问卷形式,开展了游客游览行为特征研究。【结果】①国家级地质公园边缘型旅游地主要游客群体为以核心家庭为主的本地居民;②游览新奇动机无法通过任何方式对游客忠诚度产生影响;③关系强化对忠诚度的影响属于完全中介,仅通过中介效应对旅游体验和忠诚度产生正向影响;④隔离动机和逃离动机对忠诚度不仅存在直接、正向促进作用,还存在复杂多重链式中介效应。【结论】本研究揭示了不同旅游动机对边缘旅游地游客景观游览体验、满意度和忠诚度的影响机制,发现本地游客对边缘旅游地保护和可持续发展具有重要作用。因此,对地质公园及其周边自然保护地而言,景区旅游发展应避免大拆大建以减少扰动源,利用客群特点控制扰动范围,并严控设施增量降低扰动强度。
【Objective】This study was conducted to explore the impact mechanisms of different tourism motivations on the tourism experience, satisfaction, and loyalty of tourists in the edge tourist destinations of Yandang Mountain Global Geopark, providing theoretical support and practical insights for understanding the disturbance mechanisms of edge tourist destinations. 【Method】Amos and Mplus software were employed to administer a survey questionnaire targeting the consumption behavior characteristics of tourists in the non-core scenic area of the Yandang Mountain Global Geopark, specifically the South Yandang Mountain. 【Result】(1) The primary tourist group in peripheral tourist destinations consists of local residents, predominantly core families. (2) Noelty motivation exhibited no direct or indirect effects on loyalty. (3) Relationship strengthening’s influence on loyalty was fully mediated, demonstrating positive effects on tourism experience and loyalty through mediating effects. (4) Isolation motivation and escape motivation exhibited both direct and indirect positive effects on loyalty, with complex and multiple chain-mediated impacts. These findings reveal the impact mechanisms of different tourism motivations on tourist experiences, satisfaction, and loyalty in edge tourism destinations. Local tourists were identified as playing a crucial role in the protection and sustainable development of edge tourism destinations. 【Conclusion】The study suggests that scenic spots should avoid large-scale construction, leverage customer characteristics to mitigate disturbance risks, and cautiously supplement tourist demand to prevent disturbances from expanding.
自然保护地 / 边缘旅游地 / 结构方程模型 / 动机-体验-满意度-忠诚度(MSOR)理论 / 雁荡山世界地质公园
nature reserves / marginal tourist destination / structural equation model / MSOR theory / the Yandang Mountain Global Geopark
| [1] |
黄薇薇, 沈非. 边缘型旅游地研究综述及展望[J]. 人文地理, 2015, 30(4):24-31.
|
| [2] |
赵逊, 赵汀. 中国地质公园地质背景浅析和世界地质公园建设[J]. 地质通报, 2003, 22(8):620-630.
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
何云梦, 徐菲菲, 剌利青, 等. 基于S-O-R理论的文旅消费驱动机制研究[J]. 旅游科学, 2023, 37(1):116-132.
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
刘雷, 史小强. 新冠肺炎疫情背景下体育旅游消费行为影响机制:基于S-O-R框架的MOA-TAM整合模型的实证分析[J]. 旅游学刊, 2021, 36(8):52-70.
|
| [12] |
粟路军, 何学欢, 胡东滨, 等. 服务质量对旅游者抵制负面信息意愿的影响机制研究:基于Stimulus-Organism-Response(S-O-R)分析框架[J]. 旅游科学, 2017, 31(6):30-51.
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
达婷, 李琰, Mathias Kondolf.G. 基于场所依恋的城市滨水公园社会连接研究[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2023, 47(6):227-235.
|
| [15] |
林雨辰, 赵伟. 基于时空景观的泉州蓄滞洪区城市更新研究[J]. 室内设计与装修, 2024(2):130-131.
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
周玲强, 李罕梁. 游客动机与旅游目的地发展:旅行生涯模式(TCP)理论的拓展和应用[J]. 浙江大学学报(人文社会科学版), 2015, 45(1):131-144.
|
| [20] |
陈楠, 乔光辉. 大众旅游者与生态旅游者旅游动机比较研究:以云台山世界地质公园为例[J]. 地理科学进展, 2010, 29(8):1005-1010.
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
林心影, 赖鹏程, 陈健翎, 等. 雁荡山风景名胜区旅游形象感知研究[J]. 林业资源管理, 2021(2):164-170.
|
| [23] |
余向洋, 朱国兴, 邱慧. 游客体验及其研究方法述评[J]. 旅游学刊, 2006, 21(10):91-96.
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
张欣然. 社区居民对都市近郊乡村旅游影响的感知与态度的实证研究:以成都花香果居景区为例[J]. 中国农业资源与区划, 2016, 37(12):243-248.
|
| [29] |
赵昕, 关宏志, 夏晓敬. 基于活动的游客出游模式选择行为研究[J]. 北京工业大学学报, 2013, 39(6):920-924.
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
张建国, 胡洁思. 森林运动小镇游客游憩动机与满意度关系研究[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 45(4):201-209.
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
樊友猛, 谢彦君. 具身欲求与身体失范:旅游不文明现象的一种理论解释[J]. 旅游学刊, 2016, 31(8):4-6.
|
| [35] |
廖维俊, 何有世. 非惯常环境旅游者不文明行为是如何形成的?基于相对剥夺理论视角的扎根研究[J]. 干旱区资源与环境, 2018, 32(6):194-201.
|
| [36] |
邱宏亮, 范钧, 赵磊. 旅游者环境责任行为研究述评与展望[J]. 旅游学刊, 2018, 33(11):122-138.
|
| [37] |
汪熠杰, 吕宛青, 倪向丽. 考虑羊群效应的旅游不文明行为形成与演化:基于演化博弈分析[J]. 华侨大学学报(哲学社会科学版), 2022(4):37-50.
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |