 PDF(14538 KB)
PDF(14538 KB)


景观元素对城市公园滨水空间使用者安全感的影响——以南京市玄武湖公园为例
陈宇楠, 丛昕, 张文豹, 荣晗琳, 张清海
南京林业大学学报(自然科学版) ›› 2025, Vol. 49 ›› Issue (3) : 235-244.
 PDF(14538 KB)
PDF(14538 KB)
 PDF(14538 KB)
PDF(14538 KB)
景观元素对城市公园滨水空间使用者安全感的影响——以南京市玄武湖公园为例
The effect of landscape elements on users’ sense of security in urban park waterfront spaces: taking Nanjing Xuanwu Lake Park as an example
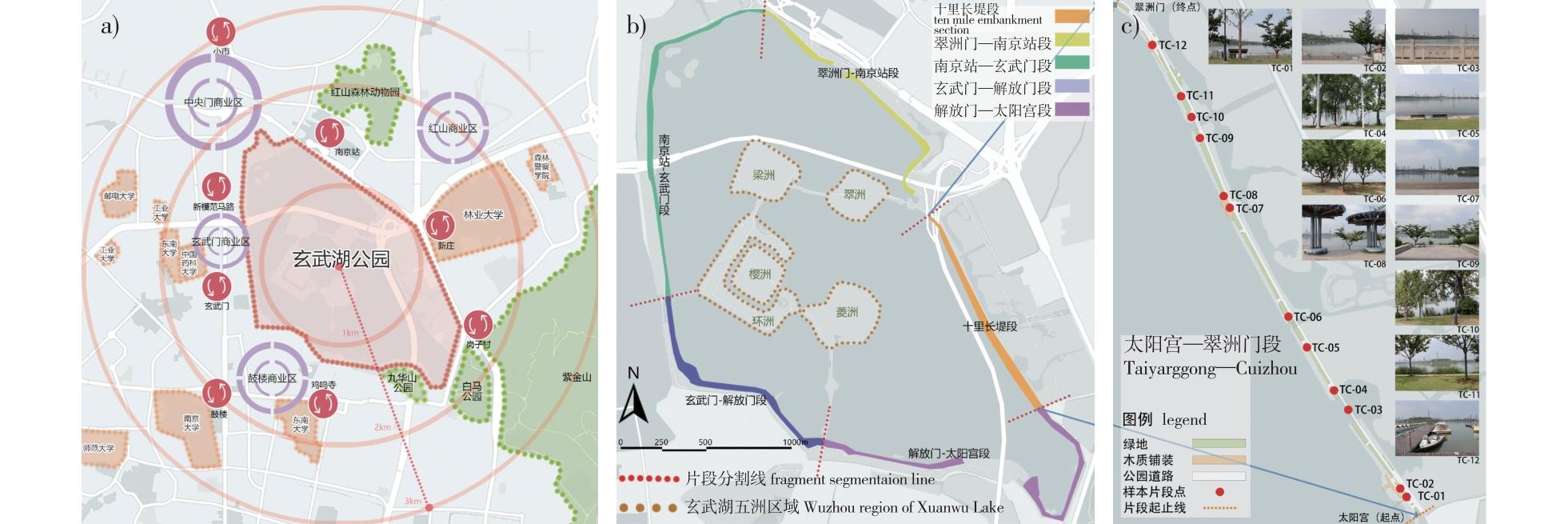
【目的】环境安全感对于使用者的身心健康具有重要影响,是景观设计需要考虑的重要因素之一,而城市公园滨水空间是公众最容易聚集的场所之一,也是相对容易使公众感到不安全的场所,值得重点研究。探究城市公园滨水空间中景观元素的占比和配置对公园使用者安全感的影响,可为城市公园滨水空间安全设计提供理论支持。【方法】以南京市玄武湖公园为例,筛选66条滨水空间样本片段进行研究。拍摄样本照片,对景观元素进行分类,统计各元素在照片中的占比。采用Pearson相关性分析法、双因素方差分析法、多元线性回归法等数理统计方法,分析了滨水空间中景观元素与使用者安全感之间的耦合关系。【结果】①对滨水空间安全感最具有正向影响的景观元素为天空和水边围栏,其Pearson相关系数分别为0.571和0.552(P<0.01);最具有负向影响的元素为水岸乔木和水岸灌木/草花,其Pearson相关系数分别为-0.450和-0.357(P<0.01)。②滨水植物元素之间、滨水植物与天空元素之间均会交互影响,并共同作用于滨水空间使用者的安全感。③滨水空间荫蔽度与滨水空间自然度均会对安全感得分产生显著的负向影响。④不同人水关系的滨水空间中,自然景观元素和人工景观元素对安全感影响的程度不同。【结论】通过对景观元素的分类,并分析其与使用者安全感间的多重耦合关系,构建了更多滨水空间景观元素与空间使用者心理间的关系桥梁,有助于针对性地提出城市公园滨水空间的景观安全优化建议。
【Objective】The perception of environmental safety significantly impacts users’ physical and mental well-being and is a key consideration in landscape design. Urban park waterfront spaces, being areas where the public congregates most and where a sense of insecurity is relatively easily experienced, merit special attention. Studying how the proportion and configuration of landscape elements in urban park waterfront spaces affect park users’ safety perception can provide theoretical support for safety-centered design of such spaces.【Method】Taking Nanjing’s Xuanwu Lake Park as a case, 66 sample segments of the waterfront space were selected. Sample photos were taken, landscape elements were classified, and the percentage of each element in the photos was calculated. Mathematical and statistical methods, such as Pearson correlation analysis, two-factor ANOVA, and multivariate linear regression, were used to analyze the coupling relationship between landscape elements and users’ sense of security in the waterfront space.【Result】(1) The landscape elements with the most significant positive impact on the sense of security in the waterfront space are the sky (0.571,P<0.01) and the waterfront fence (0.552,P<0.01), while those with the most significant negative impact are waterfront trees (-0.450,P<0.01) and waterfront shrubs/grass flowers (-0.357,P<0.01).(2) Waterfront plant elements interact with each other and with the sky element, jointly influencing the sense of security of waterfront space users.(3) Both the shade level in the waterfront space and the naturalness degree of the waterfront space have a significant negative impact on the safety perception score.(4) In different waterfront spaces with diverse human-water relationships, natural and artificial landscape elements have varying degrees of influence on the sense of security.【Conclusion】By categorizing landscape elements and analyzing their multiple coupling relationships with users’ sense of security, more connections between waterfront space landscape elements and users’ psychology were established. This is beneficial for proposing optimization suggestions for the landscape security of urban park waterfront spaces.
城市公园 / 滨水空间 / 安全感 / 景观设计元素 / 相关性分析 / 南京玄武湖
urban park / waterfront spaces / sense of security / landscape design elements / correlation analysis / Xuanwu Lake Park in Nanjing City
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
朱丽衡, 曹磊, 袁瑞伯. 基于游客安全感的城市公园空间环境安全评价研究:以唐山市凤凰山公园为例[J]. 室内设计与装修,2020(1) :136-137.
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
莫小云, 林静瑜, 林雪玲, 等. 私密性景观空间的设计元素研究[J]. 重庆科技学院学报(自然科学版), 2018, 20(1):115-120.
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
邱瑶, 罗涛, 王艳云, 等. 基于视觉关注度与审美偏好的城市景观元素感知特征研究[J]. 中国园林, 2023, 39(6):82-87.
|
| [17] |
赵静, 宣国富. 城市居民公园游憩体验质量及性别差异:以南京玄武湖公园为例[J]. 中国园林, 2015, 31(7):113-116.
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
冼宁, 方虹博. 简述城市滨水空间景观人性化设计[J]. 设计, 2017(13):68-69.
|
| [20] |
杨雨雯, 董叶文, 刘雪鸣, 等. 健康城市视角下的城市中心区滨水空间:理论机制、科学证据、关键要素[J]. 上海城市规划, 2020(2):57-63.
|
| [21] |
苏春雨, 武凤文. 基于儿童友好的滨水空间安全感设计策略[J]. 北京规划建设, 2020(3):30-34.
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
符兴源, 杨盼, 姜珊, 等. 不同景观设计元素及其组合对景观安全感的影响[J]. 城市问题, 2019(9):37-44.
|
| [26] |
段文, 袁媛, 陶楠. 商业型历史文化街区街道空间风貌管控研究:以昆明南强街为例[J]. 室内设计与装修, 2024(6):114-116.
|
| [27] |
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |