 PDF(5196 KB)
PDF(5196 KB)


碳中和背景下的中国碳汇林业生产效率时空分异及影响因素研究
师玮, 赵思雪, 乔富伟, 安怡, 王维鹃, 张国炜
南京林业大学学报(自然科学版) ›› 2025, Vol. 49 ›› Issue (3) : 254-264.
 PDF(5196 KB)
PDF(5196 KB)
 PDF(5196 KB)
PDF(5196 KB)
碳中和背景下的中国碳汇林业生产效率时空分异及影响因素研究
Spatiotemporal differentiation and influencing factors of forestry production efficiency with carbon sequestration in China under the context of carbon neutrality
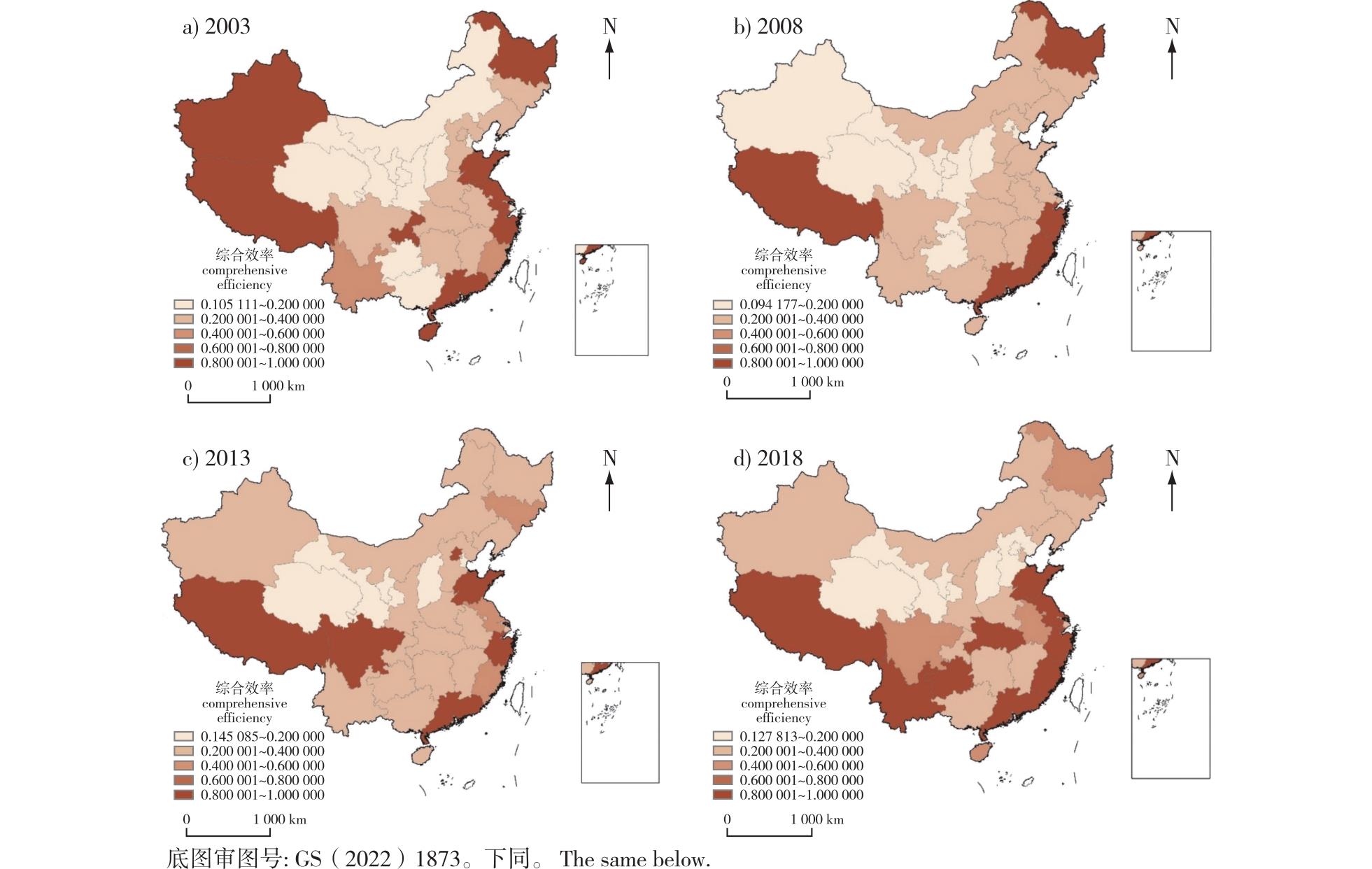
【目的】探讨碳汇林业生产效率并探究其关键影响因素是助力中国林业高质量发展的重要出发点,可为制定差异化林业发展政策提供必要的依据,也为有效促进中国林业资源优化配置和区域协同均衡发展提供参考。【方法】采用蓄积量拓展法、SBM(Slack-Based Measure)模型、Dagum基尼系数和Tobit模型等方法,分析了2003—2018年中国31个省份的碳汇林业经济价值和各项效率水平,并在此基础上深入分析了综合效率、纯技术效率和规模效率动态变化及其时空分异情况,探究其关键影响因素。【结果】中国的林业碳汇储存量整体上水平较高,其中林业碳汇经济价值最高的3个省区依次为西藏、四川、云南;综合效率、纯技术效率与规模效率呈现出显著的区域性差异,具有明显的空间集聚特征;区域间差异和区域内差异是中国碳汇林业生产效率的区域差异主要来源;林业产值比重与林业人力资本投入对中国碳汇林业生产效率起促进作用,而人均GDP和森林病虫鼠害发生情况对碳汇林业生产效率起抑制作用。【结论】中国林业发展可通过推进林业资源的高效利用、缩小区域发展的效率差异以及把握关键影响因素,从而实现碳汇林业的高质量发展。
【Objective】This study aims to investigate the production efficiency of carbon sequestration forestry and identify its key influencing factors. This exploration serves as a crucial foundation for the high-quality development of forestry in China. It not only provides essential insights for formulating differentiated forestry development policies but also facilitates the optimal allocation of forestry resources and promotes coordinated and balanced regional development across the country.【Method】The economic value and efficiency levels of carbon sequestration forestry in 31 provinces of China from 2003 to 2018 were evaluated using the volume expansion method, SBM model, Dagum Gini coefficient, and Tobit model. Building on this analysis, the study delved into the dynamic changes in comprehensive efficiency, pure technical efficiency, and scale efficiency, as well as their spatiotemporal differentiation. Additionally, the key influencing factors were systematically explored.【Result】The findings revealed that China’s forestry carbon sequestration storage level was relatively high, with Xizang, Sichuan, and Yunnan being the top three provincial area in terms of forestry carbon sequestration economic value. Comprehensive efficiency, pure technical efficiency, and scale efficiency exhibited significant regional disparities and demonstrated distinct spatial agglomeration characteristics. Both inter-regional and intra-regional differences were identified as the primary sources of regional variations in the production efficiency of carbon sequestration forestry in China. The proportion of forestry output value and investment in forestry human capital were found to positively influence the production efficiency of China’s carbon sequestration forestry, whereas per capita GDP and the incidence of forest diseases, pests, and rodents exerted a restraining effect.【Conclusion】China’s forestry development can achieve high-quality growth in carbon sequestration forestry by enhancing the efficient utilization of forestry resources, reducing regional efficiency disparities, and addressing key influencing factors. This approach will contribute to the sustainable and balanced advancement of the forestry sector.
碳汇林业 / 生产效率 / SBM模型 / Dagum基尼系数 / Tobit模型
carbon sequestration forestry / production efficiency / SBM model / Dagum Gini coefficient / Tobit model
| [1] |
邓诗宇, 张明芳, 侯怡萍, 等. 气候变化下川西地区森林碳储量对森林管理措施和干扰的长期响应[J]. 生态学报, 2025, 45(1):210-226.
|
| [2] |
吴恒, 吕大伟, 汪圣云, 等. “双碳”战略背景下的多尺度森林碳储量年度监测研究进展与思考[J]. 世界林业研究, 2024, 37(1):59-64.
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
包蕊, 李涛, 张欣怡, 等. 森林生态系统损害评估体系与管理制度研究[J]. 生态学报, 2021, 41(3):924-933.
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
石小亮, 陈珂, 曹先磊, 等. 森林生态系统管理研究综述[J]. 生态经济, 2017, 33(7):195-201.
|
| [10] |
刘亚, 黄安胜. 森林碳汇环境库兹涅茨曲线特征及其影响因素分析[J]. 世界林业研究, 2023, 36(2):132-137.
|
| [11] |
谢军安, 王爱霞. 完善森林管理增强碳汇能力[J]. 当代经济管理, 2011, 33(4):31-33.
|
| [12] |
李海萍, 李定恒, 李豪. 贵州省退耕还林还草潜在碳汇效益评估[J]. 生态学报, 2022, 42(23):9499-9510.
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
方精云. 北半球中高纬度的森林碳库可能远小于目前的估算[J]. 植物生态学报, 2000, 24 (5):635-638.
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
康惠宁, 马钦彦, 袁嘉祖. 中国森林C汇功能基本估计[J]. 应用生态学报, 1996, 7(3):230-234.
|
| [17] |
李秀娟, 周涛, 何学兆. NPP增长驱动下的中国森林生态系统碳汇[J]. 自然资源学报, 2009, 24(3):491-497.
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
闵志强, 胡云云, 刘友林, 等. 延安市林草光伏互补建设空间适宜性及固碳减排效益研究[J]. 西北林学院学报, 2023, 38(5):57-66.
|
| [24] |
范正根, 邓超, 范雨琪, 等. “双碳” 目标视角下耕地利用生态效率测度及其时空特征:以长江中下游粮食主产区为例[J]. 生态经济, 2023, 39(11):119-127.
|
| [25] |
郗婷婷, 李顺龙. 黑龙江省森林碳汇潜力分析[J]. 林业经济问题, 2006, 26(6):519-522,526.
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
施琪, 王玉玲. 基于超效率SBM模型的中国林业产业绩效评价研究[J]. 中国林业经济, 2022(1):17-23.
|
| [30] |
杨旭, 屈志光, 邓远建. 中国省域林业生产技术效率的空间收敛性及分异特征[J]. 资源科学, 2021, 43(10):1947-1960.
|
| [31] |
支玲, 许文强, 洪家宜, 等. 森林碳汇价值评价:三北防护林体系工程人工林案例[J]. 林业经济, 2008, 30(3):41-44.
|
| [32] |
吕洁华, 付思琦, 张滨. 黑龙江省国有重点林区林业经济投入产出效率研究[J]. 林业经济问题, 2019, 39(3):300-306.
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
李文博. 江西省林业产业投入产出效率及其影响因素研究:基于DEA-Tobit模型[D]. 南昌: 江西农业大学, 2021.
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |