 PDF(8079 KB)
PDF(8079 KB)


基于InVEST-PLUS-GeoDectetor模型的环杭州湾碳储量时空演变与多情景预测
孙严超, 蔡俊, 王子豪, 田凤雅, 李天龙
南京林业大学学报(自然科学版) ›› 2025, Vol. 49 ›› Issue (5) : 19-28.
 PDF(8079 KB)
PDF(8079 KB)
 PDF(8079 KB)
PDF(8079 KB)
基于InVEST-PLUS-GeoDectetor模型的环杭州湾碳储量时空演变与多情景预测
Spatio-temporal evolution and multi-scenario prediction of carbon storage around Hangzhou Bay based on InVEST-PLUS-GeoDectetor model
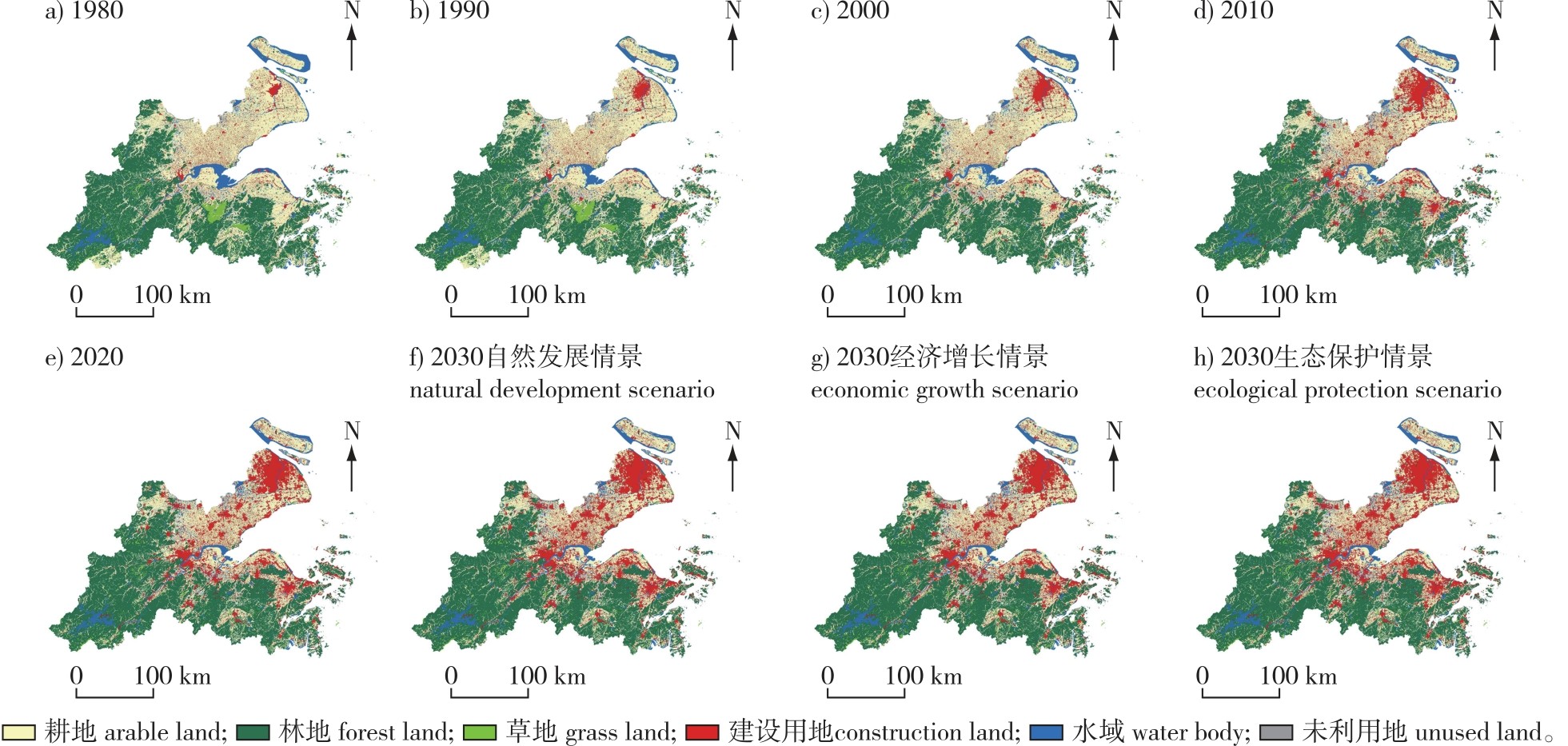
【目的】探究环杭州湾土地利用变化和碳储量时空分异特征,为未来区域碳平衡、内部土地利用结构优化和社会经济可持续发展提供思路。【方法】以环杭州湾为例,基于InVEST和PLUS模型,评估1980—2020年土地利用对碳储量变化和生态系统碳储量服务脆弱性的影响,并利用地理探测模型(GeoDectetor)分析碳储量分异变化的驱动因素,预测2030年多情景下土地利用格局和碳储量变化。【结果】①环杭州湾主要地类为耕地和林地,其土地利用强度近40年间提高了10.35,处于中等发展水平,呈逐年上升的趋势。同时,研究区碳储量总体呈现先增后减的趋势,1980—2000年整体表现为碳汇,而在2000—2020年表现为碳源。②单因子探测得出碳储量分异变化主要受坡度等自然因素影响,双因子交互探测得出碳储量的变化是诸多因素共同作用的结果。自然因素与人为因素共同制约植被覆盖度的增长,最终影响区域碳储量分布情况。③2030年除生态保护情景下碳储量有所增加,自然发展和经济增长情景下碳储量均不同程度减少,表明未来在生态保护情景下,生态用地的有效保护对碳储量的增加较自然发展情景和经济增长情景更有利。【结论】未来生态保护情景下的环杭州湾土地利用能综合统筹各地类功能,减缓碳储量损失,对区域国土空间优化具有重要意义。
【Objective】Against the backdrop of the carbon peaking and carbon neutrality goals, this study delves into the spatial-temporal differentiation characteristics of land-use changes and carbon storage. The aim of this study is to offer insights for future regional carbon balance, the optimization of the internal land-use structure, and the sustainable social-economic development around Hangzhou Bay.【Method】Taking the Hangzhou Bay area as a case study, by leveraging the InVEST and PLUS models, this paper assessed the impacts of land use on the alterations in carbon storage and the vulnerability of ecosystem carbon storage services from 1980 to 2020. The GeoDectetor model was utilized to analyze the driving factors behind the differentiation and changes in carbon storage, and forecasted the land-use patterns and changes in carbon storage under multiple scenarios in 2030.【Result】(1) Cultivated land and forest land were the predominant land types around Hangzhou Bay. Over the past nearly 40 years, the overall land-use intensity increased by 10.35 units. The land usage remained at a medium-development level and demonstrated a year-on-year upward trend. Meanwhile, the total carbon storage in the study area generally exhibited a pattern of first increasing and then decreasing. From 1980 to 2000, it was predominantly a carbon sink, while from 2000 to 2020, it turned into a carbon source. (2) The single factor detection revealed that the differentiation and changes in carbon storage were mainly and significantly influenced by natural factors such as slope. The two-factor interaction detection indicated that the changes in carbon storage resulted from the combined effects of multiple factors. Besides being affected by natural factors, human factors also impeded the growth of vegetation coverage, ultimately influencing the distribution of regional carbon storage. (3) Under the three scenarios in 2030, with the exception of an increase under future ecological protection scenario, the other two scenarios showed varying degrees of decline. This implied that in the future, under the ecological protection scenario, the effective conservation of ecological land had a substantially higher impact on the stability of carbon storage compared to the natural development scenario and the economic growth scenario.【Conclusion】The land use around Hangzhou Bay under future ecological protection scenario can comprehensively coordinate the functions of diverse land types, decelerate the loss of carbon storage, and is of great significance for the optimization of the regional territorial space.
碳储量 / 土地利用 / 多情景预测 / 地理探测器 / 环杭州湾
carbon storage / land use / multi-scenario forecast / GeoDetector / around Hangzhou Bay
| [1] |
杨宇萍, 胡文敏, 贾冠宇, 等. 基于InVEST与ANN-CA模型的环洞庭湖区土地利用碳储量情景模拟[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2023, 47(4):175-184.
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
王超越, 郭先华, 郭莉, 等. 基于FLUS-InVEST的西北地区土地利用变化及其对碳储量的影响:以呼包鄂榆城市群为例[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(8):1667-1679.
|
| [4] |
李月, 罗红芬. 基于InVEST模型的黔中普定县域生态系统碳储量时空变化[J]. 中国水土保持科学(中英文), 2023, 21(4):28-35.
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
曲福田, 卢娜, 冯淑怡. 土地利用变化对碳排放的影响[J]. 中国人口·资源与环境, 2011, 21(10):76-83.
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
刘泽淼, 黄贤金, 卢学鹤, 等. 共享社会经济路径下中国碳中和路径预测[J]. 地理学报, 2022, 77(9):2189-2201.
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
陈宁, 辛存林, 唐道斌, 等. 中国西北地区多情景土地利用优化与碳储量评估[J]. 环境科学, 2023, 44(8):4655-4665.
|
| [11] |
巩晟萱, 张玉虎, 李宇航. 基于PLUS-InVEST模型的京津冀碳储量变化及预测[J]. 干旱区资源与环境, 2023, 37(6):20-28.
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
王佳楠, 张志. 基于Markov-PLUS模型的柴北缘土地利用变化及模拟分析[J]. 西北林学院学报, 2022, 37(3):139-148,179.
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
张育诚, 韩念龙, 胡珂, 等. 海南岛中部山区土地利用变化对碳储量时空分异的影响[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2023, 47(2):115-122.
|
| [17] |
李俊, 杨德宏, 吴锋振, 等. 基于PLUS与InVEST模型的昆明市土地利用变化动态模拟与碳储量评估[J]. 水土保持通报, 2023, 43(1):378-387.
|
| [18] |
罗丹, 周忠发, 陈全, 等. 喀斯特地区碳储量对土地利用模式的响应:以南北盘江流域为例[J]. 生态学报, 2023, 43(9):3500-3516.
|
| [19] |
刘涛, 刘晓龙, 郭利彪, 等. 基于Markov-PLUS和InVEST模型的锡林郭勒草原碳储量变化预测[J]. 草原与草坪, 2023, 43(2):1-12.
|
| [20] |
罗雯, 陈佳, 卢瑛莹. 2000—2020年浙江省陆域生态系统碳库碳储量演变及提升路径[J]. 环境污染与防治, 2023, 45(3):413-418,426.
|
| [21] |
丁岳, 王柳柱, 桂峰, 等. 基于InVEST模型和PLUS模型的环杭州湾生态系统碳储量[J]. 环境科学, 2023, 44(6):3343-3352.
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
张斌, 夏秋月. 武汉城市圈碳储量的地形梯度效应及脆弱性[J]. 水土保持研究, 2023, 30(5):443-452.
|
| [24] |
牛志君, 周亚鹏, 王树涛, 等. 县域土地利用变化对碳储量的影响与评价:以黑龙港流域巨鹿县为例[J]. 水土保持研究, 2018, 25(3):292-297,304.
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
庄大方, 刘纪远. 中国土地利用程度的区域分异模型研究[J]. 自然资源学报, 1997, 12(2):105-111.
|
| [28] |
孙欣欣, 薛建辉, 董丽娜. 基于PLUS模型和InVEST模型的南京市生态系统碳储量时空变化与预测[J]. 生态与农村环境学报, 2023, 39(1):41-51.
|
| [29] |
林彤, 杨木壮, 吴大放, 等. 基于InVEST-PLUS模型的碳储量空间关联性及预测:以广东省为例[J]. 中国环境科学, 2022, 42(10):4827-4839.
|
| [30] |
谢向东, 林孝松, 王莹, 等. 基于 PLUS模型的重庆市南川区土地利用多情景模拟[J]. 长江科学院院报, 2023, 40(6):86-92,113.
|
| [31] |
张莹, 张学玲, 蔡海生. 基于地理探测器的江西省万安县生态脆弱性时空演变及驱动力分析[J]. 水土保持通报, 2018, 38(4):207-214.
|
| [32] |
施智勇, 谢慧黎, 王圳峰, 等. 基于参数最优地理探测器的福州市生境质量时空格局与驱动力分析[J]. 环境工程技术学报, 2023, 13(5):1921-1930.
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |