 PDF(2917 KB)
PDF(2917 KB)


 PDF(2917 KB)
PDF(2917 KB)
 PDF(2917 KB)
PDF(2917 KB)
山田胶锈菌效应蛋白GyHGSRE1的功能初探
Preliminary study on the function of Gymnosporangium yamadae effector GyHGSRE1
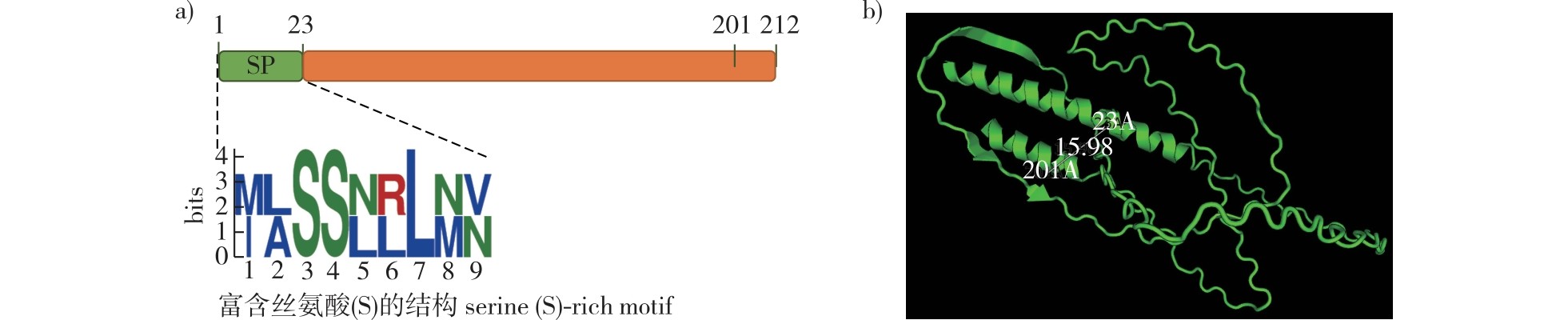
【目的】明确山田胶锈菌(Gymnosporangium yamadae)吸器中效应蛋白GyHGSRE1的基础生物学功能,为进一步揭示山田胶锈菌效应蛋白作用的分子机制,制定持久的锈病防控策略奠定基础。【方法】基于前期获得的山田胶锈菌吸器转录组数据筛选具有高表达丰度的效应蛋白;通过MEME(http://meme-suite.org/)、AI(https://drug.ai.tencent.com)等在线网站预测GyHGSRE1的蛋白质结构;利用荧光定量PCR检测GyHGSRE1基因在山田胶锈菌侵染过程中的表达水平,以酵母菌分泌系统验证GyHGSRE1信号肽的分泌功能,并通过农杆菌介导的瞬时表达技术分析GyHGSRE1在本氏烟(Nicotiana benthamiana)和苹果(Malus domestica)叶片中的功能。【结果】在山田胶锈菌吸器转录组数据中获得了FPKM(fragments per Kb per million mapped reads)值为117.92、富含甘氨酸和丝氨酸的小分子分泌蛋白GyHGSRE1。其N端具有1个富含丝氨酸motif的信号肽。qRT-PCR显示GyHGSRE1基因在山田胶锈菌的吸器形成阶段以及性、锈孢子形成及发育阶段均上调表达,并定位于本氏烟叶片细胞的细胞质和细胞核,能够诱导细胞坏死并激发基础免疫防御反应,但含有信号肽的全长效应蛋白GyHGSRE1能够诱导苹果叶片细胞坏死,去除信号肽后诱导细胞坏死的能力减弱。【结论】富含甘氨酸和丝氨酸的非典型效应蛋白GyHGSRE1定位于植物细胞的细胞质和细胞核,能够诱导本氏烟及苹果叶片细胞坏死,因此可能具有广谱性的激发子活性。GyHGSRE1在山田胶锈菌侵染苹果叶片的定殖和孢子发育阶段显著表达从而发挥功能,其信号肽可能决定着对寄主特异性识别的相关功能。
【Objective】The study determined the core biological function of the effector protein GyHGSRE1 secreted by the Gymnosporangium yamadae haustoria. This work provides foundational data for elucidating the molecular mechanisms of G. yamadae effector protein.【Method】The haustorial transcriptome of G. yamadae prioritized GyHGSRE1 as a highly expressed effector (FPKM = 117.92). MEME (http://meme-suite.org/) predicted its two-dimensional structure, while Tencent AI (https://drug.ai.tencent.com) generated the three-dimensional model. Real-time PCR quantified GyHGSRE1 expression level during fungal infection. Yeast secretion assays validated the signal peptide’s secretory capacity. Transient expression via Agrobacterium tumefaciens assessed GyHGSRE1 function in Nicotiana benthamiana and apple (Malus domestica) leaves.【Result】GyHGSRE1 contains an N-terminal serine-rich signal peptide. qRT-PCR demonstrated peak expression during haustorium maturation and spore development (pycniosporophores/aeciospores). The protein was localized to plant cell cytoplasm and nuclei, triggering cell death and immune responses in leaf cells of N. benthamiana. Full-length GyHGSRE1 induced cell death in apple leaves, but deletion of the signal peptide attenuated this activity.【Conclusion】The glycine-serine-rich atypical effector GyHGSRE1 exhibits dual localization and cell necrosis-inducing effects across plant species, implying broad-spectrum elicitor potential. Its expression correlates with critical infection stages (host colonization and sporulation). The signal peptide may mediate functional specificity, likely influencing host-pathogen recognition.
山田胶锈菌 / 非典型效应蛋白 / 激发子 / 信号肽 / 植物免疫
Gymnosporangium yamadae / atypical effector protein / elicitor / signal peptide / plant immunity
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
刘霞, 陶思齐, 翁涵, 等. 山田胶锈菌和亚洲胶锈菌吸器提取体系建立[J]. 菌物学报, 2019, 38(9): 1430-1439.
|
| [8] |
翁涵, 刘霞, 陶思齐, 等. 山田胶锈菌和亚洲胶锈菌吸器的比较转录组分析[J]. 生物工程学报, 2022, 38(10): 3825-3843.
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
赵薇, 许彤骏, 王喻元, 等. 溶藻细菌的筛选及群体感应信号对其活力的调节作用[J]. 生物加工过程, 2023, 21(4):461-470.
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |