 PDF(3462 KB)
PDF(3462 KB)


光周期对榕透翅毒蛾发育和种群增长潜能的影响
王琪, 陈辉, 唐明, 毛新杰, 廖菘凯, 卫宏健, 林浩宇
南京林业大学学报(自然科学版) ›› 2025, Vol. 49 ›› Issue (5) : 191-199.
 PDF(3462 KB)
PDF(3462 KB)
 PDF(3462 KB)
PDF(3462 KB)
光周期对榕透翅毒蛾发育和种群增长潜能的影响
Effects of development and population growth potential of Perina nuda under different photoperiods
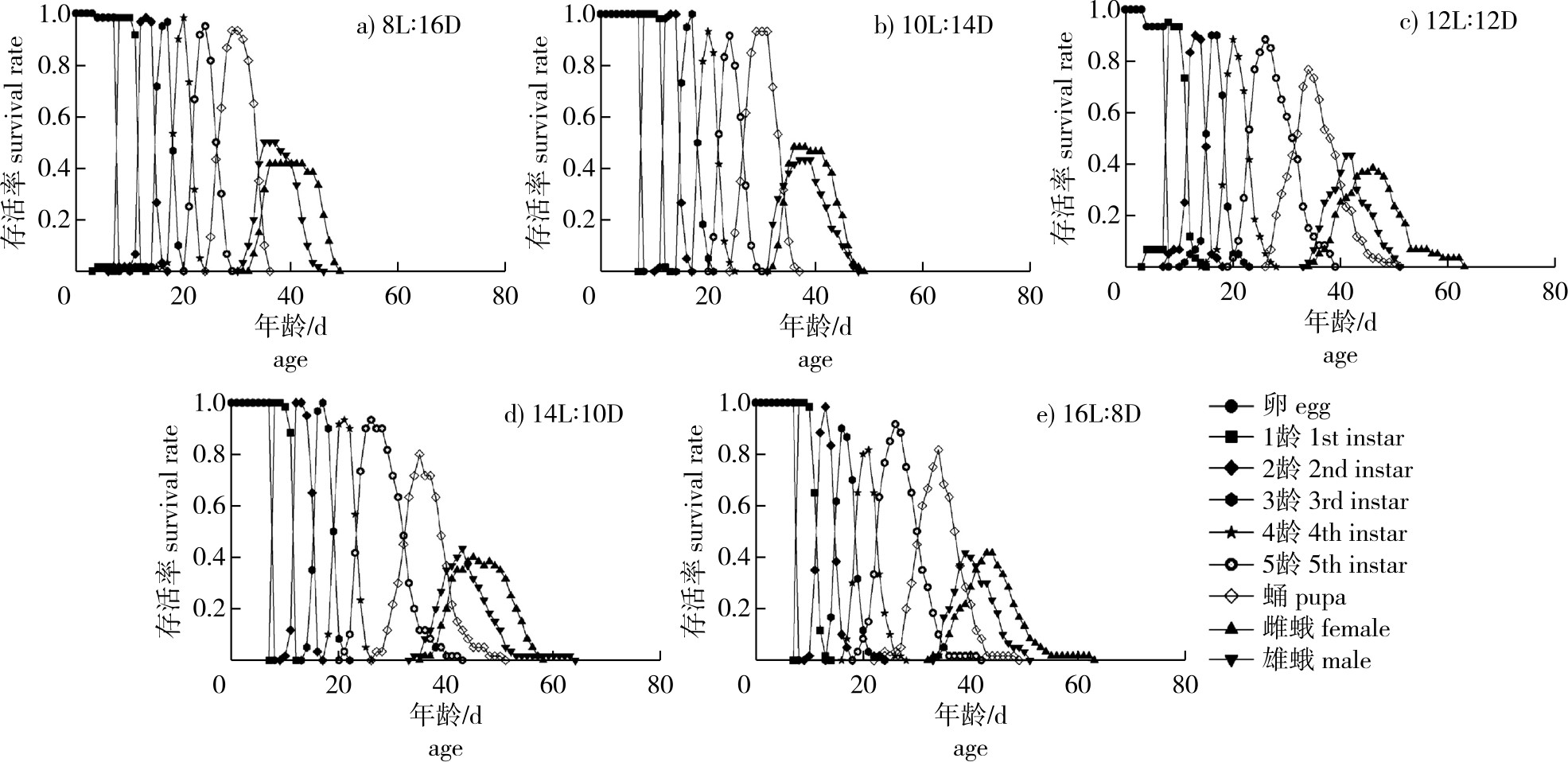
【目的】研究在不同光周期下榕透翅毒蛾(Perina nuda)试验种群的发育历期、繁殖发育等,为榕透翅毒蛾的种群密度调控提供科学依据。【方法】用榕透翅毒蛾最适宜寄主树种黄金榕(Ficus microcarpa)叶片进行试验室人工饲养,在温度(26±1) ℃、相对湿度为40%,分别设置5种光周期16 L(光)∶8 D(暗)、14 L∶10 D、12 L∶12 D、10 L∶14 D和8L∶16 D,定时观测榕透翅毒蛾试验种群的生长发育特性和繁殖能力等指标,利用TWOSEX-MSChart软件和TIMING-MSChart 软件,构建试验种群生命表并模拟榕透翅毒蛾种群在120 d内的变化趋势。【结果】光周期对榕透翅毒蛾生长发育影响显著,在 14 L∶10 D 光周期下,榕透翅毒蛾从卵发育到成虫死亡的历期最长(50.17 d),在10 L∶14 D光周期下的历期最短(44.09 d)。光周期对榕透翅毒蛾蛹质量具有显著影响,在8 L∶16 D光周期下,榕透翅毒蛾雌雄蛹质量最大,相同光周期下榕透翅毒蛾雌蛹的质量显著高于雄蛹的(P<0.01);光周期对榕透翅毒蛾雌雄成虫性比、存活率、单雌产卵量(粒)和净增殖率(R0)无显著影响,而对周限增长率(λ)影响显著(P<0.05);在10 L∶14 D、8 L∶16 D光周期下榕透翅毒蛾内禀增长率(rm)显著高于16 L∶8 D、14 L∶10 D和12 L∶12 D下的(P<0.05)。【结论】光周期对榕透翅毒蛾生长发育存在显著影响,在短光照下榕透翅毒蛾总发育历期最短,雌蛾产卵时间更加集中,这说明短光照更适宜榕透翅毒蛾种群的生存和发育。
【Objective】This study investigates the developmental period and reproductive characteristics of the experimental population of Perina nuda under different photoperiods, aiming to provide scientific basis for population density regulation of P. nuda. 【Method】Laboratory artificial rearing was conducted using leaves of the most suitable host tree, Ficus microcarpa, for P. nuda. The experiments were carried out at a temperature of (26±1) ℃ and a relative humidity of 40%, with five different photoperiods: 16 L∶8 D, 14 L∶10 D, 12 L∶12 D, 10 L∶14 D, and 8 L∶16 D. The growth and developmental characteristics as well as reproductive capacity of the experimental population of P. nuda were observed at regular intervals. Using TWOSEX-MSChart and TIMING-MSChart softwares, the life table of experimental population was constructed and the trend of population change in 120 days was simulated. 【Result】The photoperiod significantly affected the growth and development of P. nuda. Under the 14 L∶10 D photoperiod, the developmental period from egg to adult death was the longest (50.17 days), while under the 10 L∶14 D photoperiod, it was the shortest (44.09 days). The photoperiod had a significant effect on the pupal weight of P. nuda. Under the 8 L∶16 D photoperiod, the weights of female and male pupae were the largest, and under the same photoperiod, the weight of female pupae was significantly higher than that of male pupae (P<0.01). The photoperiod had no significant effect on the sex ratio, survival rate, number of eggs laid per female, and net reproductive rate (R0) of P. nuda adults (P>0.05), but it significantly affected the intrinsic rate of increase (λ) (P<0.05). Under the 10 L∶14 D, and 8 L∶16 D photoperiods, the intrinsic rate of increase (rm) of P. nuda was significantly higher than that under 16 L∶8 D, 14 L∶10 D, and 12 L∶12 D (P<0.05). 【Conclusion】The photoperiod has a significant effect on the growth and development of P. nuda. The total development period of P. nuda is the shortest under short light, and the oviposition time of female moths is more concentrated, which indicates that short light is more suitable for the survival and development of P. nuda populations.
光周期 / 榕透翅毒蛾 / 发育历期 / 生命表 / 种群参数
photoperiod / Perina nuda / developmental duration / life table / population parameter
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
林淑玲, 赵南先, 陈贻竹, 等. 榕树(Ficus)在中国的分布及其在协同进化研究上的意义[J]. 生态学报, 2007, 27(10):4278-4288.
|
| [3] |
魏丹, 郑昌辉, 叶广荣, 等. 广东省古树资源分布及文化要素研究[J]. 西北林学院学报, 2021, 36(6):181-187.
|
| [4] |
夏晞, 彭劲谕, 王大玮, 等. 3种榕属叶绿体基因组密码子偏好性分析[J]. 西北林学院学报, 2022, 37(5):88-94.
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
陈根富. 福州榕树害虫发生规律及生活习性的考察[J]. 福建师范大学学报(自然科学版), 1989, 5(4):86-89.
|
| [7] |
曾丽琼, 何学友, 潘爱芳, 等. 福州市榕透翅毒蛾生物学特性的研究[J]. 浙江林业科技, 2019, 39(1):49-54.
|
| [8] |
廖菘凯, 黄家豪, 卢隆鑫, 等. 4种榕树对榕透翅毒蛾生长发育及取食偏好的影响[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2023, 45(3):93-103.
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
胡冬春, 徐富强, 刘旭, 等. 昆虫生长阻滞肽研究进展[J]. 江苏农业学报, 2023, 39(4):1072-1079.
|
| [13] |
孟令贺, 江幸福, 李平, 等. 不同光周期下草地贪夜蛾两性生命表的比较[J]. 植物保护, 2022, 48(3):63-73.
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
姚明勇, 周吕, 王岚, 等. 光周期对叉角厉蝽生长发育及繁殖的影响[J]. 西南师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 45(3):109-114.
|
| [16] |
杜军利, 藏绮罗, 武德功, 等. 光周期对玉米蚜生长发育及种群参数的影响[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2018, 30(9):1534-1540.
|
| [17] |
曾丽琼. 不同木麻黄无性系对木毒蛾幼虫生长发育的影响[J]. 林业工程学报, 2015, 29(1):98-101.
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
王超, 陈芳, 陆永跃. 不同光周期条件下棉花粉蚧的生长发育和种群增长能力[J]. 昆虫学报, 2014, 57(4):428-435.
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
尚征, 周立峰, 冯玥瑶, 等. 拟松材线虫个体发育研究[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 43(6):11-17.
|
| [27] |
贾志怡, 陈聪, 马宇萱, 等. 温度对香樟齿喙象生长发育的影响[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 44(4):131-136.
|
| [28] |
于均屹, 徐立清, 张勇, 等. 光照和地下竞争对林冠下人工更新紫椴苗木形态和生物量分配的影响[J]. 森林工程, 2023, 39 (4): 38-47.
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
郭于蒙, 曹美琳, 白雪纯, 等. 光周期对二点委夜蛾生长发育的影响[J]. 植物保护学报, 2018, 45(4):731-738.
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
陈元生, 段德康, 陈超, 等. 光周期和温度对棉铃虫发育历期及蛹质量的影响[J]. 环境昆虫学报, 2012, 34(4):407-414.
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
王少博, 周洲, 陈怡萌, 等. 光周期和温度诱导美国白蛾滞育[J]. 林业科学, 2020, 56(4):121-127.
|
| [38] |
朱地福, 程禹朦, 龚慧蓉, 等. 暗期不同光源的光周期和温度对丝棉木金星尺蛾滞育、发育时间和蛹质量的影响[J]. 应用昆虫学报, 2023, 60(3):851-859.
|
| [39] |
|
| [40] |
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |