 PDF(1948 KB)
PDF(1948 KB)


基于干形特征的红松优良种源评价选择
李鑫, 贾炜玮, 王帆, 李丹丹, 朱万才, 梁月鹏, 李泽霖
南京林业大学学报(自然科学版) ›› 2025, Vol. 49 ›› Issue (4) : 106-116.
 PDF(1948 KB)
PDF(1948 KB)
 PDF(1948 KB)
PDF(1948 KB)
基于干形特征的红松优良种源评价选择
Evaluation and selection of excellent provenances of Pinus koraiensis based on stem shape characteristics
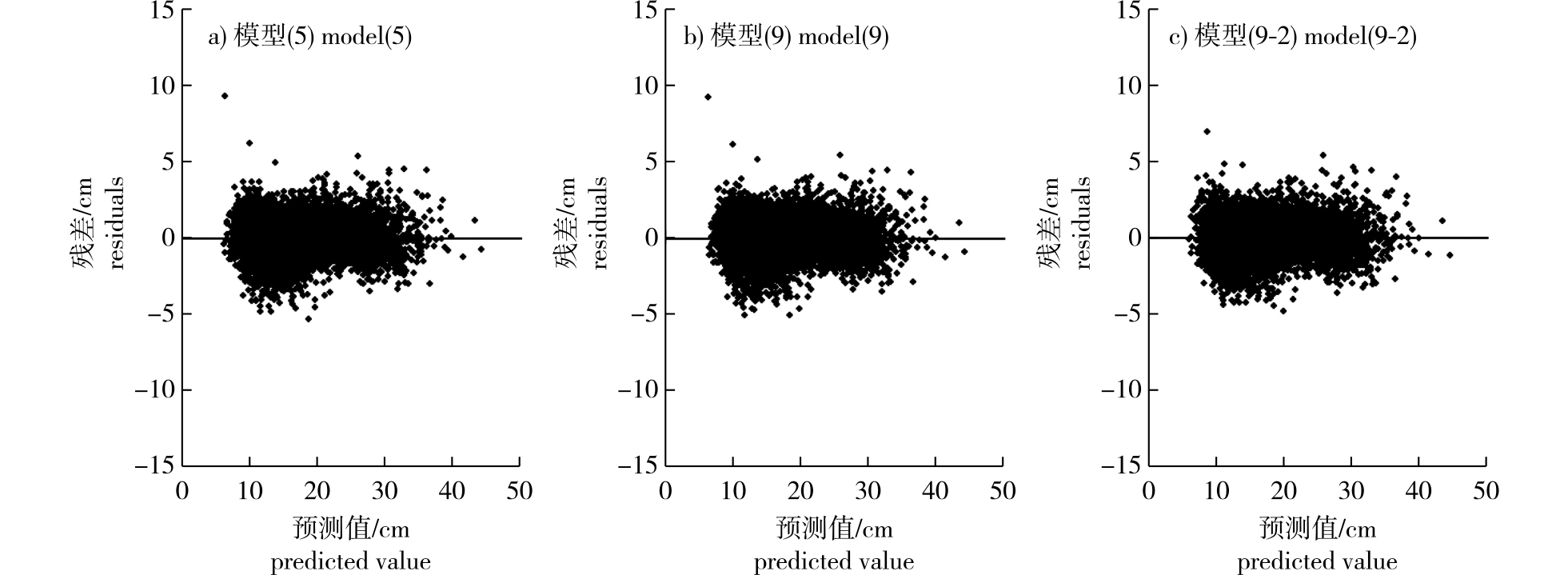
【目的】利用地基激光雷达技术(Terrestrial Laser Scanning,TLS)获取树木干形特征的可行性并对红松进行种源评价选择,为红松优良种源的综合评价提供理论依据。【方法】以黑龙江省帽儿山种源试验林中的26个红松种源为试验材料,首先借助TLS扫描样地,通过LiDAR360软件对数据进行预处理,对TLS提取的树高、胸径及不同高度处直径等参数进行评价;计算4种干形参数(胸高形数、胸高形率、实验形数、高径比)并利用TLS提取的不同高度处直径构建基于种源效应的削度方程,描述不同种源树干干形变化。【结果】地基激光雷达对单木参数提取都达到了较高的精度,其中胸径的提取效果(决定系数R2=0.979 6)优于树高(R2=0.811 4)和材积(R2=0.911 9);随着树干高度的增加相对高度处直径提取的R2逐渐增大,相对高度为0.08h(h为树高)时R2达到最大值(R2=0.984 0),相对树高大于0.08h后,相对高度处直径提取的R2逐渐减小;对26个种源红松干形指标的方差分析结果表明,各指标在种源间均达到了显著差异(P<0.05);将种源变量引入基础模型,模型的拟合精度提高,以重复作为随机效应构建非线性混合模型,模型精度进一步提高;通过绘制不同种源干形图,各种源干形变化趋势基本一致,但生长速度存在差异。【结论】TLS对单木参数提取精度较高;各干形指标在种源间均达到显著差异,具有较好的选择潜力;根据干形指标和基于种源效应的最优削度方程筛选出优良种源,可为红松的遗传改良和推广使用提供理论依据。
【Objective】This research aims to explore the feasibility of utilizing terrestrial laser scanning (TLS) technology for acquiring stem form characteristics of trees and to evaluate and select elit of Korean pine (Pinus koraiensis), providing a theoretical basis for the comprehensive evaluation of superior provenances.【Method】Using 26 P. koraiensis provenances from the provenance test forest in Maoershan, Heilongjiang Province, as experimental materials, TLS was employed to scan sample plots. Data preprocessing was conducted using LiDAR360 software, and parameters such as tree height, diameter at breast height (DBH), and diameters at different heights extracted by TLS were evaluated. Four stem form parameters (breast-height form factor, breast-height form quotient, experimental form factor, and height-to-diameter ratio) were calculated. Additionally, taper equations based on provenance effects were constructed using diameters at different heights extracted by TLS to describe stem form variations among different provenances.【Result】TLS achieved high accuracy in extracting individual tree parameters. The extraction accuracy for DBH (coefficient of determination R2= 0.979 6) was superior to that for tree height (R2=0.811 4) and volume (R2=0.911 9). As the stem height increased, the R2 for diameters at relative heights gradually increased, reaching its peak at 0.08h(R2=0.984 0, where h represents tree height). Beyond 0.08h, the R2 for diameters at relative heights gradually decreased. Variance analysis of stem form indicators for the 26 P. koraiensis provenances showed that all indicators exhibited significant differences among provenances (P<0.05). Introducing provenance variables into the base model improved the fitting accuracy, and constructing a nonlinear mixed model with replication as a random effect further enhanced model precision. By plotting stem form graphs for different provenances, it was observed that the trends in stem form variation were generally consistent across provenances, but growth rates differed.【Conclusion】TLS demonstrated high accuracy in extracting individual tree parameters. All stem form indicators showed significant differences among provenances, indicating good potential for selection. Based on stem form indicators and the optimal taper equation incorporating provenance effects, a group of superior provenances was identified, providing a foundation for genetic improvement and widespread utilization of P. koraiensis.
地基激光雷达 / 红松 / 种源 / 削度方程 / 非线性混合效应模型 / 干形
terrain laser scanning (TLS) / Pinus koraiensis (Korean pine) / provenance / taper equation / nonlinear mixed effect model / stem shape
| [1] |
李希才, 张骅, 王金国, 等. 红松坚果型优良无性系选择的研究[J]. 特产研究, 2002, 24(2):19-23.
|
| [2] |
魏嘉彤, 陈思琪, 芦贤博, 等. 基于生长与木材性状的红松优良种源评价选择[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2022, 44(3):12-23.
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
韩龙海, 潘凤刚, 刘洪志, 等. 红松种实性状变异及无性系选择[J]. 北华大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 22(2):176-181.
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
刘雪惠. 基于地基激光数据的林木参数提取及建模分析[D]. 南京: 南京林业大学, 2018.
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
邹茂胜, 孙毓蔓, 李丹丹, 等. 基于地基激光雷达数据的落叶松人工林削度方程构建[J]. 中南林业科技大学学报, 2022, 42(8):90-100.
|
| [10] |
姜立春, 刘瑞龙. 基于非线性混合模型的落叶松树干削度模型[J]. 林业科学, 2011, 47(4):101-106.
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
聂璐毅, 董利虎, 李凤日, 等. 基于两水平非线性混合效应模型的长白落叶松削度方程构建[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 46(3):194-202.
|
| [13] |
李凤日. 测树学[M]. 4版. 北京: 中国林业出版社, 2019.
|
| [14] |
常锦锦, 苗铮, 郝元朔, 等. 迎春5号杨树削度方程的建立与优化[J]. 东北林业大学学报, 2023, 51(9):59-66.
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
苏巴提·赛达合买提, 贾炜玮. 黑龙江不同区域人工红松心边材及树皮削度可加性模型系统构建[J]. 应用生态学报, 2021, 32(10):3437-3447.
|
| [17] |
朱光玉, 胡松, 符利勇. 基于哑变量的湖南栎类天然林林分断面积生长模型[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 42(2):155-162.
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
贾炜玮, 罗天泽, 李凤日. 基于抚育间伐效应的红松人工林枝条密度模型[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2021, 43(2):10-21.
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
李丹, 庞勇, 岳彩荣, 等. 基于TLS数据的单木胸径和树高提取研究[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2012, 34(4):79-86.
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
姜立春, 蒋雨航. 利用混合模型模拟树冠特征对兴安落叶松树干干形的影响[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2014, 36(2):10-14.
|
| [26] |
张中伟, 周根苗, 易烜, 等. 基于气候因子的杉木人工林削度方程构建[J]. 中南林业科技大学学报, 2023, 43(5):49-57.
|
| [27] |
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |