 PDF(1929 KB)
PDF(1929 KB)


5个冬青品种枝条抗弯力学特性及其与理化性质的关系
殷雅文, 侯召斌, 刘佳琪, 吴文平, 邹义萍, 郝明灼
南京林业大学学报(自然科学版) ›› 2025, Vol. 49 ›› Issue (5) : 95-102.
 PDF(1929 KB)
PDF(1929 KB)
 PDF(1929 KB)
PDF(1929 KB)
5个冬青品种枝条抗弯力学特性及其与理化性质的关系
Bending characteristics of branches of five Ilex varieties and their relationship with physicochemical properties
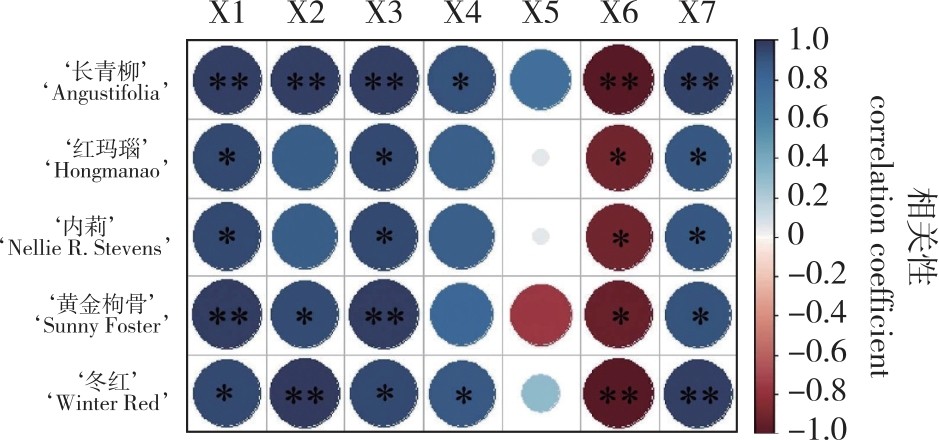
【目的】筛选宜造型冬青品种,并分析化学组分与物理性质对枝条抗弯力学特性的影响机制,为其他造型冬青品种的筛选提供理论依据。【方法】以5个冬青品种‘长青柳’(Ilex cassine ‘Angustifolia’ )、‘内莉’(I. × ‘Nellie R. Stevens’)、‘黄金枸骨’(I. × attenuata ‘Sunny Foster’)、‘红玛瑙’(I. decidua ‘Hongmanao’)、‘冬红’(I. verticillata ‘Winter Red’)为研究对象,测定2.5~7.5mm共5个径级的枝条抗弯力及抗弯弹性模量(MOE),纤维素、半纤维素和木质素的含量,以及微纤丝角(MFA)及结晶度(Crl)等指标。【结果】①5个冬青品种的抗弯力、抗弯弹性模量(MOE)随径级增加而增大,枝条化学组分及结晶度的变化与力学性质的变化类似,微纤丝角随径级增加而减小。②5个冬青品种抗弯力和MOE存在显著差异(P<0.05),‘红玛瑙’的抗弯力及MOE最高,‘冬红’最低。③纤维素含量、综纤维素含量、结晶度与枝条的MOE呈显著正相关,微纤丝角与MOE呈显著负相关(P<0.05)。【结论】‘冬红’(MOE为154.88~645.87 MPa)及‘内莉’(MOE为212.09~772.00 MPa)的MOE显著低于其他品种,表明其枝条柔韧性更优,为适宜造型的冬青品种;而枝条纤维素、综纤维素含量、微纤丝角、结晶度等指标是影响枝条抗弯特性的主要因素。
【Objective】To screen Ilex varieties suitable for topiary and to investigate the influencing mechanisms of chemical composition and physical properties on the flexural mechanical characteristics of branches, providing a theoretical basis for selecting other Ilex varieties for topiary.【Method】Five Ilex varieties—Ilex cassine ‘Angustifolia’, I. × ‘Nellie R. Stevens’), I. × attenuata ‘Sunny Foster’, I. decidua ‘Hongmanao’, and I. verticillata ‘Winter Red’—were selected as research subjects. The flexural force and flexural modulus of elasticity (MOE) in bending of branches across five diameter classes (2.5-7.5 mm), as well as the contents of cellulose, hemicellulose, and lignin, as well as microfibril angle (MFA), and crystallinity (Crl), were measured.【Result】(1) The flexural force and MOE of the five Ilex varieties increased with increasing branch diameter class. Changes in the chemical composition and crystallinity exhibited trends similar to those of the mechanical properties, while the MFA decreased with increasing diameter class. (2) Significant differences (P < 0.05) in flexural force and MOE were observed among the five varieties. ‘Hongmanao’ exhibited the highest values for both flexural force and MOE, whereas ‘Winter Red’ exhibited the lowest. (3) Cellulose content, holocellulose content, and crystallinity showed significant positive correlations with branch MOE, while the MFA showed a significant negative correlation with MOE (P < 0.05). 【Conclusion】The MOE of ‘Winter Red’ (MOE: 154.88-645.87 MPa) and ‘Nellie R. Stevens’ (MOE: 212.09-772.00 MPa) was significantly lower than that of the other varieties, indicating their branches possess greater flexibility and are thus more suitable for topiary. Cellulose content, holocellulose content, MFA, and crystallinity are identified as key factors influencing the flexural properties of branches.
冬青 / 枝条 / 抗弯弹性模量 / 微纤丝角 / 纤维素 / 结晶度
Ilex / branches / flexural modulus of elasticity / microfibril angle / cellulose / crystallinity
| [1] |
陈雪, 钱大为. 植物编艺技术原理及在园林绿化工程中的应用[J]. 绿色科技, 2019, 21(23):181-182.
|
| [2] |
李树华. 中国盆景文化史[M]. 2版. 北京: 中国林业出版社, 2019.
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
梁莉, 郭玉明. 作物茎秆生物力学性质与形态特性相关性研究[J]. 农业工程学报, 2008, 24(7):1-6.
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
刘基, 金诚谦, 梁苏宁, 等. 黄淮海地区大豆茎秆力学特性的多品种对比试验研究[J]. 农机化研究, 2018, 40(6):124-131.
|
| [8] |
成俊卿. 木材学[M]. 北京: 中国林业出版社, 1985.
|
| [9] |
王传贵, 江泽慧, 费本华, 等. 化学成分对木材细胞壁纵向弹性模量和硬度的影响[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2012, 34(3):107-110.
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
江苏省林业局. 江苏省2021年林木品种审(认)定初审结果公示[EB/OL].(2021-12-08)[2024-02-28]. https://lyj.jiangsu.gov.cn/art/2021/12/8/art_7235_10185328.html
|
| [15] |
江苏省林业局. 江苏省2019年林木品种审(认)定情况公示[EB/OL].(2019-11-25)[2024-02-28]. https://lyj.jiangsu.gov.cn/art/2019/11/25/art_7235_8824366.html
|
| [16] |
江苏省林业局. 江苏省2020年林木品种审(认)定情况公示[EB/OL].(2020-12-09)[2024-02-28]. https://lyj.jiangsu.gov.cn/art/2020/12/9/art_61275_9597827.html
|
| [17] |
武艺儒, 刘静, 张欣, 等. 3种灌木直根抗剪特性及其与化学组分的关系[J]. 干旱区资源与环境, 2019, 33(4):129-133.
|
| [18] |
国家林业和草原局. 无疵小试样木材物理力学性质试验方法第10部分:抗弯弹性模量测定:GB/T 1927.10—2021[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2021.
|
| [19] |
季必超, 薛夏, 汪佑宏, 等. 大白藤和小白藤纤维形态及主要物理力学性质[J]. 西北林学院学报, 2019, 34(3):180-184.
|
| [20] |
雷世博, 丁龙朋, 李景彬, 等. 枣树修剪枝条弯曲及压缩特性研究[J]. 农机化研究, 2022, 44(5):198-203.
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
薛冬梅, 刘静, 林凤友, 等. 3种植物枝条抗拉和抗弯特性研究[J]. 内蒙古农业大学学报(自然科学版), 2012, 33(4):87-90.
|
| [23] |
刘忠, 张素风. 制浆造纸分析与检测[M]. 2版. 北京: 中国轻工业出版社, 2020.
|
| [24] |
王成龙. 四种植物根系剪拉组合力损伤自修复后固土特性[D]. 呼和浩特: 内蒙古农业大学, 2021.
|
| [25] |
李坚. 木材波谱学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2003.
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
李坚. 木材科学[M]. 哈尔滨: 东北林业大学出版社, 1994.
|
| [30] |
李业鑫. 基于力学数值模型的青花椒枝条切割机理和切枝装置研究[D]. 重庆: 西南大学, 2023.
|
| [31] |
段涛. 基于条桑力学特性的弧形切割装置结构设计与试验[D]. 合肥: 安徽农业大学, 2022.
|
| [32] |
王淑娟, 谢宝元. 休眠期树枝抗弯弹性模量的模型分析[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2014, 36(6):130-134.
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
郭维俊, 王芬娥, 黄高宝, 等. 小麦茎秆力学性能与化学组分试验[J]. 农业机械学报, 2009, 40(2):110-114.
|
| [35] |
余雁, 江泽慧, 任海青, 等. 针叶材管胞纵向零距抗张强度的影响因子研究[J]. 中国造纸学报, 2007, 22(3):72-76.
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
王争贤, 格日乐, 崔天民, 等. 固沙先锋树种沙柳枝条力学特性及其影响因素[J]. 中国农业大学学报, 2021, 26(11):84-96.
|
| [38] |
王争贤. 沙棘枝条和根系防风固土力学特性研究[D]. 呼和浩特: 内蒙古农业大学, 2023.
|
| [39] |
吕春娟, 陈丽华. 华北典型植被根系抗拉力学特性及其与主要化学成分关系[J]. 农业工程学报, 2013, 29(23):69-78.
|
| [40] |
孙海燕, 苏明垒, 吕建雄, 等. 细胞壁微纤丝角和结晶区对木材物理力学性能影响研究进展[J]. 西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 47(5):50-58.
|
| [41] |
|
| [42] |
邓波, 杨万霞, 方升佐, 等. 青钱柳幼龄期生长与木材性状表现及其性状相关分析[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2014, 38(5):113-117.
|
| [43] |
|
| [44] |
周贤武, 邓丽萍, 王滋, 等. 沙柳的孔隙结构、微纤丝角和纤维素结晶度研究[J]. 西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 46(1):46-51.
|
| [45] |
|
| [46] |
杨欣, 刘杏娥, 杨淑敏, 等. 4种竹材微纤丝角变异及其对抗弯性质的影响[J]. 西北林学院学报, 2021, 36(2):193-197,230.
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |