 PDF(1950 KB)
PDF(1950 KB)


多地点4年生木荷生长性状家系变异与早期选择
杨梅洁, 季景勇, 张蕊, 沈斌, 姚甲宝, 徐永宏, 邱勇斌, 高凯, 周志春
南京林业大学学报(自然科学版) ›› 2025, Vol. 49 ›› Issue (5) : 154-164.
 PDF(1950 KB)
PDF(1950 KB)
 PDF(1950 KB)
PDF(1950 KB)
多地点4年生木荷生长性状家系变异与早期选择
Variation and early selection for growth traits of 4-year-old Schima superba families in multiple sites
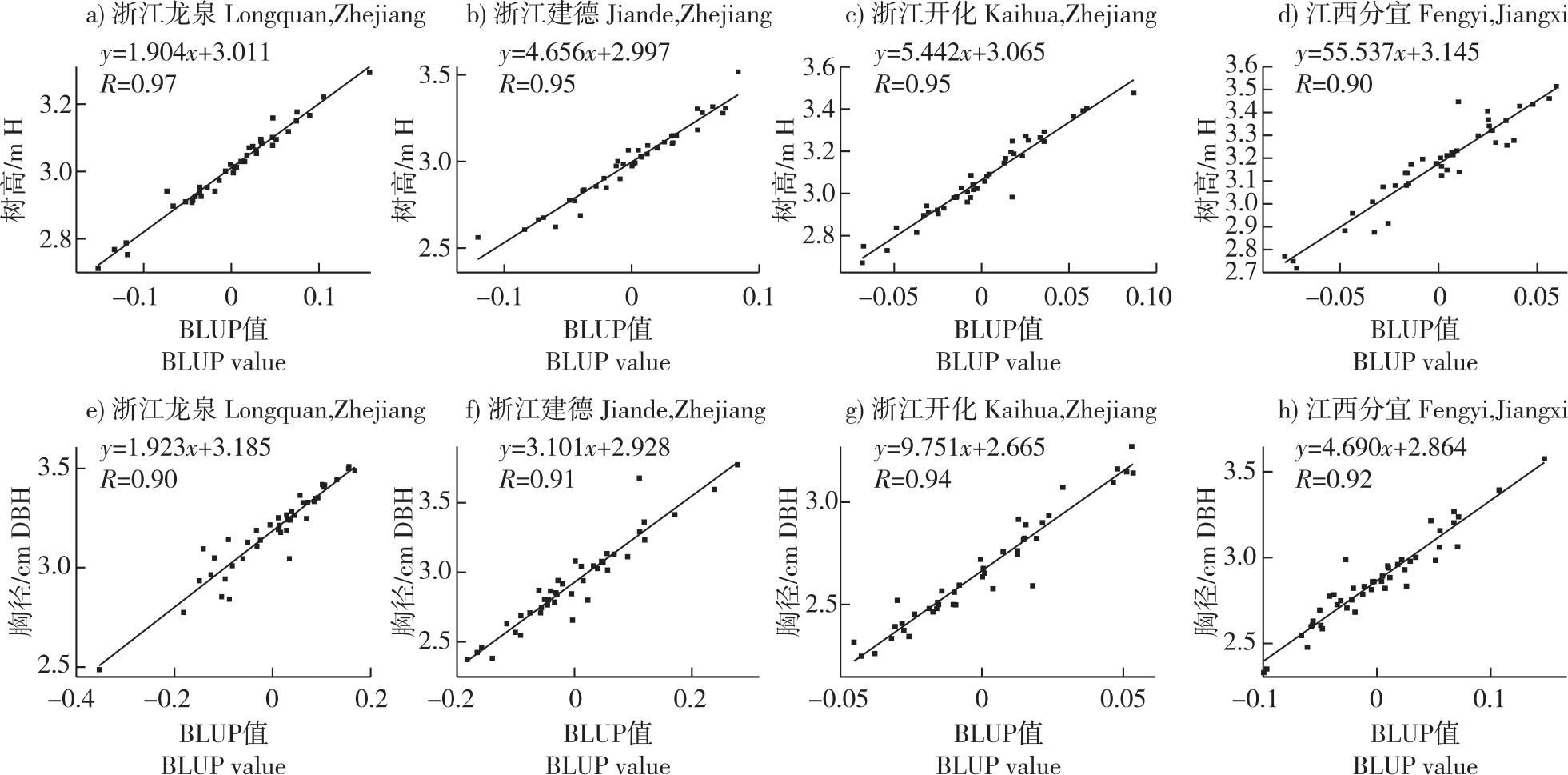
【目的】揭示木荷(Schima superba)多地点家系变异及环境互作规律,为木荷良种选育提供参考。【方法】以2019年在浙江龙泉、建德、开化和江西分宜营建的木荷优树家系林为材料,调查树高、胸径、冠幅、枝下高、最大分枝粗等的遗传变异规律及立地效应,估算所试材料的现实增益及遗传增益等。【结果】多点4年生木荷优树的树高、胸径、冠幅、最大分枝粗、最大分枝角等具有极显著的地点、家系和家系×地点的互作效应,家系生长受到遗传和环境因素共同影响。不同种植地点家系生长性状差异较大,江西分宜点的胸径和分枝性状的变异系数相对较高,其次为浙江建德和浙江开化,最低为浙江龙泉点。木荷的树高与胸径呈显著中至强的正相关(0.66< R<0.93,P<0.01),与冠幅和分枝粗呈显著中至强的正相关(0.60 < R<0.87, P<0.05),与分枝角相关性不显著。各地点的树高、胸径、冠幅等生长性状均受到中度以上的遗传力(0.50~0.78)控制。4个地点的胸径和树高性状均值与其育种值均呈现良好的线性关系(R > 0.90, P<0.001)。通过对木荷树高和胸径的BLUP-GGE分析,发现胸径的BLUP-GGE较为可靠,其中浙江建德点最具有区分力,浙江开化点最具有代表性。根据速生性和稳定性初步选出7个生长优良的家系,遗传增益(2.30%~12.12%,平均7.37%)和现实增益(3.48%~18.30%,平均11.12%)较高。【结论】木荷生长性状受家系以及种植点环境影响,以胸径进行遗传分析和品种筛选较为可靠,综合多地点木荷生长表现初步选出7个优良家系,分别来自福建建瓯和浙江龙泉产区。
【Objective】In order to treveal the genetic variation of Schima superba families in multiple sites and their interaction with the environment, we performed the forest survey, the tree growth and branching performance. The results would provide a theoretical basis for selecting S. superba varieties with strong adaptability, stability, and fast-growing among multiple sites. At the same time, these super varieties could be applied in multiple locations. 【Method】A systematic investigation was conducted on the growth and branching traits of S. superba family forests built in Longquan, Jiande, Kaihua Cities (County) in Zhejiang Province, and Fenyi County in Jiangxi Province in 2019, including tree height (H), breast height diameter (DBH), crown width (C), maximum branch diameter (MBD), and maximum branch angle (MBA). Using a combination of GGE (genotype main effects and genotype-by-enviroment interactions) and BLUP (best linear unbiased prediction), this study revealed genetic differences among families of S. superba, evaluated the effects of environmental factors on growth and branching traits, explored the adaptability, stability, and rapid-growth among these families in multiple sites, and estimated the genetic and real-gains of these tested materials. 【Result】The H, DBH, C, MBD and MBA of the 4-year-old S. superba families in Longquan, Jiande, Kaihua in Zhejiang Province and Fenyi in Jiangxi Province showed highly significant interactions among sites, families, and family × sites. The growth and branching traits of these families were influenced by both genetic and environmental factors. There were significant differences in growth traits among families from different sites. For example, the coefficient of variation in DBH and branching traits were relatively high among families in Fenyi, followed by Jiande and Kaihua, and relatively low in Longquan. There was a significant medium to strong positive correlation between H and DBH among families (0.66<R<0.93, P<0.01). At the same time, a significant medium to strong positive correlation showed between H and C and MBD (0.60<R<0.87, P<0.05), but no significant correlation found between H and MBA. The growth and branching traits of families were controlled by moderate to high heritability across different sites, with a heritability range from 0.50 to 0.78. That was indicating that genetic factors play an important role in the growth of S. superba. A linear regression model was established between the mean value of DBH and H of families from four locations and their breeding values (BLUP). The results showed a good linear relationship (R>0.90, P<0.001). The BLUP-GGE combined method was used to evaluate the H and DBH of S. superba, and the results showed that the BLUP-GGE model for DBH was more reliable. Among them, the families from the Jiande showed strong differentiation, followed by Longquan. While the families from Longquan had the most representativeness, followed by Kaihua and Jiande. Based on the fast-growing and stability results, we selected 7 excellent growth performing families, whose genetic gains ranged from 2.30% to 12.12% (average 7.37%), and the real-gains ranged from 3.48% to 18.30% (average 11.12%). These families demonstrated a high breeding potential and application value. 【Conclusion】The growth and branching traits of 4-year-old multi-site S. superba families were influenced by the family and planting environment. It was more reliable to use DBH as a key indicator in genetic analysis and selection. Based on the genetic gain performance, we had selected 7 superior families with excellent growth and stable traits.
遗传变异 / 立地效应 / 遗传增益 / 家系选择 / 木荷
genetic variation / site effect / genetic gain / family selection / Schima superba
| [1] |
欧阳芳群, 祁生秀, 范国霞, 等. 青海云杉自由授粉家系遗传变异与基于BLUP的改良代亲本选择[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 43(6):53-59.
|
| [2] |
王文月, 张振, 金国庆, 等. 两地点8年生柏木生长性状家系变异及选择[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2023, 47(2):42-48.
|
| [3] |
贾庆彬, 刘庚, 赵佳丽, 等. 红松半同胞家系生长性状变异分析与优良家系选择[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 46(4):109-116.
|
| [4] |
芦贤博, 徐连峰, 庞忠义, 等. 胡桃楸种源家系幼龄期生长变异及选择研究[J]. 林业科学研究, 2022, 35(1):20-30.
|
| [5] |
肖兴翠, 王树山, 杨勇智, 等. 香椿半同胞家系在川中丘陵区生长变异及早期选择[J]. 中南林业科技大学学报, 2022, 42(1):9-19.
|
| [6] |
周燕, 黄盛怡, 杨孟晴, 等. 赤皮青冈不同家系苗期生长和叶片性状遗传变异[J]. 西部林业科学, 2022, 51(5):75-80.
|
| [7] |
曹昆彬, 杨勇智, 郭洪英, 等. 大花序桉半同胞家系苗期测定及家系选择[J]. 四川林业科技, 2022, 43(5):66-72.
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
金国庆, 张振, 余启新, 等. 马尾松2个世代种子园6年生家系生长的遗传变异与增益比较[J]. 林业科学, 2019, 55(7):57-67.
|
| [10] |
孙英豪, 张含国, 郝俊飞, 等. 3年生长白落叶松高生长遗传变异与多点稳定性[J]. 东北林业大学学报, 2018, 46(8):1-7.
|
| [11] |
谭长强, 陈云峰, 潘会彪, 等. 2.5年生台湾桤木次生种源/家系早期选择[J]. 广西林业科学, 2020, 49(3):415-419.
|
| [12] |
何霞, 李景剑, 王芳, 等. 苦楝种源/家系幼林的性状变异及选择[J]. 东北林业大学学报, 2019, 47(6):1-7.
|
| [13] |
姜秀英, 马作斌, 王庆新, 等. 基于R语言的GGE双标图在水稻品种区域试验中的应用[J]. 中国稻米, 2024, 30(2):57-60.
|
| [14] |
郑聪慧, 张鸿景, 王玉忠, 等. 基于BLUP和GGE双标图的华北落叶松家系区域试验分析[J]. 林业科学, 2019, 55(8):73-83.
|
| [15] |
林元震. 林木基因型与环境互作的研究方法及其应用[J]. 林业科学, 2019, 55(5):142-151.
|
| [16] |
周志春. 中国木荷[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2020.
|
| [17] |
欧阳天林, 朱柯帆, 邱建勋, 等. 木荷种子园自由授粉家系生长遗传变异及初选[J]. 中南林业科技大学学报, 2022, 42(9):17-23.
|
| [18] |
辛娜娜, 张蕊, 范辉华, 等. 5年生木荷生长和形质性状的家系变异和选择[J]. 林业科学研究, 2014, 27(3):316-322.
|
| [19] |
范辉华, 陈碧华, 陈柳英, 等. 木荷优良家系和优良单株初步选择[J]. 湖北林业科技, 2015, 44(4):5-8.
|
| [20] |
彭华贵, 陈琪, 汪迎利, 等. 木荷家系生长性状的反向逐步剔除法回归分析[J]. 亚热带植物科学, 2017, 46(4):323-328.
|
| [21] |
王胤, 姚瑞玲, 陈振华, 等. 马尾松无性系生长性状基因型与环境互作效应初步研究[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2023, 45(5):47-56.
|
| [22] |
王云鹏, 张蕊, 周志春, 等. 木荷优树自由授粉家系早期生长性状遗传变异动态规律[J]. 林业科学, 2020, 56(9):77-86.
|
| [23] |
王恬, 云岚, 李珍, 等. 基于GGE双标图分析新麦草种质部分性状的基因型-环境互作[J]. 草地学报, 2023, 31(2):489-497.
|
| [24] |
吴云燕, 张露, 刘远生, 等. 不同种源/家系毛红椿连年生长性状变异及早期选择[J]. 江西农业大学学报, 2024, 46(1):106-117.
|
| [25] |
王云鹏, 张蕊, 周志春, 等. 10年生木荷生长和材性性状家系变异及选择[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 44(5):85-92.
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
邓丽, 李绍伟, 郭敏杰, 等. 基于BLUP和GGE双标图的大果型花生丰产稳产适应性分析[J]. 种子, 2023, 42(7):117-121,150.
|
| [28] |
林磊, 周志春, 范辉华, 等. 木荷优树子代苗期生长遗传和变异研究[J]. 林业科学研究, 2009, 22(2):155-160.
|
| [29] |
王秀花, 陈柳英, 马丽珍, 等. 7年生木荷生长和木材基本密度地理遗传变异及种源选择[J]. 林业科学研究, 2011, 24(3):307-313.
|
| [30] |
周志春, 范辉华, 金国庆, 等. 木荷地理遗传变异和优良种源初选[J]. 林业科学研究, 2006, 19(6):718-724.
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
王家燚, 陈焕伟, 张蕊, 等. 木荷全同胞家系生长与分枝性状的遗传变异及效应分析[J]. 浙江农林大学学报, 2023, 40(4):738-746.
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
黄逢龙, 焦一杰, 丁辉, 等. 不同林分密度下杨树树冠结构与溃疡病的关系[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2010, 34(4):79-82.
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
赵连春, 赵成章, 陈静, 等. 秦王川湿地不同密度柽柳枝-叶性状及其光合特性[J]. 生态学报, 2018, 38(5):1722-1730.
|
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
|
| [40] |
李金花. 基于BLUP和GGE双标图的黑杨派无性系生长性状基因型与环境互作效应[J]. 林业科学, 2021, 57(6):64-73.
|
| [41] |
任丽, 郭敏杰, 苗建利, 等. 基于BLUP和GGE双标图的高油酸花生品种综合分析[J]. 分子植物育种, 2024, 22(5):1568-1574.
|
浙江省龙泉市林业科学研究院、建德市林业总场、开化县林场以及中国林科院亚热带林业实验中心等实验基地对本研究给予支持!同时,金国庆、陈焕伟、肖纪军、曾平生对本研究做出了贡献!
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |