 PDF(2502 KB)
PDF(2502 KB)


青藏高原东缘城市表土磁化率特征及其环境意义——以海东市为例
王彦瑜, 刘亮, 赖涓涓, 马璠, 佟帆
南京林业大学学报(自然科学版) ›› 2026, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (1) : 121-132.
 PDF(2502 KB)
PDF(2502 KB)
 PDF(2502 KB)
PDF(2502 KB)
青藏高原东缘城市表土磁化率特征及其环境意义——以海东市为例
Characteristics and environmental significance of topsoil magnetic susceptibility in cities on the eastern of Qinghai-Xizang Plateau: a case study of Haidong City
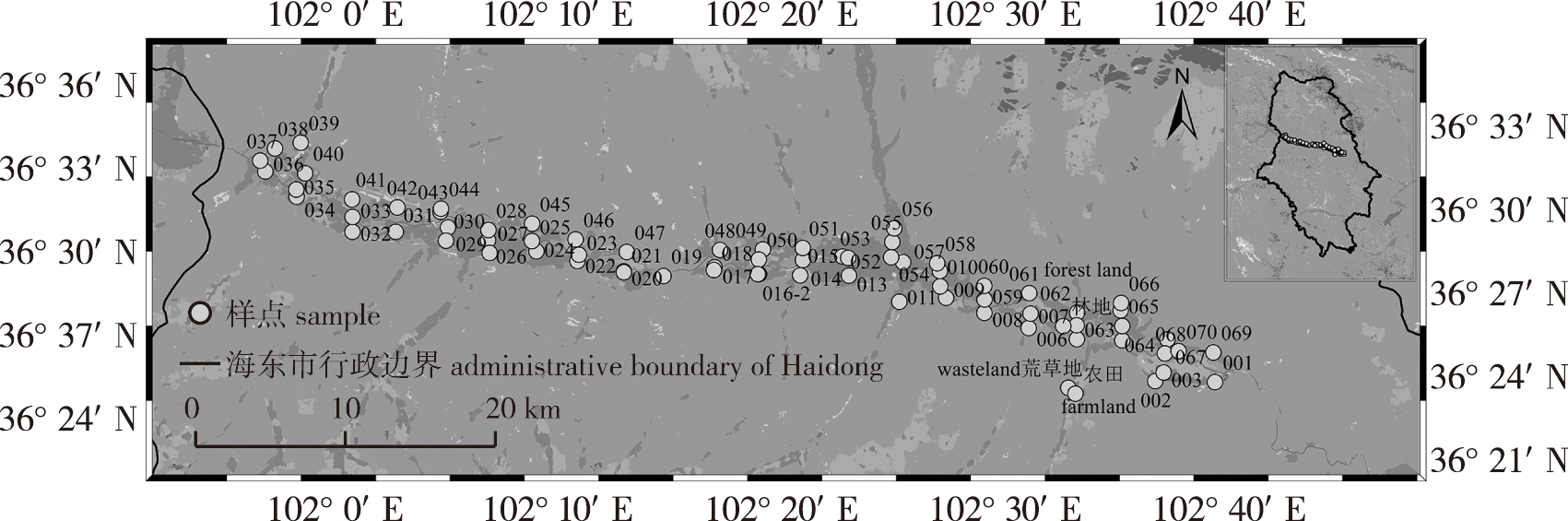
【目的】 廉价、高效、样品无损伤的磁化率技术在城市土壤重金属污染监测与评价研究中有诸多成功应用案例。青藏高原东缘地区具有独特的高原生态系统和脆弱的环境条件,为保障该区居民的健康,研究青藏高原东缘地区城市土壤中重金属的分布、来源及其潜在的健康风险现状。【方法】以青藏高原东缘典型城市海东市表层土壤为研究对象,通过典型城市表土采样试验与文献解析相结合的研究方法,系统评价研究区表土磁性物质的空间分布与污染特征;分析海东市城区不同功能区表土磁化率分布特征及在0~6 cm深度上表土剖面的变化规律,并综合分析青藏高原东缘及周边地区土壤磁化率分布特征。【结果】①海东市表土的质量磁化率具有强变异水平(变异系数0.65),质量磁化率在垂直剖面上呈随深度增加而减小的趋势;表土中超顺磁颗粒含量较少,主要由成土作用形成。②基于磁化率浓集因子和污染负荷指数的污染评价结果表明,海东市表土处于轻度污染或无污染状态,重金属Cr、Cu、Mn、Fe、Ni主要来自成土过程,Cd、Pb、Zn主要来源于人为活动。③低频质量磁化率(χlf)的半定量化模型结果为χlf<59.7×10-8 m3/kg时土壤为清洁状态;χlf为[59.7×10-8, 498.0×10-8) m3/kg时土壤受轻度污染;χlf为[498.0×10-8, 998.0×10-8) m3/kg时土壤受中度污染;χlf≥998.0×10-8 m3/kg时土壤受重度污染。④青藏高原东部地区表土的磁化率远小于其周边重工业城市。【结论】海东市表土磁化率与重金属元素之间的相关系数存在差异,但均有显著的相关性、磁化率可以作为快速监测和评价青藏高原东缘地区土壤重金属污染的有效指标。
【Objective】 Magnetic susceptibility technology, known for its affordability, efficiency, and non-destructive nature, is widely used for monitoring and evaluating heavy metal pollution in urban soil. The eastern margin of the Qinghai-Xizang Plateau, with its unique plateau ecosystem and fragile environmental conditions, presents significant challenges. Understanding the distribution, sources and potential health risks of heavy metals in this region’s urban soil is crucial for protecting local residents’ health. 【Method】This study focused on Haidong, a representative city on the eastern margin of the Qinghai-Xizang Plateau. It systematically evaluated the spatial distribution and pollution characteristics of the surface soil through a combination of soil sampling and literature analysis. The analysis included the distribution of surface magnetic susceptibility in different functional areas of Haidong and the variation of magnetic susceptibility in soil profiles at a depth of 0-6 cm. Additionally, the study examined the distribution characteristics of soil magnetic susceptibility in the eastern margin of the Qinghai-Xizang Plateau and surrounding areas. 【Result】(1) The mass magnetic susceptibility of surface soil in Haidong showed significant variation (CV=0.65), decreasing with depth. The topsoil contains few superparamagnetic particles, mainly due to soil formation. (2) Pollution evaluation using magnetic susceptibility concentration factors and pollution load indices indicated that Haidong’s topsoil was either slightly polluted or non-polluted. Heavy metals such as Cr, Cu, Mn, Fe, and Ni originated primarily from soil formation, while Cd, Pb, and Zn were mainly from human activities. (3) The low frequency mass magnetic susceptility χlf semi-quantization model results were as follows: χlf < 59.7 × 10-8 m3/kg indicates clean soil; [59.7 × 10-8, 498.0 × 10-8) m3/kg indicated slight pollution; [498.0 × 10-8, 998.0 × 10-8) m3/kg indicated moderate pollution; χlf ≥ 998.0 × 10-8 m3/kg indicated severe pollution. (4) The magnetic susceptibility of the eastern Qinghai-Xizang Plateau was significantly lower than that of surrounding heavy industry cities. 【Conclusion】While the coefficients between surface magnetic susceptibility and heavy metal elements in Haidong varies, a significant correlation exists. Magnetic susceptibility serves as an effective index for rapid monitoring and evaluation of soil heavy metal pollution on the eastern margin of the Qinghai-Xizang Plateau.
表土磁化率 / 土壤重金属 / 土壤污染评价 / 青藏高原东缘 / 海东市
magnetic susceptibility in topsoil / soil heavy metal / soil pollution assessment / eastern margin of Qinghai-Xizang Plateau / Haidong City
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
余涛, 蒋天宇, 刘旭, 等. 土壤重金属污染现状及检测分析技术研究进展[J]. 中国地质, 2021, 48(2):460-476.
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
刘青松, 邓成龙. 磁化率及其环境意义[J]. 地球物理学报, 2009, 52(4):1041-1048.
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
夏敦胜, 杨丽萍, 马剑英, 等. 中国北方城市大气降尘磁学特征及其环境意义[J]. 中国科学(D辑:地球科学), 2007, 37(8):1073-1080.
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
闫倩, 戴霜, 刘海娇, 等. 兰州某钢厂附近土壤磁化率特征及其环境意义[J]. 中国环境科学, 2011, 31(10):1732-1737.
|
| [10] |
王冠, 陈裕颖, 夏敦胜, 等. 上海城市表土磁性特征对重金属污染的指示作用[J]. 环境科学学报, 2018, 38(8):3302-3312.
|
| [11] |
琚宜太, 王少怀, 张庆鹏, 等. 福建三明地区被污染土壤的磁学性质及其环境意义[J]. 地球物理学报, 2004, 47(2):282-288.
|
| [12] |
周洪英. 徐州城市表层土壤重金属污染特征与环境磁学响应[D]. 徐州: 中国矿业大学, 2016.
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
赵庆磊, 李凤全, 王天阳, 等. 金华城区表层土壤剖面磁化率变化规律[J]. 水土保持研究, 2015, 22(2):340-344.
|
| [15] |
陈明, 刘亮. 采样间隔对城市表土剖面磁化率变化的影响[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2023, 47(6):61-69.
|
| [16] |
陈轶楠, 张永清, 张希云, 等. 晋南某钢厂周边土壤重金属与磁化率分布规律及其相关性研究[J]. 干旱区资源与环境, 2014, 28(1):85-91.
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
刘晓宇, 杨文采, 陈召曦, 等. 青藏高原东部地块的属性与演化[J]. 地学前缘, 2023, 30(3):233-241.
|
| [19] |
青海省统计局·国家统计局青海调查总队. 2022年青海省统计年鉴[M]. 北京: 中国统计出版社, 2022.
Qinghai Provincial Bureau of Statistics· Qinghai Survey Corps of National Bureau of Statistics. Qinghai provincial statistical yearbook 2022[M]. Beijing: China Statistics Press, 2022.
|
| [20] |
陈霞, 刘亮, 王彦瑜, 等. 青藏高原东缘海东市表土重金属污染特征及源解析[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2026, 50(1):112-120.
|
| [21] |
旺罗, 刘东生, 吕厚远. 污染土壤的磁化率特征[J]. 科学通报, 2000, 45(10):1091-1093.
|
| [22] |
陈雅敏, 宋效东, 刘峰, 等. 青藏高原表土磁化率空间分布特征及影响因素[J]. 土壤学报, 2024, 61(2):361-371.
|
| [23] |
陈慧, 杨胜利, 成婷, 等. 青藏高原东部表土磁化率特征与环境意义[J]. 冰川冻土, 2018, 40(6):1187-1194.
|
| [24] |
陈亮, 陈克龙, 张志军. 青海湖周边地区表土磁化率与土壤重金属的相关性研究[J]. 中国人口·资源与环境, 2017, 27(S1):51-54.
|
| [25] |
陈梓炫, 吕镔, 郑兴芬, 等. 川西地区表土磁学性质及其环境意义[J]. 土壤学报, 2019, 56(3):661-671.
|
| [26] |
史运坤, 鄂崇毅, 张晶, 等. 青海湖地区不同海拔黄土磁化率环境指示意义[J]. 地球环境学报, 2021, 12(3):256-268.
|
| [27] |
王新, 夏敦胜, 王博, 等. 西北干旱区农田土壤磁性特征及其环境意义[J]. 环境科学, 2017, 38(8):3507-3518.
|
| [28] |
王博, 夏敦胜, 余晔, 等. 兰州城市表层土壤重金属污染的环境磁学记录[J]. 科学通报, 2012, 57(32):3078-3089.
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
闫倩. 兰州某钢厂附近土壤重金属与磁化率测量及环境意义[D]. 兰州: 兰州大学, 2011.
|
| [31] |
赖涓涓, 杨德钰, 刘亮, 等. 中国西北地区银川市浅表土重金属污染特征及来源解析[J/OL]. 中国环境科学, 2024:1-12.( 2024-03-28).https://link.cnki.net/doi/ 10.19674/j.cnki.issn1000-6923.20240326.006.
|
| [32] |
陈泽华, 焦思, 余爱华, 等. 土壤重金属污染评价方法探析:以南京市为例[J]. 森林工程, 2020, 36(3):28-36.
|
| [33] |
宋扬, 郝青振, 葛俊逸, 等. 黄土高原表土磁化率与气候要素的定量关系研究[J]. 第四纪研究, 2012, 32(4):679-689.
|
| [34] |
张连科, 李海鹏, 黄学敏, 等. 包头某铝厂周边土壤重金属的空间分布及来源解析[J]. 环境科学, 2016, 37(3):1139-1146.
|
| [35] |
杨昱莹, 刘亮, 陈明, 等. 长三角地区南京市表土重金属污染特征及源解析[J]. 中国环境科学, 2024, 44(7):3910-3918.
|
| [36] |
师发苗, 陈琳, 郭霞, 等. 基于发生分类的青海东部林地栗钙土基层分类研究[J]. 青海农林科技, 2022(2):28-31.
|
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
任二慧, 李海侠, 张小凌, 等. 人为Pb,Cd污染条件下土壤磁性与重金属的关系[J]. 有色金属工程, 2021, 11(12):122-128.
|
| [39] |
国家环境保护局中国环境监测总站. 中国土壤元素背景值[M]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社, 1990.
State Environmental Protection Bureau,China Environmental Monitoring Station. Background values of soil elements in China[M]. Beijing: China Environmental Science Press, 1990.
|
| [40] |
曾静静. 兰州城市表层土壤重金属Cu、Zn、Pb的分布及磁化率特征[D]. 兰州: 兰州大学, 2007.
|
| [41] |
薛勇, 胡雪峰, 叶荣. 上海宝山不同功能区表土磁化率特征及对重金属污染的指示作用[J]. 土壤通报, 2016, 47(5):1245-1252.
|
| [42] |
王博, 夏敦胜, 余晔, 等. 典型沙漠绿洲城市表土磁性特征及环境指示意义[J]. 地球物理学报, 2014, 57(3):891-905.
|
| [43] |
黄来明, 邵明安, 陈留美, 等. 水耕人为土时间序列铁氧化物与磁化率演变特征[J]. 土壤学报, 2017, 54(1):1-13.
|
| [44] |
|
| [45] |
吕厚远, 韩家懋, 吴乃琴, 等. 中国现代土壤磁化率分析及其古气候意义[J]. 中国科学 (b辑化学生命科学地学), 1994, 24(12):1290-1297.
|
| [46] |
王冠, 夏敦胜, 刘秀铭, 等. 兰州市城市街道尘埃磁学特征时空变化规律[J]. 科学通报, 2008, 53(4):446-455.
|
| [47] |
张曼, 胡忠行, 李文, 等. 金华市武义江沉积物磁性特征及其对重金属污染的指示意义[J]. 浙江师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2016, 39(2):219-226.
|
| [48] |
袁大刚, 张甘霖. 城市道路区土壤的磁学性质及其发生学意义[J]. 土壤学报, 2008, 45(2):216-221.
|
| [49] |
王学松. 城市表层土壤重金属富集淋滤特征与磁学响应[M]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社, 2009.
|
| [50] |
仝致琦, 谷蕾, 段海静, 等. 基于Kriging插值的路旁土壤重金属含量空间分布:以310国道郑州-开封段为例[J]. 环境科学学报, 2012, 32(12):3030-3038.
|
| [51] |
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |