 PDF(6192 KB)
PDF(6192 KB)


文冠果BZR1基因家族鉴定及功能分析
许慧慧, 班卓, 王晨雪, 毕泉鑫, 刘肖娟, 王利兵
南京林业大学学报(自然科学版) ›› 2025, Vol. 49 ›› Issue (2) : 12-22.
 PDF(6192 KB)
PDF(6192 KB)
 PDF(6192 KB)
PDF(6192 KB)
文冠果BZR1基因家族鉴定及功能分析
The identification and functional analysis of BZR1 genes in yellowhorn
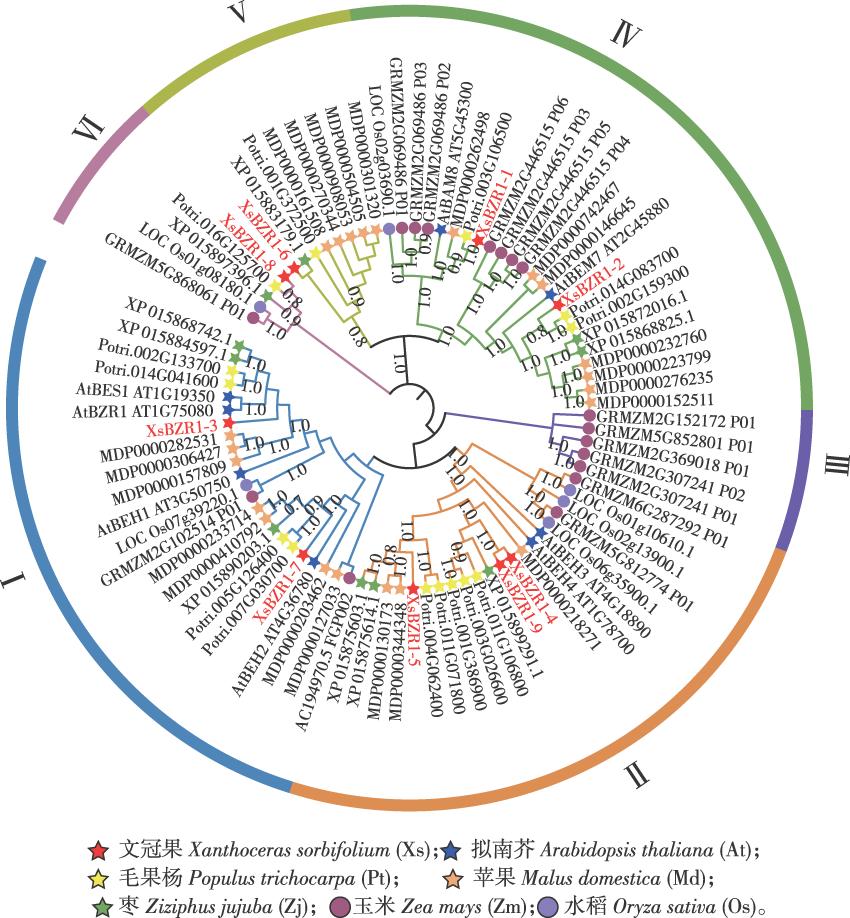
【目的】探究文冠果(Xanthoceras sorbifolium)Brassinazole Resistance 1(BZR1)基因家族成员的特征及其在非生物胁迫响应中的作用,为文冠果XsBZR1基因功能的研究和抗逆新品种的选育提供理论参考。【方法】利用生物信息学方法鉴定并系统分析文冠果XsBZR1基因家族;构建35S::XsBZR1-eYFP融合蛋白,对XsBZR1进行亚细胞定位分析;通过实时荧光定量PCR技术分析XsBZR1基因在非生物胁迫下的表达模式;构建XsBZR1- 9基因的过表达载体并转化到拟南芥(Arabidopsis thaliana)中,观察转基因株系与野生型植株在盐胁迫处理下的生长情况。【结果】①在文冠果基因组中共鉴定出9个BZR1基因,分别命名为XsBZR1-1—XsBZR1-9,这些基因不均匀地分布在6条染色体上。②系统进化和共线性分析表明,XsBZR1蛋白与双子叶植物的BZR 1转录因子亲缘关系更为密切。③XsBZR1基因的启动子区域具有大量的光响应、激素响应元件以及胁迫应答响应元件。④亚细胞定位结果和预测结果一致,9个XsBZR1均定位于细胞核。⑤qRT-PCR分析表明,9个XsBZR1基因在不同的非生物胁迫下表现出不同的表达模式。除XsBZR1-7外,其余XsBZR1基因在低温胁迫下3 h时迅速上调表达;盐胁迫下XsBZR1的表达量呈现较大的差异性,XsBZR1-3/4/5/7的表达受到盐胁迫的显著抑制,而XsBZR1-1和XsBZR1-9在盐胁迫处理9 h时表达量提高到约20倍;XsBZR1-3/7/8/9在干旱处理9 h时表达量提高到2倍以上,而其余XsBZR1在干旱处理下的表达水平变化不大;9个XsBZR1均受到ABA的诱导表达,其中XsBZR1-8在ABA处理9 h时表达量提高到35倍。⑥在拟南芥中过表达XsBZR1-9发现,转基因植株在盐胁迫处理后的主根长度显著高于野生型植株。【结论】XsBZR1家族成员参与了文冠果非生物胁迫响应,过表达XsBZR1-9显著提高植物对盐胁迫的耐受性,这为进一步分析XsBZR1基因在文冠果抗逆机制中的作用奠定了基础。
【Objective】This study aimed to systematically characterize the BZR1 transcription factor family in yellowhorn (Xanthoceras sorbifolium) and elucidate its functional roles in abiotic stress response, thereby providing insights for breeding stress-resistant cultivars.【Method】Genome-wide identification of XsBZR1 genes was performed using bioinformatics tools. Subcellular localization of XsBZR1 proteins was validated via 35S::XsBZR1-eYFP fusion constructs. Expression profiles under abiotic stresses (low temperature, salt, drought) and abscisic acid (ABA) treatment were analyzed by qRT-PCR. Functional validation was conducted by overexpressing XsBZR1- 9 in Arabidopsis thaliana and assessing salt tolerance phenotypes.【Result】Nine XsBZR1 genes (XsBZR1-1 to XsBZR1-9) were identified and distributed unevenly across six chromosomes. Phylogenetic and synteny analyses revealed close evolutionary relationships with dicotyledonous BZR1 orthologs. Promoter regions harbored abundant cis-regulatory elements associated with light responsiveness (48.9%), hormone signaling (35.0%) and stress adaptation (24.6%). The nuclear localization of all XsBZR1 proteins was experimentally confirmed. Differential expression patterns were observed under stress conditions: low temperature (4 ℃) rapidly induced eight XsBZR1 genes (1.3- to 6.0-fold upregulation at 3 h; P<0.05), except XsBZR1-7. Salt stress (150 mmol/L NaCl) suppressed XsBZR1-3/4/5/7 but strongly upregulated XsBZR1-1 (26.1-fold) and XsBZR1-9 (19.6-fold) at 9 h (P<0.001). Drought stress (mass fraction 25% PEG6000) elevated XsBZR1- 3/7/8/9 expression (>1.9-fold at 9 h), while others remained stable. ABA treatment (100 μmol/L) universally induced XsBZR1 genes, with XsBZR1-8 showing a 35.4-fold increase (P<0.001).Transgenic Arabidopsis overexpressing XsBZR1-9 exhibited enhanced salt tolerance, with taproot lengths twice that of the wild-type under 100 mmol/L NaCl (P<0.01).【Conclusion】The XsBZR1 gene family plays pivotal roles in yellowhorn’s abiotic stress response, with XsBZR1-9 demonstrating significant potential for improving salt tolerance. These findings advance the molecular understanding of stress adaptation mechanisms in woody plants and provide targets for precision breeding.
文冠果 / BZR1转录因子 / 非生物胁迫 / 基因过表达 / 盐胁迫响应 / XsBZR1-9
yellowhorn(Xanthoceras sorbifolium) / BZR1 transcription factor / abiotic stress tolerance / gene overexpression / salt stress response / XsBZR1- 9
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
王孟珂, 杨晓明, 汪贵斌, 等. 外施24-表油菜素内酯(EBR)对银杏叶片发育和生理特征影响[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2023, 47(4):81-87.
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
沈春洋. 番茄BZR基因家族生物信息学分析及抗逆基因功能鉴定[D]. 哈尔滨: 东北农业大学, 2022.
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
麻云霞. 文冠果种子特性变异及优良砧用种源选择[D]. 呼和浩特: 内蒙古农业大学, 2021.
|
| [21] |
刘志. 文冠果WRKY转录因子家族的鉴定及非生物胁迫响应模式分析[D]. 哈尔滨: 东北林业大学, 2020.
|
| [22] |
常巧颖. 文冠果bZIP转录因子家族鉴定和非生物胁迫应答模式分析[D]. 哈尔滨: 东北林业大学, 2020.
|
| [23] |
杨娟, 姜阳明, 周芳, 等. PEG模拟干旱胁迫对不同抗旱性玉米品种苗期形态与生理特性的影响[J]. 作物杂志, 2021(1):82-89.
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
周晔, 赵璇, 王璐, 等. 植物BZR家族基因调控非生物胁迫应答和生长发育的研究进展[J]. 中国油料作物学报, 2020, 42(4):499-511.
|
| [27] |
王黎明, 杨瑞珍, 孙加强. 油菜素内酯调控作物农艺性状和非生物胁迫响应的研究进展[J]. 生物工程学报, 2022, 38(1):34-49.
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
尹魁林, 程莎莎, 艾长丰, 等. 枣BZR基因家族的鉴定及其在果实发育中的表达分析[J/OL]. 分子植物育种:1-13[2024-03-26].
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
明川. 玉米BES1/BZR1转录因子基因鉴定[D]. 雅安: 四川农业大学, 2019.
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
杜巧丽, 刘均霞, 陈美晴, 等. 高粱BR信号转录因子BZR1基因家族的鉴定及激素应答分析[J]. 植物保护学报, 2022, 49(3):848-856.
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
陈旭, 沈春洋, 莫福磊, 等. 番茄BZR基因家族鉴定及非生物胁迫下表达模式分析[J]. 东北农业大学学报, 2021, 52(11):9-17.
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
|
| [40] |
|
| [41] |
|
| [42] |
|
| [43] |
|
| [44] |
|
| [45] |
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |