 PDF(29108 KB)
PDF(29108 KB)


漳河上游土地利用与生态系统服务时空演变及预测
李斌, 王贺封, 张安兵, 魏凯濠, 李斯林
南京林业大学学报(自然科学版) ›› 2025, Vol. 49 ›› Issue (4) : 206-214.
 PDF(29108 KB)
PDF(29108 KB)
 PDF(29108 KB)
PDF(29108 KB)
漳河上游土地利用与生态系统服务时空演变及预测
Spatiotemporal evolution and prediction of land use and ecosystem services in the upper reaches of Zhanghe River basin
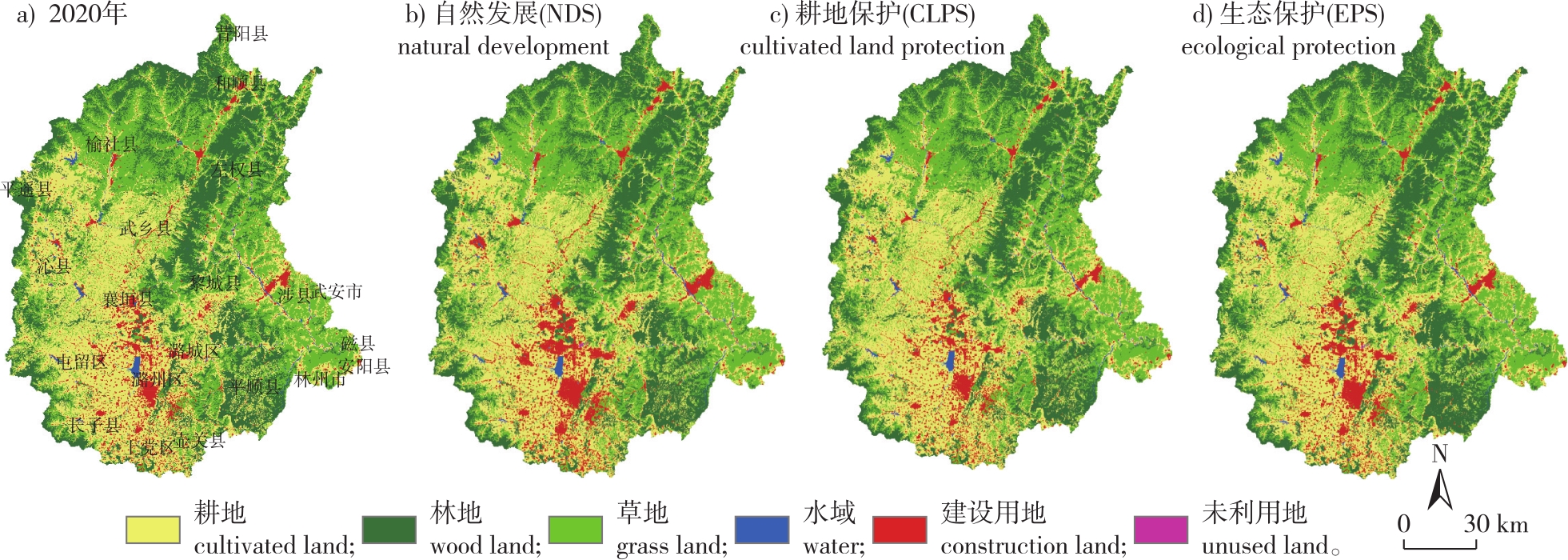
【目的】探究我国中部地区流域土地利用动态和生态系统服务时空演变特征,为粮食主产区生态环境保护和国土空间规划提供科学依据。【方法】以2000—2020年漳河上游土地利用变化为基础,基于InVEST、PLUS等模型,探讨漳河上游过去及未来不同情景下土地利用变化及生态系统服务时空演变规律。【结果】①2000—2020年,流域内土地利用变化主要表现为耕地迅速减少及建设用地持续扩张;2035年,自然发展情景下建设用地持续高速扩张,挤占了耕地、草地和林地,而耕地保护和生态保护情景下建设用地扩张得到抑制,耕地、林地得到了有效保护。②2000—2020年,研究区产水量和土壤保持量呈上升趋势,碳储量和生境质量呈下降趋势;碳储量、生境质量和土壤保持量高值区位于中部偏东和东南部的林地,低值区位于中南部的建设用地,产水量则呈相反空间分布格局;从地形梯度上看,产水量随地形梯度上升而减小,碳储量、生境质量、土壤保持量随地形梯度上升而增加。③生态保护情景下研究区生态系统服务获得最大提升。【结论】生态保护情景更适宜研究区今后发展模式,可为漳河上游生态环境保护和土地开发提供决策参考。流域未来需着重关注建设用地与耕地的冲突问题,针对性地优化国土空间开发策略,促进区域内土地利用结构向高生态系统服务发展。
【Objective】This research aims to investigate the spatiotemporal evolution characteristics of land use dynamics and ecosystem services in the central China river basins, and provide a scientific basis for ecological environment protection and territorial space planning in major grain-producing regions.【Method】Based on land use changes in the upper reaches of the Zhanghe River basin from 2000 to 2020, this study employed models such as InVEST and PLUS to explore the spatiotemporal evolution patterns of land use and ecosystem services under different scenarios in the past and future of the basin.【Result】(1) From 2000 to 2020, the basin experienced rapid cultivated land reduction and continuous construction land expansion. By 2035, under the natural development scenario, construction land expanded rapidly, encroaching on cultivated, grassland, and forest land. However, under cultivated land protection and ecological protection scenarios, construction land expansion was curbed, effectively preserving cultivated and forest land. (2) During 2000-2020, water yield and soil conservation increased, while carbon storage and habitat quality decreased. High-value areas for carbon storage, habitat quality, and soil conservation were found in the basin’s east-central and southeastern forests, whereas low-value areas were in the south-central construction land. Water yield exhibited an opposite spatial pattern, decreasing with increasing topographic gradient. (3) The ecological protection scenario yielded the greatest ecosystem service improvements and is suitable for future development.【Conclusion】The ecological protection scenario offers decision-making support for ecological protection and land development in the basin’s upper reaches. Future efforts should focus on resolving construction land-cultivated land conflicts and optimizing territorial space development strategies to promote land use structure transformation toward high ecosystem service provision.
土地利用模拟 / 生态系统服务 / InVEST模型 / PLUS模型 / 漳河上游
land use simulation / ecosystem services / InVEST model / PLUS model / upper reaches of Zhanghe River basin
| [1] |
任胤铭, 刘小平, 许晓聪, 等. 基于FLUS-InVEST模型的京津冀多情景土地利用变化模拟及其对生态系统服务功能的影响[J]. 生态学报, 2023, 43(11):4473-4487.
|
| [2] |
李广东, 戚伟. 中国建设用地扩张对景观格局演化的影响[J]. 地理学报, 2019, 74(12):2572-2591.
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
张徐, 李云霞, 吕春娟, 等. 基于InVEST模型的生态系统服务功能应用研究进展[J]. 生态科学, 2022, 41(1):237-242.
|
| [8] |
戚丽萍, 栾兆擎, 魏勉, 等. 基于土地利用的江苏省各市生态系统服务价值时空变化研究[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2023, 47(4):200-208.
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
赵筱青, 石小倩, 李驭豪, 等. 滇东南喀斯特山区生态系统服务时空格局及功能分区[J]. 地理学报, 2022, 77(3):736-756.
|
| [12] |
徐梓津, 张雪松, 陈明曼. 山地岩溶区生态系统服务时空演变特征分析:以贵州省为例[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(7):1196-1206.
|
| [13] |
辛会超, 王贺封, 张安兵, 等. 2000—2020年漳河上游生态环境质量动态监测及驱动因素分析[J]. 水土保持通报, 2023, 43(1):92-103.
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
许丁雪, 吴芳, 何立环, 等. 土地利用变化对生态系统服务的影响:以张家口—承德地区为例[J]. 生态学报, 2019, 39(20):7493-7501.
|
| [16] |
李俊, 杨德宏, 吴锋振, 等. 基于PLUS与InVEST模型的昆明市土地利用变化动态模拟与碳储量评估[J]. 水土保持通报, 2023, 43(1):378-387.
|
| [17] |
李克让, 王绍强, 曹明奎. 中国植被和土壤碳贮量[J]. 中国科学:D辑, 2003, 33(1):72-80.
|
| [18] |
解宪丽, 孙波, 周慧珍, 等. 中国土壤有机碳密度和储量的估算与空间分布分析[J]. 土壤学报, 2004, 41(1):35-43.
|
| [19] |
巩晟萱, 张玉虎, 李宇航. 基于PLUS-InVEST模型的京津冀碳储量变化及预测[J]. 干旱区资源与环境, 2023, 37(6):20-28.
|
| [20] |
赫晓慧, 徐雅婷, 范学峰, 等. 中原城市群区域碳储量的时空变化和预测研究[J]. 中国环境科学, 2022, 42(6):2965-2976.
|
| [21] |
韩晶, 崔金芳, 杨威, 等. 基于InVEST模型的低山丘陵区土壤侵蚀变化与驱动因素分析[J]. 水土保持研究, 2022, 29(5):32-39.
|
| [22] |
黄木易, 岳文泽, 冯少茹, 等. 基于InVEST模型的皖西大别山区生境质量时空演化及景观格局分析[J]. 生态学报, 2020, 40(9):2895-2906.
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
汤国安, 宋佳. 基于DEM坡度图制图中坡度分级方法的比较研究[J]. 水土保持学报, 2006, 20(2):157-160,192.
|
| [25] |
喇蕗梦, 勾蒙蒙, 李乐, 等. 三峡库区生态系统服务权衡时空动态与情景模拟:以秭归县为例[J]. 生态与农村环境学报, 2021, 37(11):1368-1377.
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
陈万旭, 李江风, 曾杰, 等. 中国土地利用变化生态环境效应的空间分异性与形成机理[J]. 地理研究, 2019, 38(9):2173-2187.
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
张薇, 王凤春, 贾悦, 等. 张承水源涵养区土地利用演变及产水量的响应[J]. 中国农村水利水电, 2022(5):138-146.
|
| [30] |
张锦琳, 游巍斌, 蔡新瑜, 等. 武夷山小流域生态系统服务(簇)权衡/协同及对地形起伏度的响应[J]. 生态学报, 2023, 43(12):4892-4903.
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |