 PDF(2128 KB)
PDF(2128 KB)


 PDF(2128 KB)
PDF(2128 KB)
 PDF(2128 KB)
PDF(2128 KB)
植物病原真菌聚酮类次级代谢产物研究进展
Research progress on the polyketone secondary metabolites from phytopathogenic fungi
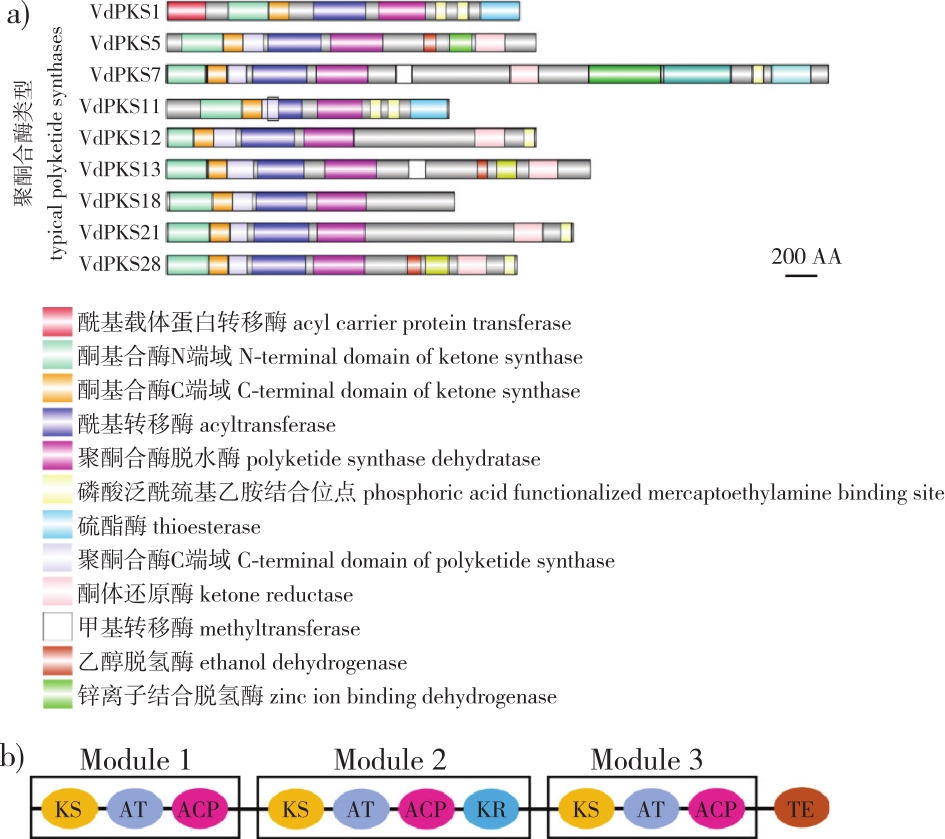
在植物与病原真菌相互作用过程中,病原真菌通过产生次级代谢产物协助其对植物的入侵和致病。由聚酮合酶(polyketide synthase, PKS)参与合成的真菌聚酮类化合物是真菌中最丰富的次级代谢产物,通过合成重要的色素、致病因子和真菌毒素帮助病原真菌逃避和破坏寄主植物的免疫机制,从而成功侵染。笔者综述了真菌Ⅰ型聚酮合酶多功能域重复串联催化的结构特点;独立及偶联其他酶类催化基因簇合成包括真菌毒素、抗生素和色素在内的多种化合物,赋予真菌发育、抗逆和致病等诸多功能;总结了转录因子、表观遗传学修饰和次级代谢通路对聚酮化合物合成的调控方式;着重列举近年来主要植物病原真菌聚酮类产物及其合成基因簇;并对真菌聚酮类次级代谢产物调控网络解析、合成生物学和产物鉴定等研究方向进行展望。通过分析以期为揭示病原真菌致病机制和植物真菌病害的防控提供研究思路和策略。
During host-pathogen interaction, pathogenic fungi facilitate host invasion and pathogenesis through the production of secondary metabolites. Fungal polyketides, catalyzed by polyketide synthase (PKS), represent the most abundant class of bioactive metabolites in fungi, they can establish phytopathogenic fungi successful infections, by synthesizing key pigments, virulence factors, and mycotoxins to evade and disrupt host plant immune mechanisms. This review systematically examines the structural characteristics, classification, biological functions, and metabolic regulation of fungal type Ⅰ PKS. Furthermore, we highlight recent advances in characterizing polyketide compounds and their biosynthetic gene clusters in plant-pathogenic fungi. Potential future research directions for fungal polyketides are prospected, with emphasis on their role in fungal pathogenicity. Collectively, this work aims to provide novel insights and methodological frameworks for elucidating pathogenic mechanisms of fungal infections and developing targeted disease control strategies.
丝状真菌 / 聚酮化合物 / 基因簇 / 致病功能 / 调控机制
filamentous fungi / polyketide / gene cluster / pathogenic function / regulation mechanism
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
许杨, 魏康霞. 真菌聚酮合酶基因的研究进展[J]. 食品与生物技术学报, 2008, 27(2):1-5.
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
朱赫, 纪明山. 具有除草活性植物病原真菌毒素的作用模式[J]. 杂草科学, 2014, 32(4):1-7.
|
| [20] |
陈锡玮, 许蒙, 冯程, 等. 真菌聚酮化合物生物合成研究进展[J]. 生物工程学报, 2018, 34(2):151-164.
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
王洪秀, 张倩, 王玲杰, 等. 链格孢菌毒素合成相关基因研究进展[J]. 中国生物工程杂志, 2015, 35(11):92-98.
|
| [24] |
刘思远, 申东晨, 刘峥, 等. 不同水曲柳褐斑病病级叶片的微生物多样性[J]. 森林工程, 2024, 40 (1): 1-8.
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
赵彦婷. 拟南芥和番茄对神经鞘脂类似类真菌毒素的抗性机理研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2014.
|
| [29] |
曹志艳, 杨胜勇, 董金皋. 植物病原真菌黑色素与致病性关系的研究进展[J]. 微生物学通报, 2006, 33(1):154-158.
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
|
| [40] |
|
| [41] |
|
| [42] |
|
| [43] |
|
| [44] |
|
| [45] |
|
| [46] |
|
| [47] |
|
| [48] |
|
| [49] |
|
| [50] |
|
| [51] |
|
| [52] |
|
| [53] |
|
| [54] |
|
| [55] |
|
| [56] |
|
| [57] |
|
| [58] |
|
| [59] |
|
| [60] |
|
| [61] |
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |