 PDF(2636 KB)
PDF(2636 KB)


不同平茬机械切口对平茬后北沙柳光合和生长状态的影响
张世纪, 韩易良, 何金军, 裴志永, 李志华, 杨建军, 王海超, 朱心宇, 韩青池, 刘文娟
南京林业大学学报(自然科学版) ›› 2025, Vol. 49 ›› Issue (5) : 113-122.
 PDF(2636 KB)
PDF(2636 KB)
 PDF(2636 KB)
PDF(2636 KB)
不同平茬机械切口对平茬后北沙柳光合和生长状态的影响
The influence of different stubble treatment on the post-pruning photosynthesis and growth conditions of Salix psammophila
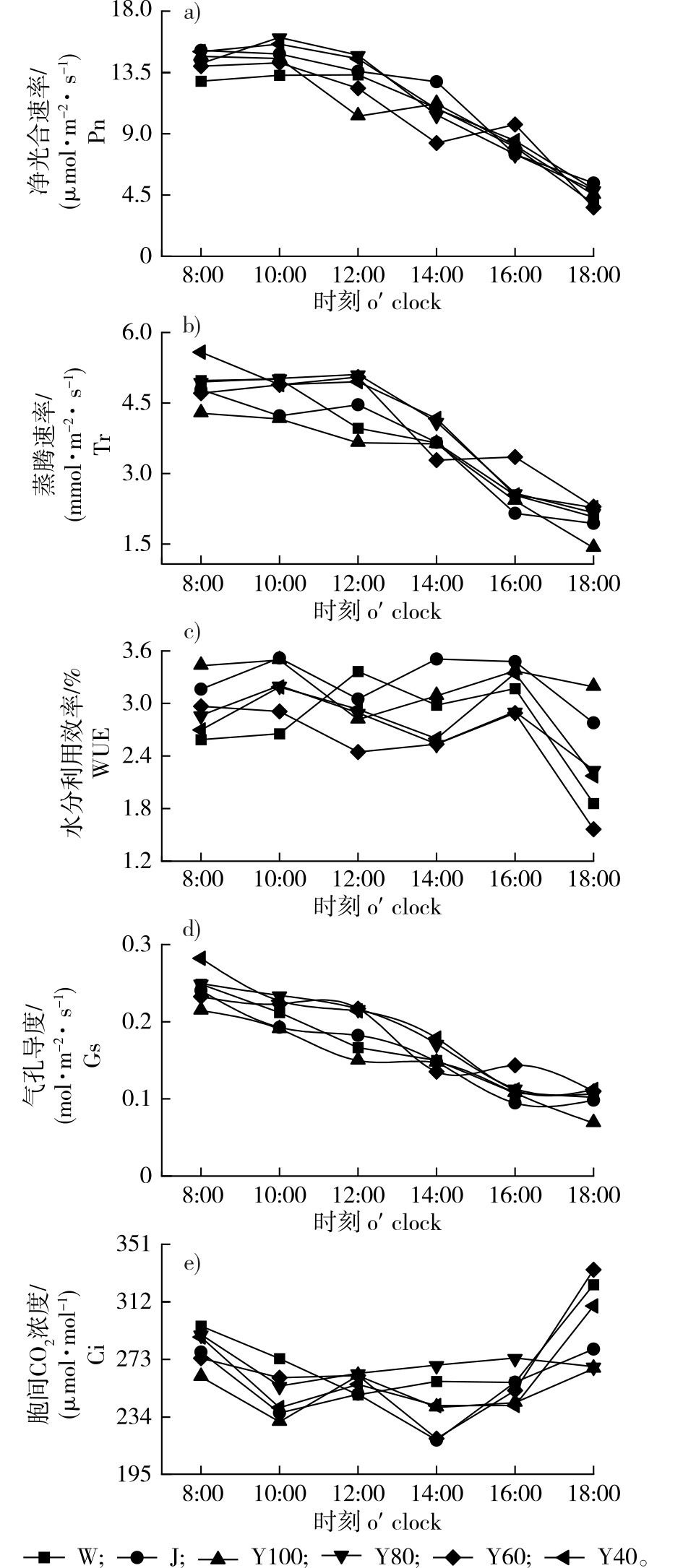
【目的】研究不同平茬处理对北沙柳切口的损伤,分析不同茬口对北沙柳光合及生长发育的影响,为北沙柳平茬机械的设计和可持续利用提供参考。【方法】于2023年,在国家北沙柳种质资源库实施一项完全随机设计的田间实验,系统考察6种不同平茬处理方式[圆盘式40齿(Y40)、圆盘式60齿(Y60)、圆盘式80齿(Y80)、圆盘式100齿(Y100)、往复式(W)、剪切式(J)]对植株茬口特征的影响,并探究茬口与北沙柳生理生态的关联性。【结果】不同平茬处理对北沙柳茬口特性影响显著不同,Y60、Y80、Y100处理与W、J处理间烧焦率差异显著(P<0.05),Y40与W处理间劈裂率差异显著(P<0.05),Y100与J处理间毛刺分布差异显著(P<0.05),其余处理对劈裂率及毛刺调控效果无显著差异。萌蘖期测定显示,不同平茬处理对北沙柳基径和枝条萌发数无显著影响,Y80处理组株高显著优于其他处理(P<0.05),Y60处理株高较低且与Y80、Y40、W处理差异显著(P<0.05)。光合日动态分析表明,不同平茬措施显著调控北沙柳光合特性:Y100与Y60处理的净光合速率(Pn)呈“双峰”曲线,其余处理的Pn为“单峰”且J组持续下降;水分利用效率(WUE)普遍呈现“双峰”特征,日均值以J、Y100处理最高;气孔导度(Gs)与Pn、蒸腾速率(Tr)同步单峰递减,而胞间CO2浓度(Ci)呈“W”形波动;相关性分析发现Y100处理组切口烧焦率与平均株高极显著正相关(P<0.01),Y40处理北沙柳的烧焦率与萌发枝条数和最短枝长呈显著负相关(P<0.05),与平均枝高呈极显著负相关。综合主成分分析与指标权重评估,Y80平茬策略在促进北沙柳存活与萌芽方面表现突出,是较为合理的平茬措施。【结论】使用Y80型锯片作为标准平茬工具,可提升北沙柳林的生态与经济效益。
【Objective】Stubble management plays a critical role in shrub restoration and desert ecological rehabilitation. While existing studies primarily focus on stubble height and cutting cycles, the impacts of stump characteristics on shrub regrowth and photosynthetic performance remain poorly understood, and standardized criteria for evaluating mechanical damage during stubble operations are lacking. 【Method】A completely randomized field experiment was conducted in 2023 at the National Salix psammophila Germplasm Repository to systematically assess the effects of six stubble treatments: disk-type 40-tooth (Y40), 60-tooth (Y60), 80-tooth (Y80), 100-tooth (Y100), reciprocating (W), and shearing (J), on stump morphology and their correlations with physiological and ecological traits. 【Result】Stump analysis revealed significant differentiation in damage characteristics: the charring rate showed significant differences among the Y60, Y80, Y100 treatments and the W, J treatments (P < 0.05), while splitting rate showed significance only between Y40 and W (P<0.05), and burr distribution varied solely between Y100 and J (P<0.05). No significant differences were observed in other treatments. During sprouting period, photosynthetic parameters showed no treatment specific variations, indicating limited photosynthetic sensitivity to stubble methods. Sprouting-phase measurements demonstrated negligible effects of treatments on basal diameter or sprout number, though Y80 plant height (P<0.05). The plant height of the Y60 treatment was lower and showed significant differences among Y80, Y40, and W (P<0.05). Diurnal photosynthetic dynamics indicated treatment-specific regulation: Y100 and Y60 displayed bimodal net photosynthetic rate (Pn) curves, whereas others followed unimodal patterns (J declined continuously). Water use efficiency (WUE) exhibited bimodal peaks, with J and Y100 showing the highest daily means. Stomatal conductance (Gs) and transpiration rate (Tr) decreased unimodally, while intercellular CO2 concentration (Ci) fluctuated in a “W” shape (P<0.05). Correlation analysis identified a strongly positive relationship between scorch rate and mean plant height in Y100 (P<0.01), and a negative correlation between splitting rate and sprout number in Y80 (P<0.05). Principal component analysis highlighted Y80’s dominance in survival rate and sprouting potential. Y80 is the most reasonable pruning measure. 【Conclusion】Using the Y80-type saw blade as a standard stubble cutting tool can improve the ecological and economic benefits of S. psammophila forests
平茬措施 / 切口特性 / 光合作用 / 生长指标 / 北沙柳
stubble treatment / plant incision characteristic / photosynthesis / growth indicator / Salix psammophila
| [1] |
郝媛媛, 颉耀文, 张文培, 等. 荒漠黑果枸杞研究进展[J]. 草业科学, 2016, 33(9):1835-1845.
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
温健. 平茬措施对柠条锦鸡儿细根生长及生理特征的影响[D]. 呼和浩特: 内蒙古农业大学, 2018.
|
| [4] |
于瑞鑫, 王磊, 蒋齐, 等. 不同平茬年限人工柠条林光合特性及土壤水分的响应变化[J]. 西北植物学报, 2019, 39(3):506-515.
|
| [5] |
马天琴. 不同平茬高度对沙柳生长状况的影响研究[D]. 呼和浩特: 内蒙古农业大学, 2017.
|
| [6] |
| [7] |
路东晔, 张国盛, 张磊, 等. 北沙柳研究进展[J]. 分子植物育种, 2020, 18(10):3427-3432.
|
| [8] |
张泽宁, 李芳, 郭彩云, 等. 中国沙棘伐桩萌枝能力对平茬高度的响应[J]. 西南林业大学学报(自然科学), 2020, 40(6):34-39.
|
| [9] |
段广东, 裴志永, 郝少荣, 等. 毛乌素沙地沙柳人工林最优平茬周期的确定[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2019, 19(7):65-69.
|
| [10] |
段明泽. 沙柳平茬圆锯片的磨损机理研究及参数优化[D]. 呼和浩特: 内蒙古工业大学, 2021.
|
| [11] |
程卫华, 刘志刚, 裴承慧, 等. 基于LS-DYNA的沙柳锯切仿真分析及试验研究[J]. 林产工业, 2023, 60(2):35-38,45.
|
| [12] |
冀振, 刘志刚, 余剑南, 等. 灌木平茬机仿形机构的设计及仿真分析[J]. 机械设计与制造, 2021(8):70-74.
|
| [13] |
李健, 左合君, 闫敏, 等. 库布齐沙漠柠条锦鸡儿灌木林健康评价[J]. 西北林学院学报, 2024, 39(1):177-184.
|
| [14] |
翟昊, 郝乐乐, 李国庆, 等. 不同时期平茬对柠条生长和成活率的影响[J]. 饲料研究, 2023, 46(22):106-109.
|
| [15] |
王瑜, 李江飞, 车凤仙, 等. 不同季节平茬对云南松苗木萌蘖能力的影响[J]. 西南林业大学学报(自然科学), 2023, 43(4):26-31.
|
| [16] |
任晓亮, 黄东晨, 谷明远, 等. 平茬高度对香椿生长及其光合特性和非结构性碳水化合物含量的影响[J]. 西北植物学报, 2023, 43(4):648-655.
|
| [17] |
董雪, 迟悦春, 郝玉光, 等. 平茬年限对沙冬青光合特性与比叶面积的影响[J]. 中南林业科技大学学报, 2021, 41(2):105-111,122.
|
| [18] |
王霞, 海莲, 赵晨光, 等. 不同锯割方式对柽柳生长的影响[J]. 内蒙古林业科技, 2021, 47(3):39-42,59.
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
杨春梅, 高海洋, 刘九庆. 灌木平茬机切割系统参数优化设计与验证[J]. 农机化研究, 2024, 46(8):42-49.
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
薛树媛, 王菊花, 黄娟, 等. 沙柳等灌木类植物饲料化利用技术和研究现状[J]. 畜牧与饲料科学, 2022, 43(2):56-60.
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
薄仕文, 李耀翔, 王海滨. 圆锯式灌木切割试验装置设计与试验[J]. 农机化研究, 2023, 45(5):165-172.
|
| [28] |
李宁, 俞国胜. 灌木收割机理及装备研究[J]. 安徽农业科学, 2009, 37(4):1862-1864.
|
| [29] |
孙健峰, 邢凯峰, 杨洲, 等. 基于ANSYS/LS-DYNA的果枝修剪过程仿真与试验研究[J]. 华南农业大学学报, 2022, 43(4):113-124.
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
孔蓓蓓, 刘超, 尹伟伦, 等. 沙柳、黄柳和杞柳光合作用的日变化[J]. 河南科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2009, 30(3):79-83,114.
|
| [33] |
郭飞, 吉喜斌, 金博文, 等. 干旱区荒漠-绿洲过渡带3种典型灌木气孔导度对环境变化的响应及其对蒸腾的调控[J]. 高原气象, 2021, 40(3):632-643.
|
| [34] |
曹恭祥, 刘新前, 季蒙, 等. 沙柳和黄柳光合特征及干旱胁迫下的光响应研究[J]. 内蒙古林业科技, 2018, 44(4):12-17.
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
赵育鹏. 盐胁迫条件下竹柳光合作用日变化特征研究[J]. 安徽农业科学, 2024, 52(4):87-89.
|
| [37] |
杨佳鹤, 何进宇, 刘飞杨, 等. 不同土壤水分对植物光合作用的影响研究进展[J]. 节水灌溉, 2023(11):39-46.
|
| [38] |
董雪, 高永, 虞毅, 等. 平茬措施对天然沙冬青生理特性的影响[J]. 植物科学学报, 2015, 33(3):388-395.
|
| [39] |
王鑫. 砒砂岩区不同平茬模式对沙棘生长和生理特征的影响研究[D]. 呼和浩特: 内蒙古农业大学, 2022.
|
| [40] |
|
| [41] |
|
| [42] |
李根秋, 安珍. 平茬方式对沙柳再萌生能力的影响[J]. 林业机械与木工设备, 2015, 43(1):29-31.
|
| [43] |
白双成, 姜准, 张增悦, 等. 中国沙棘平茬萌蘖能力对内源激素的响应[J]. 西南林业大学学报(自然科学), 2020, 40(3):82-87.
|
| [44] |
|
| [45] |
王丹, 李熙颜, 颜廷雨, 等. 不同季节平茬对云南松生物量分配与异速生长的影响[J]. 西南农业学报, 2023, 36(1):47-52.
|
| [46] |
|
| [47] |
|
| [48] |
|
| [49] |
|
| [50] |
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |