 PDF(99855 KB)
PDF(99855 KB)


 PDF(99855 KB)
PDF(99855 KB)
 PDF(99855 KB)
PDF(99855 KB)
基于慢特征分析与生成对抗网络的林业光学遥感影像薄云去除方法
Thin cloud removal method for forestry optical remote sensing images based on slow feature analysis and generative adversarial network
【目的】 针对光学遥感影像薄云去除后易出现影像失真、可用性降低的问题,提出一种融合慢特征分析(SFA)与生成对抗网络(GANs)的薄云去除方法(SFGAN),以提升影像质量,为林业遥感数据分析提供可靠支持。【方法】首先,设计慢变特征模块,通过计算初始影像的云反射率及高维特征慢变化度,将慢变特征向量与随机初始向量融合作为生成网络输入,增强生成器对云层特征的辨识能力;其次,利用云反射率作为鉴别器约束因子,通过对抗博弈迭代优化生成高质量无云影像,提升网络对云层与地物的区分能力。【结果】在公开数据集RICE1和PRSC上的试验表明:SFGAN模型在RICE1数据集上表现较为出色,无云影像的峰值信噪比(PSNR值)为33.740 7,结构相似性(SSIM值)为0.958 2;在PRSC数据集上,PSNR值为24.341 3,SSIM值为0.879 2,即本方法的性能量化指标及视觉质量均优于其他方法。基于Landsat 8影像的泛化实验进一步验证,SFGAN在真实云与模拟云场景中均能有效恢复地物细节,且处理单幅影像仅需0.98 s。【结论】SFGAN通过融合慢特征分析与生成对抗网络,能显著降低薄云对林业光学遥感影像的干扰,从数据源头提升影像可用性与分析准确性。
To address the issue of image distortion and reduced usability caused by thin cloud removal in optical remote sensing images, this study proposes a novel thin cloud removal method: SFGAN, that integrates slow feature analysis (SFA) with generative adversarial networks (GANs), aiming to enhance image quality and provide reliable data support for forestry remote sensing analysis.【Method】First, a slow-varying feature module is designed to calculate cloud reflectance and high-dimensional feature slowness. The slow-varying feature vectors are concatenated with random initial vectors as the generator input, improving cloud feature recognition. Second, cloud reflectance is utilized as a discriminative constraint factor to iteratively optimize the discriminator, thereby generating high-quality cloud-free images through adversarial training.【Result】Experiments on public datasets RICE1 and PRSC demonstrate that the SFGAN outperforms existing methods in both quantitative metrics (e.g., PSNR=33.740 7 and SSIM=0.958 2 on RICE1,PSNR=24.341 3 and SSIM=0.879 2 on PRSC) and visual assessments. Validation using Landsat 8 imagery shows SFGAN achieves superior cloud removal effects in both real and simulated cloud scenarios, with a processing time of 0.98 seconds per image.【Conclusion】The SFGAN framework effectively mitigates thin cloud interference in forestry optical remote sensing images by synergizing SFA and GANs, significantly improving data usability and analytical accuracy at the source level.
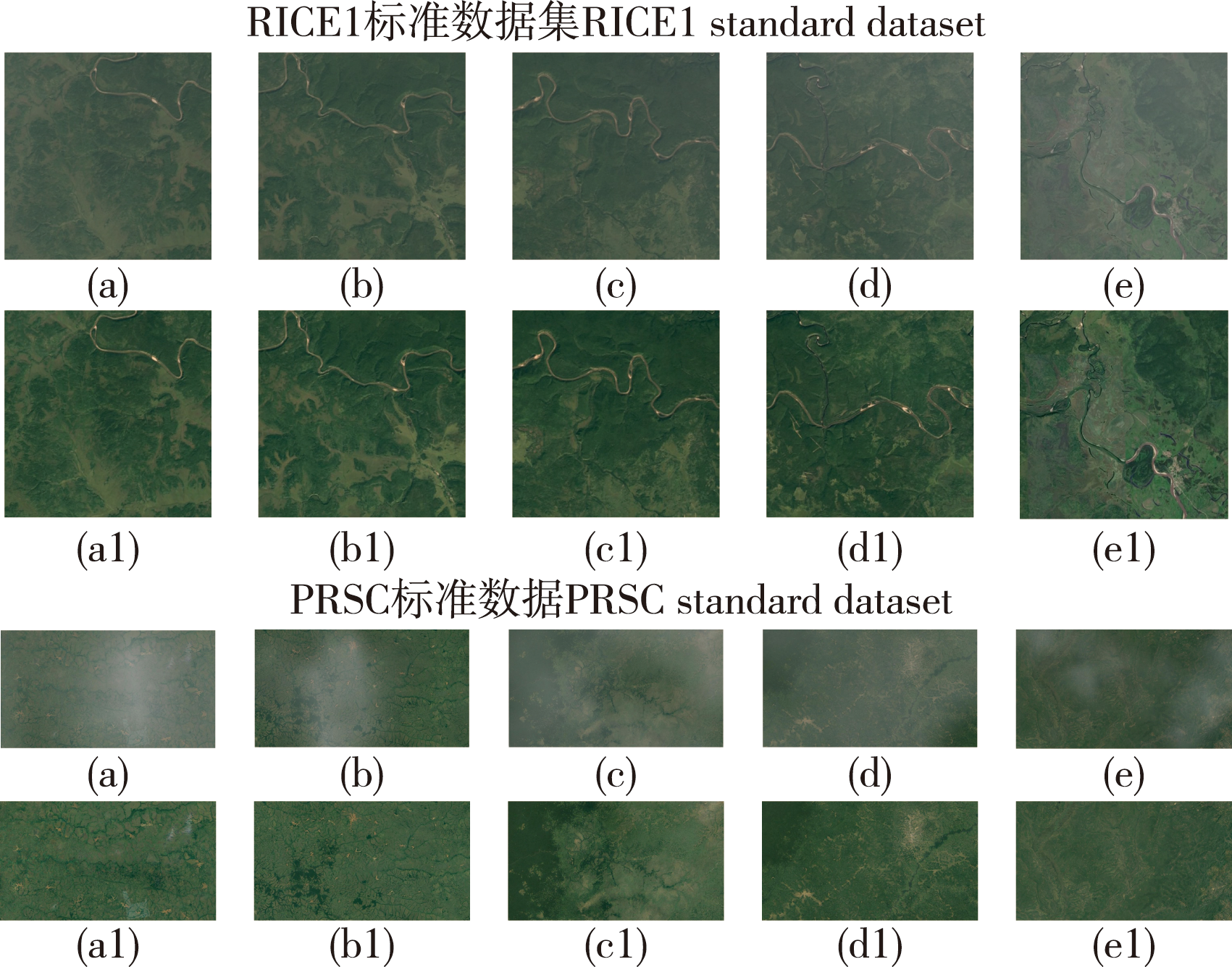
林业光学遥感影像 / 薄云去除 / 慢特征分析(SFA) / 生成对抗网络(GANs)
forestry optical remote sensing images / thin cloud removal / slow feature analysis (SFA) / generative adversarial networks (GANs)
| [1] |
李增元, 陈尔学. 中国林业遥感发展历程[J]. 遥感学报, 2021, 25(1):292-301.
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
徐萌, 王思涵, 郭仁忠, 等. 遥感影像云检测和云去除方法综述[J]. 计算机研究与发展, 2024, 61(6):1585-1607.
|
| [4] |
郭庭威, 黄红莲, 孙晓兵, 等. 环境二号卫星多光谱图像的薄云检测及去除[J]. 大气与环境光学学报, 2023, 18(4):383-400.
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
郑其光, 王仁芳, 邱虹, 等. 基于注意力机制和生成对抗网络的遥感影像云去除[J]. 遥感学报, 2025, 29(3):752-761.
|
| [17] |
蔡志丹, 方明, 李喆, 等. 基于高斯曲率和加权图总变分正则化的遥感图像盲去模糊算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(9):2649-2658.
|
| [18] |
刘万军, 程裕茜, 曲海成. 基于生成对抗网络的图像自增强去雾算法[J]. 系统仿真学报, 2024, 36(5):1093-1106.
|
| [19] |
马得草, 鲜勇, 苏娟, 等. 基于改进的条件生成对抗网络的可见光红外图像转换算法[J]. 光子学报, 2023, 52(4):0410003.
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
向俊, 严恩萍, 姜镓伟, 等. 基于全卷积神经网络和低分辨率标签的森林变化检测研究[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2024, 48 (1) :187-195.
|
| [24] |
杨帆, 赵增鹏, 张磊. 基于高斯混合模型的遥感影像云检测技术[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 42(4):134-140.
|
| [25] |
牛弘健, 刘文萍, 陈日强, 等. 基于Resnet的林地无人机图像去雾改进算法[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版). 2024, 48(2): 175-181.
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |