 PDF(1812 KB)
PDF(1812 KB)


流苏树叶片代谢物地理变异及其综合评价
牛牧歌, 刘来硕, 王锦楠, 陈荣, 武玉柱, 郭历阳, 李际红
南京林业大学学报(自然科学版) ›› 2025, Vol. 49 ›› Issue (5) : 123-130.
 PDF(1812 KB)
PDF(1812 KB)
 PDF(1812 KB)
PDF(1812 KB)
流苏树叶片代谢物地理变异及其综合评价
Geographical variation of metabolites in Chionanthus retusus leaves and its comprehensive evaluation
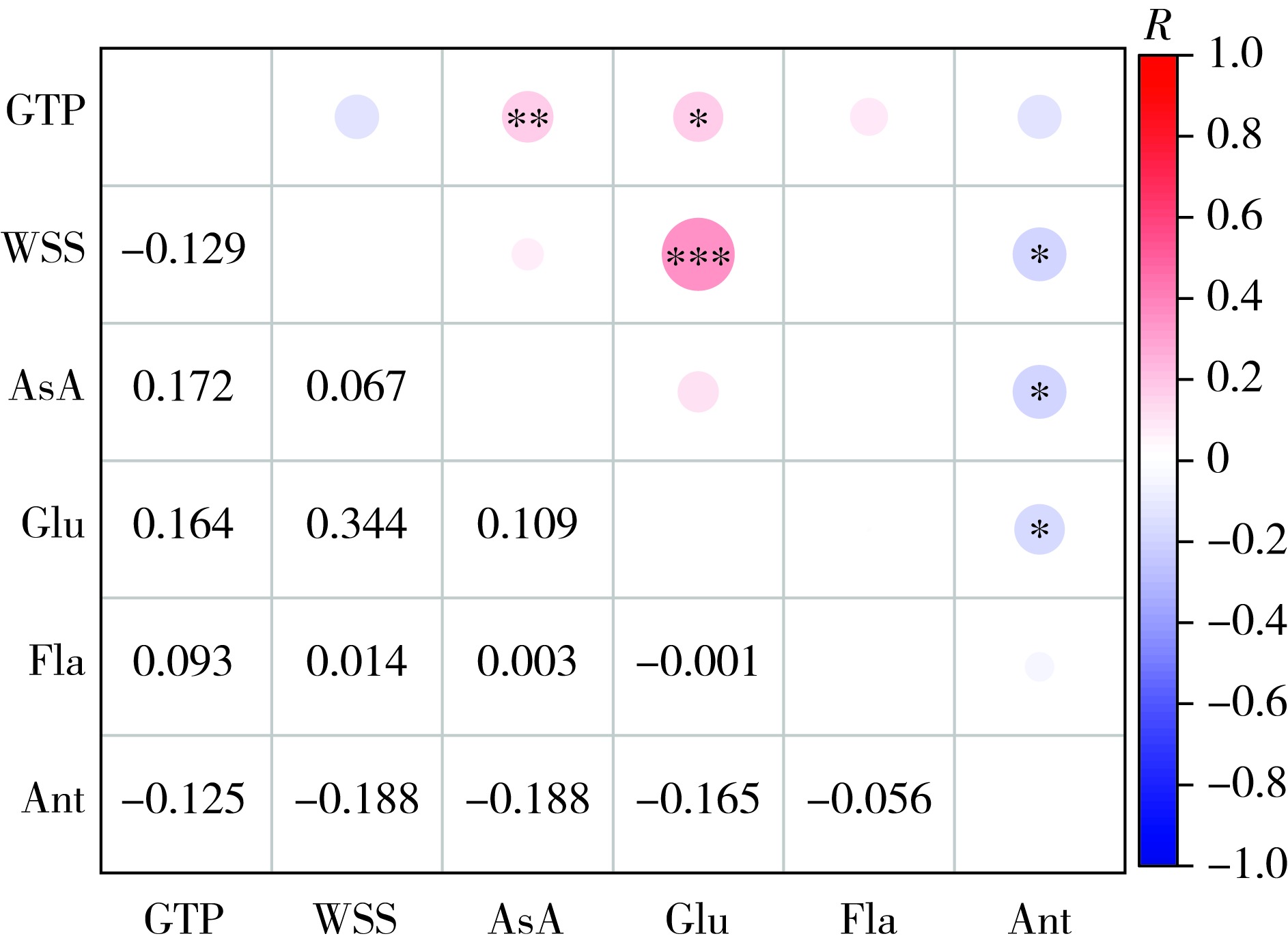
【目的】探究流苏树(Chionanthus retusus)叶片代谢物的地理变异,筛选代谢物含量优良的种源,为流苏树茶用品种选育和流苏树种质资源的保护、开发提供理论基础。【方法】以8个省份15个种源的150份流苏树单株叶片为材料,对其茶多酚、可溶性糖、谷氨酸、抗坏血酸、类黄酮和花青素含量指标进行研究,通过方差分析、变异分析、相关性分析、聚类分析、主成分分析及综合评价,筛选代谢物含量优良的流苏树种源。【结果】种源间和种源内流苏树叶片的6种代谢物指标的差异均达到极显著水平(P<0.001),流苏树种质资源性状变异丰富;代谢物相关性结果显示,流苏树叶片中谷氨酸与可溶性糖含量呈极显著正相关,茶多酚和抗坏血酸、谷氨酸的含量呈显著正相关。种源地气候因子与代谢物相关性结果显示,等温性与谷氨酸含量间、年降水量与花青素含量间存在显著的正相关关系;聚类分析将15个流苏树种源划分为3个类群,并未按照地理位置分布进行聚类分析。通过综合评价筛选出4个优良种源,即河南南召、湖北宜昌、山东临沂和河北承德种源。【结论】15个种源流苏树叶片6类代谢物在种源内与种源外均存在显著差异,筛选出的河南南召、湖北宜昌、山东临沂和河北承德4个优良种源遗传变异丰富,代谢物含量优良。
【Objective】To investigate the geographical variation of leaf metabolites in Chionanthus retusus and select provenances with superior metabolite content, this study provides a foundation for breeding tea-oriented varieties of Chionanthus retusus, as well as the conservation and utilization of its germplasm resources. 【Method】Using leaf samples from 150 individual Chionanthus retusus trees representing 15 provenances across eight provinces, this study analyzed the contents of tea polyphenols, soluble sugars, glutamig acid, ascorbic acid, flavonoids, and anthocyanins. Through variance analysis, coefficient of variation assessment, correlation analysis, cluster analysis, principal component analysis (PCA), and comprehensive evaluation, we identified provenances with superior metabolite profiles. 【Result】Both inter-provenance and intra-provenance differences reached highly significant levels (P < 0.001), indicating rich trait variation in Chionanthus retusus germplasm resources. Metabolite correlation analysis revealed a highly significant positive correlation between glutamic acid and soluble sugars, as well as significant positive correlations between tea polyphenols and ascorbic acid, and between tea polyphenols and glutamic acid. Climate-metabolite correlation analysis demonstrated significant positive relationships between isothermality (bio-climatic factor) and glutamic acid, and between annual precipitation and anthocyanins. Cluster analysis grouped the 15 Chionanthus retusus provenances into three distinct clusters, which did not align with their geographical distribution. Comprehensive evaluation finally identified four superior provenances: Nanzhao (Henan), Yichang (Hubei), Linyi (Shandong), and Chengde (Hebei). 【Conclusion】Significant differences were detected in six classes of leaf metabolites both within and among 15 Chionanthus retusus provenances. Through comprehensive evaluation, four superior provenances were identified: Nanzhao (Henan), Yichang (Hubei), Linyi (Shandong), and Chengde (Hebei).
Chionanthus retusus / germplasm resources / metabolite / comprehensive evaluation
| [1] |
李际红, 解孝满, 党成禄. 流苏树种质资源描述规范和数据标准[M]. 北京: 中国林业出版社, 2022.
|
| [2] |
曲凯, 国浩平, 王宝锐, 等. 基于SRAP分子标记的流苏树天然群体遗传多样性研究[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2020, 42(12):40-50.
|
| [3] |
樊莉丽, 党远, 樊巍, 等. 珍稀树种流苏研究进展与保护利用策略[J]. 江苏农业科学, 2016, 44(6): 20-24.
|
| [4] |
梁学忠, 吴京民, 孙大力. 河北保健代茶植物资源开发利用[J]. 林业科技开发, 1993(1):47-48.
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
胡喜兰, 姜琴, 尹福军, 等. 花果山“糯米茶” 中黄酮化合物的分离纯化及活性研究[J]. 食品科学, 2012, 33(5):106-108.
|
| [7] |
邓瑞雪, 张创峰, 刘普, 等. 流苏花黄酮类化学成分的分离鉴定[J]. 食品科学, 2014, 35(1):74-78.
|
| [8] |
北京市农业农村局. 北京延庆:珍珠泉乡流苏茶迎来首个采摘季[EB/OL]. 2020-5-28. https://nyncj.beijing.gov.cn/nyj/snxx/gqxx/10808574/.
|
| [9] |
刘梦月, 孙悦, 韦朝领, 等. 茶树功能性成分的遗传多样性分析及综合评价[J]. 植物资源与环境学报, 2023, 32(5):28-38.
|
| [10] |
戴前莉, 朱恒星, 卢敏, 等. 重庆老鹰茶种质资源调查与评价[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2022, 34(3):447-456.
|
| [11] |
郭倩文, 杜璇, 倪穗. 6种抹茶产品的主要成分比较分析[J]. 中国野生植物资源, 2019, 38(3):31-36.
|
| [12] |
刘政权, 张惠, 王会芳, 等. 不同贮藏温度下抹茶品质变化及其货架期预测[J]. 食品科学, 2020, 41(3):198-204.
|
| [13] |
孙梦月. 桑黄黄酮降尿酸作用评价及降尿酸代用茶的研制[D]. 武汉: 华中农业大学, 2023.
|
| [14] |
田野, 殷中琼, 唐茜. 紫嫣茶中花青素水提工艺及其提取物抗癌活性[J]. 安徽农业大学学报, 2019, 46(1): 1-7.
|
| [15] |
陈弯, 樊莉丽, 许笑蒙, 等. 14个类型流苏树叶片和叶柄解剖学特征的比较研究[J]. 中国农业大学学报, 2018, 23(5): 38-51.
|
| [16] |
赵丹丹, 李晓, 张鸽香. 流苏树与美国流苏形态及解剖结构研究[J]. 中国野生植物资源, 2021, 40(7): 1-6.
|
| [17] |
程佳雪, 万映伶, 巫丽华, 等. 园林树木吸收汞(Hg)的评价方法[J]. 西北林学院学报, 2020, 35(4): 249-255.
|
| [18] |
党远. 不同类型流苏光合生理及叶绿素荧光特征[D]. 郑州: 河南农业大学, 2016.
|
| [19] |
徐泽俊, 齐玉军, 邢兴华, 等. 黄淮海大豆种质农艺与品质性状分析及综合评价[J]. 植物遗传资源学报, 2022, 23(2):468-480.
|
| [20] |
周卫龙, 徐建峰, 许凌. 茶叶中茶多酚和儿茶素类含量的检测方法:GB/T 8313—2018[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2018.
|
| [21] |
邓祥, 韩伟. 酒石酸亚铁-标准曲线法检测绿茶提取物中茶多酚含量[J]. 南京工业大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 42(5):677-682.
|
| [22] |
杨若熙, 王贝, 刘桂艳. 酒石酸亚铁-标准曲线法对沙棘茶中茶多酚含量的测定[J]. 科学技术创新, 2022(23):15-18.
|
| [23] |
梁光纤, 王华. 两种分光光度法测定茶类产品中茶多酚含量的比较[J]. 化工管理, 2021(7):50-51,86.
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
侯文赫, 郭子微, 郭彩珍, 等. 欧李果实发育期原花青素组分、含量及抗氧化分析[J]. 山西农业科学, 2023, 51(1):38-44.
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
曾建伟, 张凌燕, 蔡巧燕, 等. 柱前在线衍生-HPLC法测定大鼠脑脊液中天冬氨酸和谷氨酸的含量[J]. 福建中医药, 2012, 43(6):49-50.
|
| [29] |
解孝满, 李景涛, 赵合娥, 等. 柳树无性系苗期遗传测定与选择[J]. 江苏林业科技, 2008, 35(3):6-9,14.
|
| [30] |
余青富, 王正德, 葛婉婷, 等. 不同种源香椿无性系苗期表型性状变异及其与地理-气候因子的相关性[J]. 植物资源与环境学报, 2024, 33(5):13-21.
|
| [31] |
罗晓雨, 韩爱芝, 丁杰, 等. 新疆伊犁野生杏种仁矿质元素及氨基酸含量分析[J]. 果树学报, 2024, 41(4):: 1-21.
|
| [32] |
徐嘉娟, 陈婷敬, 谢涛, 等. 山桐子天然居群果实表型多样性分析及综合评价[J]. 种子, 2021, 40(9):64-71.
|
| [33] |
王晓鸣, 邱丽娟, 景蕊莲, 等. 作物种质资源表型性状鉴定评价:现状与趋势[J]. 植物遗传资源学报, 2022, 23(1):12-20.
|
| [34] |
吴承金, 陈火云, 宋威武. 国内育成马铃薯品种资源的表型及品质性状综合评价[J]. 中国瓜菜, 2021, 34(7):43-49.
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
王治会, 彭华, 岳翠男, 等. 江西茶树资源功能成分综合评价与种质优选[J]. 河南农业科学, 2020, 49(8):54-62.
|
| [38] |
罗理勇, 曾亮, 李洪军. 重庆地区主要茶树栽培品种生化特性分析[J]. 食品科学, 2015, 36(4):119-125.
|
| [39] |
赵洋, 杨培迪, 刘振, 等. 22个茶树品种春梢生化成分分析[J]. 茶叶通讯, 2016, 43(3):19-22.
|
| [40] |
李文新, 王乐, 马燕, 等. 植物中L-谷氨酸代谢与信号转导研究进展[J]. 食品安全质量检测学报, 2023, 14(14):45-51.
|
| [41] |
张小利, 朱灵龙, 李付振, 等. 115份花生种质资源农艺与品质性状鉴评及分析[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2023, 35(9):2033-2044.
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |