 PDF(14201 KB)
PDF(14201 KB)


江苏条子泥人工修复高潮位栖息地鸻鹬类动态及影响因素
方泽, 肖梓蔚, 盛凡, 薛建辉, 杨洪燕, 郭佳, 付婷, 孙莉莉, 贾亦飞, 周延
南京林业大学学报(自然科学版) ›› 2026, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (1) : 65-73.
 PDF(14201 KB)
PDF(14201 KB)
 PDF(14201 KB)
PDF(14201 KB)
江苏条子泥人工修复高潮位栖息地鸻鹬类动态及影响因素
Shorebird dynamics and its influencing factors in artificially restored high-tide roosts: a case study of Tiaozini wetland, Jiangsu
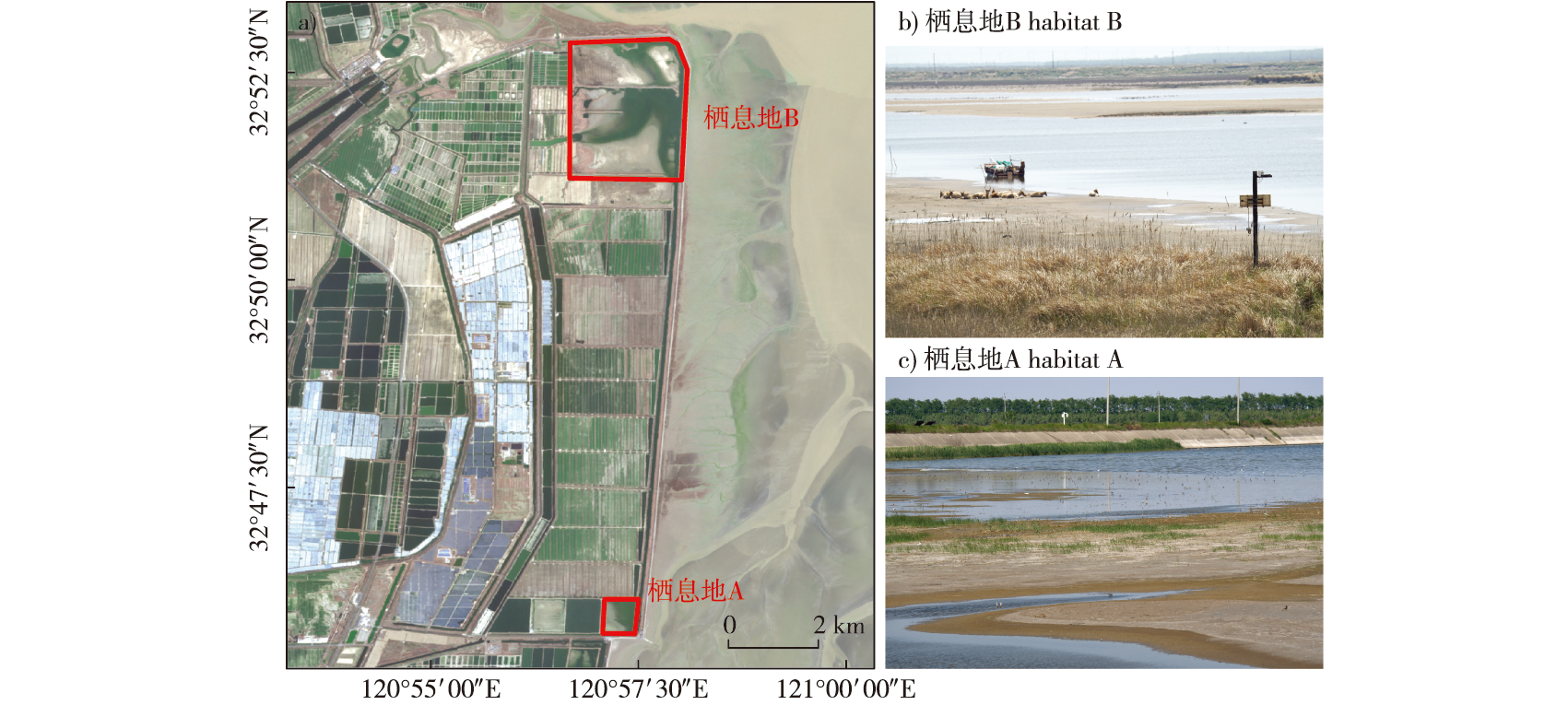
【目的】 黄海生态区滨海湿地围垦导致适宜高潮位栖息地匮乏,已成为制约鸻鹬类水鸟保护的关键瓶颈。探究鸻鹬类对高潮位栖息地的利用方式及其栖息地选择的环境影响因素,有助于指导黄海生态区高潮位栖息地修复与优化管理,进而提升滨海湿地生物多样性保护成效。【方法】于2021—2023年,在江苏条子泥湿地两处人工修复高潮位栖息地开展鸻鹬类水鸟群落调查。采用对齐秩变换方差分析(ARTNOVA)比较不同栖息地间差异,并运用广义加性模型(GAM)分析鸻鹬类群落数据(物种丰富度及数量)与环境变量(地点、年份、日期、潮汐高度及景观指标)的关系,通过筛选最优模型揭示影响其栖息地选择的关键因素。【结果】① 3年间共记录鸻鹬类45种,占东亚—澳大利西亚迁飞通道鸻鹬类物种总数的68%,其中国家一级保护动物2种,二级保护动物7种;26种鸻鹬类的数量超过其迁飞通道种群数量的1%。② 条子泥湿地2023年鸻鹬类数量显著增加,其迁徙高峰期为春季5月与秋季8月,且秋季的物种丰富度高于春季。③ 鸻鹬类物种丰富度受日期与水域景观形状指数显著影响;物种数量则显著受潮汐高度、日期、泥滩斑块平均形状指数及水域分离指数的影响。【结论】对高潮位栖息地的修复与管理应重点关注鸻鹬类的迁徙物候特征。形状简单的泥滩斑块与破碎化程度较高的水域能吸引更多数量的鸻鹬类聚集,而形状简单的水域斑块则有助于提升鸻鹬类物种丰富度。同一高潮位栖息地内,应根据当地的具体条件,因地制宜地制定修复与管理策略,以保障栖息地的有效利用。在黄海生态区及整个迁飞区范围内,开展针对性的高潮位栖息地修复与管理,可显著提升鸻鹬类保护成效。
【Objective】 The reclamation of coastal wetlands in the Yellow Sea Ecoregion has led to a scarcity of suitable high-tide roosts (HTR5), which has become a key bottleneck restricting the conservation of shorebirds. Investigating shorebirds’ utilization patterns of high-tide roosts and the environmental factors influencing their habitat selection can inform the restoration and optimized management of high-tide roosts in the Yellow Sea Ecoregion, thereby enhancing the efficacy of biodiversity conservation in coastal wetlands. 【Method】From 2021 to 2023, shorebird community surveys have been conducted in two artificially restored high-tide roosts in the Tiaozini wetland, Jiangsu Province. Aligened ranks transformation analysis of variance (ARTNOVA) was employed to compare differences between two habitats, while generalized additive models (GAMs) were used to examine the relationships between shorebird community metrics (species richness and abundance) and environmental variables, including site, year, date, tide height, and landscape metrics. Optimal models were selected to identify the key factors influencing habitat selection. 【Result】(1) A total of 45 shorebird species were documented during the three-year study period, accounting for 68% of the total shorebird species in the East Asia-Australasian Flyway (EAAF). This included two nationally Grade Ⅰ protected species and seven nationally Grade Ⅱ protected species. The populations of 26 shorebird species exceeded 1% of their respective flyway populations. (2) In 2023, the abundance of shorebirds in the Tiaozini wetland significantly increased compared to previous years. Shorebird migration peaked in May (spring) and August (autumn), with species richness being higher in autumn than in spring. (3) Shorebird species richness was significantly influenced by date and landscape shape index of water. Their abundance was significantly affected by tide height, date, mean shape index of mudflats, and splitting index of water areas. 【Conclusion】The restoration and management of high-tide roosts should focus on the migratory phenology of shorebirds. Simple-shaped mudflat patches and highly fragmented water areas can attract higher shorebirds abundances, while simple-shaped water areas can enhance shorebird species richness. Within the same high-tide roosts, restoration and management strategies should be context-specific to ensure effective habitat utilization. Targeted restoration and management of high-tide roosts in the Yellow Sea Ecoregion and across the migratory flyway can notably enhance the conservation efficacy for shorebirds.
滨海湿地 / 鸻鹬类 / 高潮位栖息地 / 栖息地管理 / 景观指标 / 广义加性模型 / 江苏条子泥湿地
coastal wetland / shorebirds / high-tide roost / habitat management / landscape metric / generalized additive model (GAM) / Tiaozini wetland of Jiangsu
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
陈克林, 杨秀芝, 吕咏. 鸻鹬类鸟东亚-澳大利西亚迁飞路线上的重要驿站:黄渤海湿地[J]. 湿地科学, 2015, 13(1):1-6.
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
俞学志, 季耀波, 王炼, 等. 江苏条子泥垦区景观格局变化与驱动机理研究[J]. 南京师大学报(自然科学版), 2022, 45(1):55-63.
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
郑光美. 中国鸟类分类与分布名录[M]. 4版. 北京: 科学出版社, 2023.
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
王玉龙, 华育平. 禽流感病毒在野鸟种群中的分布特点[J]. 林业科学, 2009, 45(3):128-133.
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |