 PDF(1989 KB)
PDF(1989 KB)


3种松材线虫病预防注干剂在马尾松树体内残留动态及防病效果
孙国宏, 张婉君, 叶建仁, 程浩, 胡贤秀
南京林业大学学报(自然科学版) ›› 2025, Vol. 49 ›› Issue (6) : 64-72.
 PDF(1989 KB)
PDF(1989 KB)
 PDF(1989 KB)
PDF(1989 KB)
3种松材线虫病预防注干剂在马尾松树体内残留动态及防病效果
Residue dynamics and disease prevention efficacy of three pine wilt disease preventive trunk-injection agents in masson pine trees
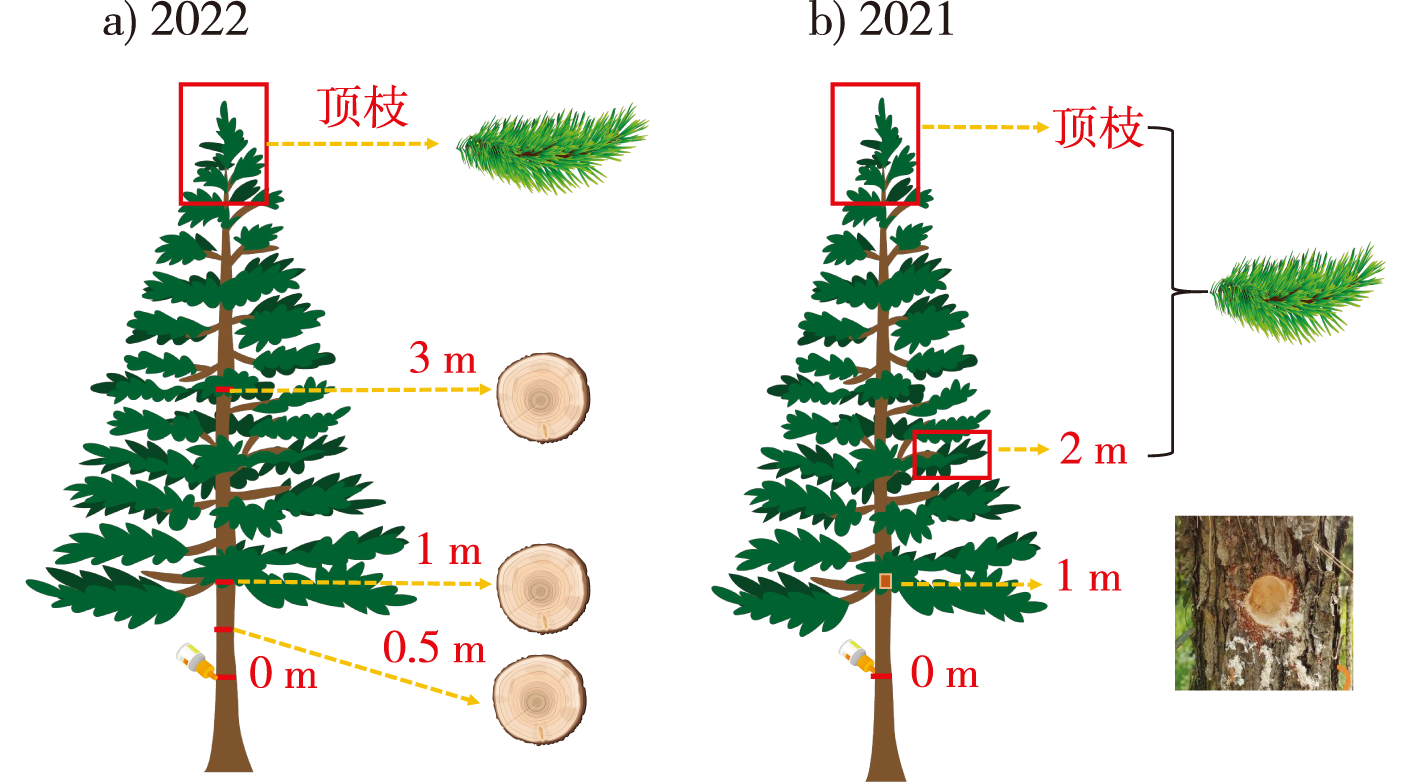
【目的】探究不同注干剂的残存期和持效期,系统评估5%(质量分数,下同)甲维盐可溶性液剂、5%阿维菌素乳油及1%甲维盐-9%吡虫啉可溶性液剂在松树体内的输导分布、残留动态,为松材线虫(Bursaphelenchus xylophilus)病的科学防控提供技术支撑。【方法】以马尾松(Pinus massoniana)为对象,通过在松树不同部位分层取样,结合液相色谱-质谱法(LC-MS),定量分析药剂在树体内的输导分布与残留动态;在注干后对松树进行松材线虫接种,并设计二次接种以模拟线虫持续侵染,观察并统计松树的发病情况,评估药剂的持续防病效果。【结果】3种注干药剂注干后,都可以输导至马尾松的各个部位,其中主干最多,枝梢略少。在树体内残留总体上可以维持3 a左右,但还是以注药第1年残留最高,第2年次之,第3年进一步衰减。相比之下,5%甲维盐的输导效率和残留量最高,胸径为12 cm的马尾松注药3 a后离注干点1 m处残留含量(质量分数,下同)仍达24.609 mg/kg,3 a后2次接种防治效果仍然可达37.50%;5%阿维菌素因亲脂性强、降解快,3 a后顶枝残留量未检出,2次接种防治效果仅为12.50%;1%甲维盐-9%吡虫啉抑制线虫能力不足,发病最早。同种药剂高剂量(60 mL)注药可以有效提升残留量,胸径为15 cm的马尾松注射60 mL 5%甲维盐1 a后离注干点1 m处的残留含量(质量分数,下同)达33.900 mg/kg,远高于注射30 mL 5%甲维盐的2.405 mg/kg。在注射方式上,微孔注射与自流式在注射1和2 a时并不存在明显差异,均对残留分布影响较小。【结论】3种注干药剂在注干后,可以输导至树体的各个部位。相比之下,5%甲维盐输导效率和残留量更高,是长效防控松材线虫病的优选药剂。3种药剂在注干后均可以较长时间预防松材线虫病,注干1或2 a后的残留量高且防治效果良好,注干3 a后防治效果明显下降。
【Objective】This study aims to investigate the residual efficacy and duration of various trunk-injected agents on masson pine (Pinus massoniana). Assess transport distribution, residue dynamics, and control effects on pine wilt disease. Evaluate 5% (mass fraction) emamectin benzoate soluble liquid, 5% abamectin emulsion, and 1% emamectin benzoate-9% imidacloprid soluble liquid agents.【Method】Sampled at different parts of the pine tree in layers. Analyzed residue dynamics in the tree using liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS). Quantitatively analyzed the translocation, distribution, and residue dynamics of the chemical within pine trees. Following trunk injection, inoculate the pines and design a secondary inoculation to simulate continuous nematode infestation; continuously monitor and record disease development to evaluate the chemical's long-term protective efficacy.【Result】Three trunk-injected agents effectively reached various parts of Pinus massoniana, with the main trunk showing the highest residue levels and branches less so. Residues generally lasted about three years, peaking in the first year, then declining. The 5% emamectin benzoate had the best transport and residue, maintaining a 24.609 mg/kg residue level after three years, and remained at a 37.50% control efficacy after a second inoculation. Abamectin showed rapid degradation, with no residue detected in top branches after three years, and only 12.50% efficacy after a second inoculation. The 1% emamectin benzoate-9% imidacloprid had lower nematode control, resulting in the earliest onset. Higher doses effectively increased residue levels, with 60 mL 5% emamectin benzoate reaching 33.900 mg/kg after one year, much higher than 30 mL 5% emamectin benzoate's 2.405 mg/kg. Injection methods had little effect on residue distribution at 1 and 2 a.【Conclusion】Three trunk-injected agents can be transported to all parts of the tree after injection. Compared with the other two, 5% emamectin benzoate has higher transport efficiency and residual amount, making it the preferred agent for long-term prevention and control of pine wilt disease. All three agents can effectively prevent pine wilt disease for a relatively long time after injection. The residual amount and control effect are still significant one or two years after injection, but the control effect decreases significantly three years after injection.
松材线虫 / 马尾松 / 树干注射 / 药剂残留 / 防病效果 / 杀线剂
Bursaphelenchus xylophilus / Pinus massoniana / trunk injection / pesticide residue / disease control efficacy / nematicide
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
孙永春. 南京中山陵发现松材线虫[J]. 江苏林业科技, 1982, 9(4):47-27.
|
| [3] |
Pine wilt disease is a major plant epidemic that has significantly impaired the ecological safety of pine wood, the national economy, and peoples’ livelihood. It is challenging to accurately assess the loss from pine wilt disease through academic research or field work. Based on the 342,000 subcompartments of epidemic data of pine wilt disease in China in 2020, this study builds a refined assessment indicator system and measurement model for economic loss from disasters at the subcompartment scale and assesses direct economic loss and ecological service value loss. The results show that through direct economic loss and ecological service value loss, China lost USD 7.40 billion in 2020, including a direct economic loss of USD 1.11 billion and ecological service value loss of USD 6.29 billion. Of the direct economic loss, the forest material resource loss and protection expense reached USD 0.17 billion and USD 0.94 billion, respectively; of the ecological system service losses, regulation service, supporting service, and cultural service losses reached USD 4.58 billion, USD 1.35 billion, and USD 0.36 billion. Spatial distribution analysis showed that the loss declined from southeast to northwest, with Shandong, Zhejiang, and Jiangxi suffering the greatest losses. Based on the subcompartment scale, this study employs a more refined assessment indicator system and measurement model to provide accurate real-world assessment results.
|
| [4] |
王钱晴, 赵丽媛, 张建, 等. 物理方法在松材线虫病疫木处理中的应用[J]. 世界林业研究, 2024, 37(1):65-70.
|
| [5] |
叶建仁. 松材线虫病在中国的流行现状、防治技术与对策分析[J]. 林业科学, 2019, 55(9):1-10.
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
来燕学, 何月秋, 池树友, 等. 高效松材线虫病预防注射药剂配制与林间药效研究[J]. 江西农业大学学报, 2016, 38(5):871-878.
|
| [8] |
王勇军, 唐光辉, 陈祖海, 等. 树干注药防治松材线虫病研究进展[J]. 中国森林病虫, 2022, 41(3):59-63.
|
| [9] |
杨帆. 甲氨基阿维菌素苯甲酸盐毒杀松材线虫机理[D]. 哈尔滨: 东北林业大学, 2022.
|
| [10] |
王广成, 张忠明, 高立明, 等. 阿维菌素的作用机理及其应用现状[J]. 植物医生, 2006(1):4-5.
|
| [11] |
徐颂明, 刘元靖, 潘洪峰, 等. 2种甲维盐剂型在松树中的溶脂性、吸收及其对松材线虫病的防治效果[J]. 世界农药, 2024, 46(10):51-55.
|
| [12] |
徐勇, 陈虹宇, 徐正梅, 等. 2%甲维盐乳油对松材线虫病的防治效果测定[J]. 林业科学研究, 2024, 37(5):116-123.
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
叶建仁, 吴小芹. 松材线虫病研究进展[J]. 中国森林病虫, 2022, 41(3):1-10.
|
| [19] |
李留彬, 方文, 马玲, 等. 间伐措施对松材线虫病疫区马尾松林土壤微生物多样性的影响[J]. 森林工程, 2024, 40(5):82-93.
|
| [20] |
陆琦, 胡丹丹, 张瑞花, 等. 句容市近60 a气候变化特征的统计分析[J]. 农业灾害研究, 2021, 11(3):68-70.
|
| [21] |
朱丽华, 林丽, 蒋鹏, 等. 不同致病力松材线虫的繁殖能力和移动能力比较[J]. 东北林业大学学报, 2017, 45(12):76-79.
|
| [22] |
国家质量监督检验检疫总局. 水果和蔬菜中450种农药及相关化学品残留量的测定液相色谱-串联质谱法:GB/T 20769-2008[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2009.
General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People's Republic of China. Determination of 450 pesticides and related chemicals residues in fruits and vegetables-LC-MS-MS method:GB/T 20769-2008[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2009.
|
| [23] |
谈家金, 杨荣铮, 吴慧平. 不同地理种群的松材线虫对马尾松的致病力差异[J]. 植物检疫, 2000, 14(6):324-325.
|
| [24] |
王圣印, 周仙红, 张安盛, 等. 甲氨基阿维菌素苯甲酸盐研究进展[J]. 江西农业学报, 2012, 24(12):123-126.
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
姜壮, 宋林松, 李云帆, 等. 甲氨基阿维菌素苯甲酸盐在马尾松树体内的代谢产物研究[J]. 农药学学报, 2025, 27(1):107-115.
|
| [27] |
黄素芳, 王振亮, 李开森, 等. 树干注药后阿维菌素在枣树体内的传导分布及消长动态[J]. 中国森林病虫, 2019, 38(3):15-19,24.
|
| [28] |
尹华阳, 董广平. 两种注干药剂防治松材线虫病效果研究[J]. 安徽林业科技, 2022, 48(6):21-24,31.
|
| [29] |
肖婷, 陈小龙, 许媛, 等. 防控桃蚜注干药剂筛选及残留分析[J]. 江苏农业科学, 2024, 52(8):116-120.
|
| [30] |
向帆, 刘玉琢, 叶建仁, 等. 注干施用3种药剂防治松材线虫病研究[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2025, 49(6):95-101.
|
| [31] |
封云涛, 徐宝云, 吴青君, 等. 杀虫剂分子靶标烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体研究进展[J]. 农药学学报, 2009, 11(2):149-158.
|
| [32] |
张娇, 叶建仁, 陈婷婷, 等. 松材线虫高效复配制剂的药效分析[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2025, 49(3):73-80.
|
| [33] |
王君, 罗治建, 吕晓君, 等. 不同剂量免疫激活剂防治松材线虫病试验研究[J]. 湖北林业科技, 2023, 52(3):38-42.
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |