 PDF(2355 KB)
PDF(2355 KB)


大青杨PuZFP103基因的序列特征及逆境胁迫的表达分析
张馨, 马苗苗, 吕婉秋, LEE Joobin, 杨静莉
南京林业大学学报(自然科学版) ›› 2021, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (1) : 36-44.
 PDF(2355 KB)
PDF(2355 KB)
 PDF(2355 KB)
PDF(2355 KB)
大青杨PuZFP103基因的序列特征及逆境胁迫的表达分析

Sequence characteristics and expression pattern analyses of PuZFP103 gene under abiotic stress in Populus ussuriensis

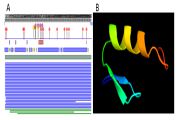
【目的】通过研究大青杨(Populus ussuriensis)PuZFP103基因的序列特征及其在不同组织部位、激素处理与胁迫应答中的表达特性,为揭示PuZFP103在大青杨生长发育中的功能提供依据。【方法】利用各种生物信息学方法对PuZFP103基因进行分析,采用实时荧光定量 PCR(real time quantitative polymerase chain reaction, RT-qpCR)技术分析PuZFP103基因在不同组织、激素处理与胁迫应答中的表达模式,并用基因枪轰击法进行亚细胞定位分析。【结果】生物信息学分析发现,PuZFP103 CDS序列全长504 bp,编码168个氨基酸。分析得出PuZFP103蛋白含有ZnF-C2H2结构域,其二级结构中α螺旋、无规则卷曲和β-折叠分别占24%、84%和1%。进化树构建图显示,其与同属毛果杨、胡杨、毛白杨及番木瓜聚类到一起,亲缘关系最近。RT-qPCR分析结果显示,NaCl、脱落酸(abscisic acid, ABA)和PEG 6000胁迫处理后PuZFP103基因在大青杨叶和根中的表达量在大多数时间内相对于未处理都有所提高。另外,PuZFP103基因定位于细胞核中。【结论】PuZFP103基因在NaCl、ABA和PEG 6000胁迫处理后呈正调控的应答模式,可能参与了大青杨对渗透胁迫的代谢途径或信号传导,属于逆境胁迫下的调控因子。本研究初步证明大青杨PuZFP103基因与胁迫响应相关,但是关于其信号传导与调控机制需进一步研究。
【Objective】 This study aimed to investigate the function of the PuZFP103 gene in the growth and development process of Populus ussuriensis Kom. We analyzed the sequence characteristics, expression patterns in different tissues, and the PuZFP103 gene response to hormones and abiotic stresses. 【Method】 The sequence characteristics of the PuZFP103 gene were analyzed using bioinformatics methods. The expression characteristics of the PuZFP103 gene in different tissues, as well as its response to hormones and abiotic stresses, were analyzed by real-time quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR). In addition, the subcellular localization of the PuZFP103 gene was detected using particle bombardment. 【Result】 The bioinformatic analysis showed that the PuZFP103 gene had 505 bp coding sequences, which encoded a polypeptide of 168 amino acids. The conserved domain analysis revealed that there was a conserved ZnF-C2H2 domain in the PuZFP103 protein. The secondary structure analysis of PuZFP103 showed that the percentage of amino acids of α-helix, random coil, and β-sheet were 24%, 84% and 1%, respectively. The evolutionary tree map showed that it was closely related to the common P. ussuriensis, P. euphratica, P. tomentosa, and Carica papaya. The results of RT-qPCR analysis demonstrated that the expression level of PuZFP103 was increased after NaCl, ABA and PEG 6000 treatment. The subcellular localization assay showed that PuZFP103 was a nuclear protein. 【Conclusion】 The results indicate that the gene is positively regulated by NaCl, ABA and PEG 6000. The PuZFP103 gene may be involved in the metabolic and signaling pathways of osmotic and salt stress and, thus, is a regulatory factor under stress. This study provides preliminarily evidence that the PuZFP103 gene is associated with stress response, but further studies on its signal transduction and regulation mechanism are needed. This is the first study to perform bioinformatics analysis of the PuZFP103 gene in P. ussuriensis.
大青杨 / PuZFP103基因 / 逆境胁迫 / 生物信息学 / RT-qPCR
Populus ussuriensis / PuZFP103 gene / abiotic stress / bioinformation / RT-qPCR
| [1] |
王含. 毛果杨C2H2型锌指蛋白基因PtZFP103功能研究[D]. 哈尔滨:东北林业大学, 2017.
|
| [2] |
张佳, 刘俊芳, 赵婷婷, 等. 植物C2H2型锌指蛋白研究进展[J]. 分子植物种, 2018,16(2), 427-433.
|
| [3] |
Abiotic stresses, such as drought and salinity, lead to crop growth damage and a decrease in crop yields. Stomata control CO(2) uptake and optimize water use efficiency, thereby playing crucial roles in abiotic stress tolerance. Hydrogen peroxide (H(2)O(2)) is an important signal molecule that induces stomatal closure. However, the molecular pathway that regulates the H(2)O(2) level in guard cells remains largely unknown. Here, we clone and characterize DST (drought and salt tolerance)-a previously unknown zinc finger transcription factor that negatively regulates stomatal closure by direct modulation of genes related to H(2)O(2) homeostasis-and identify a novel pathway for the signal transduction of DST-mediated H(2)O(2)-induced stomatal closure. Loss of DST function increases stomatal closure and reduces stomatal density, consequently resulting in enhanced drought and salt tolerance in rice. These findings provide an interesting insight into the mechanism of stomata-regulated abiotic stress tolerance, and an important genetic engineering approach for improving abiotic stress tolerance in crops.
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
安琳君, 栾嘉豫, 任丽, 等. 白桦BpTCP8基因生物信息学及表达特性分析[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2019,43(5):67-73.
|
| [6] |
付国勇, 张永永, 刘新春, 等. 青稞幼苗期叶片中SBEⅡa基因的克隆及其表达分析[J]. 麦类作物学报, 2019,39(6):645-652. DOI: 10.7606/j.issn.1009-1041.2019.06.03.
|
| [7] |
吕金东, 刘灿, 屈亦潇, 等. 大豆GmGW2基因的生物信息学分析[J]. 大豆科学, 2019,38(3):379-384.
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
Receptor-like protein kinases (RLKs) are a large group of transmembrane proteins playing critical roles in cell-cell and cell-environment communications. Based on extracellular domain structures, RLKs were classified into more than 21 subfamilies, among which leucine-rich repeat RLKs (LRR-RLKs) belong to the largest subfamily in plants such as Arabidopsis and rice. In Arabidopsis, there are approximately 223 LRR-RLKs, but only about 60 of which have been functionally described to date. To systematically investigate the roles of LRR-RLKs in regulating plant growth, development, and stress adaptations, we generated promoter::GUS transgenic plants for all 223 LRR-RLK genes in Arabidopsis and analyzed their detailed expression patterns at various developmental stages. The results provide valuable resources for functionally elucidating this large and essential signaling protein subfamily.
|
| [10] |
齐帆, 范兴, 陈义, 等. 基于RNA-seq数据发掘响应干旱的谷子C2H2型锌指蛋白基因[J]. 江苏农业科学, 2019,47(2):41-45.
|
| [11] |
Zinc finger proteins utilize zinc for structural purposes: zinc binds to a combination of cysteine and histidine ligands in a tetrahedral coordination geometry facilitating protein folding and function. While much is known about the classical zinc finger proteins, which utilize a Cys(2)His(2) ligand set to coordinate zinc and fold into an anti-parallel beta sheet/alpha helical fold, there are thirteen other families of 'non-classical' zinc finger proteins for which relationships between metal coordination and protein structure/function are less defined. This 'Perspective' article focuses on two classes of these non-classical zinc finger proteins: Cys(3)His type zinc finger proteins and Cys(2)His(2)Cys type zinc finger proteins. These proteins bind zinc in a tetrahedral geometry, like the classical zinc finger proteins, yet they adopt completely different folds and target different oligonucleotides. Our current understanding of the relationships between ligand set, metal ion, fold and function for these non-classical zinc fingers is discussed.
|
| [12] |
狄建军, 孙佳欣, 杨智慧, 等. 蓖麻PLA2α基因启动子的克隆及生物信息学分析[J]. 分子植物育种, 2019,17(15):4961-4966.
|
| [13] |
The Arabidopsis trichome is a model system for studying cell development, cell differentiation and the cell cycle in plants. Our previous studies have shown that the ZINC FINGER PROTEIN5 (ZFP5) controls shoot maturation and epidermal cell fate through GA signaling in Arabidopsis. We have identified a novel C2H2 zinc finger protein ZINC FINGER PROTEIN 6 (ZFP6) which plays a key role in regulating trichome development in Arabidopsis. Overexpression of ZFP6 results in ectopic trichomes on carpels and other inflorescence organs. Gain- and loss-of-function analyses have shown that the zfp6 mutant exhibits a reduced number of trichomes in sepals of flowers, cauline leaves, lateral branch and main inflorescence stems in comparison to wild-type plants. Molecular and genetic analyses suggest that ZFP6 functions upstream of GIS, GIS2, ZFP8, ZFP5 and key trichome initiation regulators GL1 and GL3.We reveal that ZFP6 and ZFP5 mediate the regulation of trichome initiation by integrating GA and cytokinin signaling in Arabidopsis. These findings provide new insights into the molecular mechanism of plant hormone control of epidermal trichome patterning through C2H2 transcriptional factors.
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
Plant Q-type C2H2 zinc finger transcription factors play an important role in plant tolerance to various environmental stresses such as drought, cold, osmotic stress, wounding and mechanical loading. To carry out an improved analysis of the specific role of each member of this subfamily in response to mechanical loading in poplar, we identified 16 two-fingered Q-type C2H2-predicted proteins from the poplar Phytozome database and compared their phylogenetic relationships with 152 two-fingered Q-type C2H2 protein sequences belonging to more than 50 species isolated from the NR protein database of NCB1. Phylogenetic analyses of these Q-type C2H2 proteins sequences classified them into two groups G1 and G2, and conserved motif distributions of interest were established. These two groups differed essentially in their signatures at the C-terminus of their two QALGGH DNA-binding domains. Two additional conserved motifs, MALEAL and LVDCHY, were found only in sequences from Group G1 or from Group G2, respectively. Functional significance of these phylogenetic divergences was assessed by studying transcript accumulation of six poplar C2H2 Q-type genes in responses to abiotic stresses; but no group specificity was found in any organ. Further expression analyses focused on PtaZFP1 and PtaZFP2, the two genes strongly induced by mechanical loading in poplars. The results revealed that these two genes were regulated by several signalling molecules including hydrogen peroxide and the phytohormone jasmonate.
|
| [16] |
张佳. 番茄C2H2型锌指蛋白生物信息学分析及抗逆相关基因鉴定[D]. 哈尔滨:东北农业大学, 2018.
|
| [17] |
Seed germination is controlled by environmental signals, including light and endogenous phytohormones. Abscisic acid (ABA) inhibits, whereas gibberellin promotes, germination and early seedling development, respectively. Here, we report that ZFP3, a nuclear C2H2 zinc finger protein, acts as a negative regulator of ABA suppression of seed germination in Arabidopsis (Arabidopsis thaliana). Accordingly, regulated overexpression of ZFP3 and the closely related ZFP1, ZFP4, ZFP6, and ZFP7 zinc finger factors confers ABA insensitivity to seed germination, while the zfp3 zfp4 double mutant displays enhanced ABA susceptibility. Reduced expression of several ABA-induced genes, such as RESPONSIVE TO ABSCISIC ACID18 and transcription factor ABSCISIC ACID-INSENSITIVE4 (ABI4), in ZFP3 overexpression seedlings suggests that ZFP3 negatively regulates ABA signaling. Analysis of ZFP3 overexpression plants revealed multiple phenotypic alterations, such as semidwarf growth habit, defects in fertility, and enhanced sensitivity of hypocotyl elongation to red but not to far-red or blue light. Analysis of genetic interactions with phytochrome and abi mutants indicates that ZFP3 enhances red light signaling by photoreceptors other than phytochrome A and additively increases ABA insensitivity conferred by the abi2, abi4, and abi5 mutations. These data support the conclusion that ZFP3 and the related ZFP subfamily of zinc finger factors regulate light and ABA responses during germination and early seedling development.
|
| [18] |
Abscisic acid (ABA) is a phytohormone that positively regulates seed dormancy and stress tolerance. PYL/RCARs were identified an intracellular ABA receptors regulating ABA-dependent gene expression in Arabidopsis thaliana. However, their function in monocot species has not been characterized yet. Herein, it is demonstrated that PYL/RCAR orthologues in Oryza sativa function as a positive regulator of the ABA signal transduction pathway. Transgenic rice plants expressing OsPYL/RCAR5, a PYL/RCAR orthologue of rice, were found to be hypersensitive to ABA during seed germination and early seedling growth. A rice ABA signalling unit composed of OsPYL/RCAR5, OsPP2C30, SAPK2, and OREB1 for ABA-dependent gene regulation was further identified, via interaction assays and a transient gene expression assay. Thus, a core signalling unit for ABA-responsive gene expression modulating seed germination and early seedling growth in rice has been unravelled. This study provides substantial contributions toward understanding the ABA signal transduction pathway in rice.
|
| [19] |
The Orange (Or) gene is responsible for the accumulation of carotenoids in plants. We isolated the Or gene (IbOr) from storage roots of orange-fleshed sweetpotato (Ipomoea batatas L. Lam. cv. Sinhwangmi), and analyzed its function in transgenic sweetpotato calli. The IbOr gene has an open reading frame in the 942 bp cDNA, which encodes a 313-amino acid protein containing a cysteine-rich zinc finger domain. IbOr was strongly expressed in storage roots of orange-fleshed sweetpotato cultivars; it also was expressed in leaves, stems, and roots of cultivars with alternatively colored storage roots. IbOr transcription increased in response to abiotic stress, with gene expression reaching maximum at 2 h after treatment. Two different overexpression vectors of IbOr (IbOr-Wt and IbOr-Ins, which contained seven extra amino acids) were transformed into calli of white-fleshed sweetpotato [cv. Yulmi (Ym)] using Agrobacterium. The transgenic calli were easily selected because they developed a fine orange color. The expression levels of the IbOr transgene and genes involved in carotenoid biosynthesis in IbOr-Wt and IbOr-Ins transgenic calli were similar, and both transformants displayed higher expression levels than those in Ym calli. The contents of beta-carotene, lutein, and total carotenoids in IbOr-Ins transgenic lines were approximately 10, 6, and 14 times higher than those in Ym calli, respectively. The transgenic IbOr calli exhibited increased antioxidant activity and increased tolerance to salt stress. Our work shows that the IbOr gene may be useful for the biotechnological development of transgenic sweetpotato plants that accumulate increased carotenoid contents on marginal agricultural lands.
|
| [20] |
Photoinhibition reduces photosynthetic productivity; however, it is difficult to quantify accurately in complex canopies partly because of a lack of high-resolution structural data on plant canopy architecture, which determines complex fluctuations of light in space and time. Here, we evaluate the effects of photoinhibition on long-term carbon gain (over 1 d) in three different wheat (Triticum aestivum) lines, which are architecturally diverse. We use a unique method for accurate digital three-dimensional reconstruction of canopies growing in the field. The reconstruction method captures unique architectural differences between lines, such as leaf angle, curvature, and leaf density, thus providing a sensitive method of evaluating the productivity of actual canopy structures that previously were difficult or impossible to obtain. We show that complex data on light distribution can be automatically obtained without conventional manual measurements. We use a mathematical model of photosynthesis parameterized by field data consisting of chlorophyll fluorescence, light response curves of carbon dioxide assimilation, and manual confirmation of canopy architecture and light attenuation. Model simulations show that photoinhibition alone can result in substantial reduction in carbon gain, but this is highly dependent on exact canopy architecture and the diurnal dynamics of photoinhibition. The use of such highly realistic canopy reconstructions also allows us to conclude that even a moderate change in leaf angle in upper layers of the wheat canopy led to a large increase in the number of leaves in a severely light-limited state.
|
| [21] |
The seed is an important organ of higher plants regarding plant survival and species dispersion. The transition between seed dormancy and germination represents a critical stage in the plant life cycle and it is an important ecological and commercial trait. A dynamic balance of synthesis and catabolism of two antagonistic hormones, abscisic acid (ABA) and giberellins (GAs), controls the equilibrium between seed dormancy and germination. Embryonic ABA plays a central role in induction and maintenance of seed dormancy, and also inhibits the transition from embryonic to germination growth. Therefore, the ABA metabolism must be highly regulated at both temporal and spatial levels during phase of dessication tolerance. On the other hand, the ABA levels do not depend exclusively on the seeds because sometimes it becomes a strong sink and imports it from the roots and rhizosphere through the xylem and/or phloem. All theses events are discussed in depth here. Likewise, the role of some recently characterized genes belonging to seeds of woody species and related to ABA signaling, are also included. Finally, although four possible ABA receptors have been reported, not much is known about how they mediate ABA signalling transduction. However, new publications seem to shown that almost all these receptors lack several properties to consider them as such.
|
| [22] |
李科, 何炎森, 陈晓静. 多花水仙HMGS基因的克隆[J]. 福建农林大学学报(自然科学版), 2014,43(3):289-294.
|
| [23] |
The genetic improvement of drought resistance is essential for stable and adequate crop production in drought-prone areas. Here we demonstrate that alteration of root system architecture improves drought avoidance through the cloning and characterization of DEEPER ROOTING 1 (DRO1), a rice quantitative trait locus controlling root growth angle. DRO1 is negatively regulated by auxin and is involved in cell elongation in the root tip that causes asymmetric root growth and downward bending of the root in response to gravity. Higher expression of DRO1 increases the root growth angle, whereby roots grow in a more downward direction. Introducing DRO1 into a shallow-rooting rice cultivar by backcrossing enabled the resulting line to avoid drought by increasing deep rooting, which maintained high yield performance under drought conditions relative to the recipient cultivar. Our experiments suggest that control of root system architecture will contribute to drought avoidance in crops.
|
| [24] |
MAIN CONCLUSION: IbZFP1, encoding a Cys 2/His 2 zinc finger protein gene from sweetpotato, enhances salt and drought tolerance in transgenic Arabidopsis by regulating ABA signaling pathway, proline biosynthesis, stress responses and ROS scavenging. In plants, Cys2/His2 zinc finger proteins play important roles in regulating the growth and development or responses to abiotic stresses. In this study, a novel Cys2/His2 zinc finger protein gene, named IbZFP1, was isolated from drought-tolerant sweetpotato [Ipomoea batatas (L.) Lam.] line Xu55-2. Subcellular localization analysis in onion epidermal cells indicated that IbZFP1 was localized to the nucleus. Expression analysis in yeast showed that the full length of IbZFP1 exhibited transcriptional activation. Expression of IbZFP1 was induced by NaCl, polyethylene glycol and abscisic acid (ABA). Overexpression of IbZFP1 significantly enhanced salt and drought tolerance in transgenic Arabidopsis plants. Real-time quantitative PCR (qRT-PCR) analysis showed that overexpression of IbZFP1 up-regulated the genes involved in ABA signaling pathway, proline biosynthesis, stress responses, and ROS scavenging under salt and drought stresses. Meanwhile, Western blot and enzymatic analyses showed that the activities of 9-cis-epoxycarotenoid dioxygenase, pyrroline-5-carboxylate synthase, superoxide dismutase, catalase, ascorbate peroxidase, and peroxidase were also increased. Further component analyses indicated that the significant increase of ABA, proline, soluble sugar and total chlorophyll content and the significant reduction of H2O2 and malonaldehyde content were observed under salt and drought stresses. In addition, the rates of electrolyte leakage and water loss were reduced in transgenic plants. The overall results demonstrate the explicit role of IbZFP1 in conferring salt and drought tolerance in transgenic Arabidopsis plants. The IbZFP1 gene has the potential to be used to enhance the tolerance to abiotic stresses in plants.
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
韩杰, 熊显荣, 蔡雯祎, 等. 牦牛KDM4A基因克隆、组织表达谱及其在卵母细胞和颗粒细胞中的表达[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2018,49(2):291-299.
|
| [27] |
杨召恩, 杨作仁, 刘坤, 等. 一个亚洲棉MYB家族新基因的克隆及特征分析[J]. 中国农业科学, 2013,46(1):195-204.
【目的】克隆亚洲棉MYB家族的一个新基因(GaMYB2),研究其表达模式,分析其预期编码蛋白。【方法】利用RT-PCR和RACE技术克隆亚洲棉MYB2的cDNA序列全长;应用生物信息学软件分析该基因及预期编码蛋白的特征;采用实时荧光定量PCR技术对该基因的组织特异性和PEG6000模拟干旱胁迫处理下的表达模式进行分析。【结果】从亚洲棉(Gossypium arboreum L.)中克隆了MYB家族的一个新基因MYB2,该基因全长1 117 bp,ORF全长840 bp,编码279个氨基酸,含有MYB保守域,氨基酸的BALSTP分析表明GaMYB2氨基酸序列与已报道的水稻(BAA23338.1)、小麦(AAT37168.1)等的序列有40.50%到68.20%的相似性。亚细胞定位表明该基因在细胞核中表达,实时荧光定量PCR结果表明该基因在根和花中的表达量较高,并且响应17%的PEG6000模拟干旱胁迫处理,上调表达。【结论】GaMYB2是亚洲棉MYB家族的一个新基因,并认为该基因可能在棉花调控干旱胁迫的生理适应过程中发挥重要作用。
|
| [28] |
胡军华, 王大伟, 杨明磊, 等. 番茄C2H2型锌指蛋白的鉴定及生物信息学分析[J]. 江苏农业科学, 2018,46(12):23-27.
|
| [29] |
王静毅, 刘菊华, 贾彩红, 等. 香蕉C2H2类锌指蛋白基因MaZAT10的克隆及表达分析[J]. 分子植物育种, 2019,17(14):4551-4559.
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |