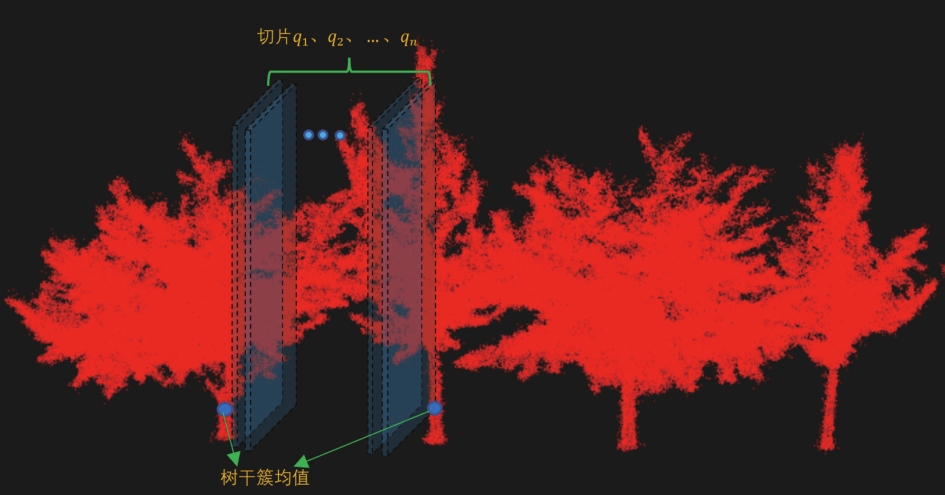
【目的】针对行道树资源调查中的行道树单木分割问题,研究面向侧视移动激光扫描(mobile laser scanning,MLS)点云的行道树单木分割方法,对沿道路方向扫描采集到的街道两侧的点云,建立能够准确实现行道树单木分割的点云实例分割算法。【方法】对点云中的点提取局部特征,将局部特征输入行道树点云检测器,在点云中识别出行道树点云;对于识别出的行道树点云采用基于密度的聚类算法(density-based spatial clustering of applications with noise,DBSCAN)进行聚类,在聚类簇中筛选出行道树簇并滤除非行道树点云;提取各行道树簇的树干点云,使用DBSCAN算法聚类得到若干个树干簇,统计每个行道树簇中包含的树干簇个数;对于包含多个树干簇的行道树簇使用垂直切片与垂直切割结合的方法将其粗分割为多棵单株行道树;使用DBSCAN与K近邻(K-nearest neighbor,KNN)相结合的方法对单株行道树进行细分割,得到最终的行道树单木分割结果。采集街道两侧的点云数据,开展了行道树点云检测器训练、细分割精度测试及算法对比试验。【结果】面向侧视MLS点云的行道树单木分割方法在点云数据上的精确度、召回率、F1分数分别为0.970 4、0.951 0、0.960 6,优于以往研究报道的两种先识别再分割的方法。【结论】提出的方法可以准确实现对MLS点云中行道树的单木分割,为行道树资源调查工作节省人力成本。
【Objective】Aiming at the problem of single tree segmentation of street trees in the investigation of street tree resources, a single tree segmentation method of street trees facing the side looking mobile laser scanning (MLS) point cloud was studied. The point clouds on both sides of the street scanned along the road direction were collected. A point cloud instance segmentation algorithm which can accurately implement single tree segmentation of street trees is established.【Method】The local features were extracted from the points in the point cloud, and the local features were input into the street tree point cloud detector to identify the street tree point cloud in the point cloud. For the identified street tree point clouds, the density-based spatial clustering of applications with noise (DBSCAN) was used to cluster the street tree clusters and filter out the street tree point clouds. The trunk point cloud of each street tree cluster was extracted, and several tree clusters were obtained using DBSCAN algorithm. The number of tree clusters contained in each street tree cluster was counted. For street tree clusters containing multiple trunk clusters, the method of vertical slicing and vertical cutting was used to divide the cluster into multiple single tree. The method of combining DBSCAN and K-nearest neighbor (KNN) was used to segment a single street tree in fine order to obtain the final tree segment result. The point cloud data on both sides of the street were collected, and three sets of experiments were carried out: street tree point cloud detector training, fine segmentation accuracy test and algorithm comparison.【Result】The accuracy rate, recall rate and F1 score of the street tree segmentation method facing side-looking MLS point cloud were 0.970 4, 0.951 0 and 0.960 6, respectively, which were superior to the two existing methods of first recognition and then segmentation.【Conclusion】The proposed method can accurately segment street trees in MLS point cloud, and save labor cost for street tree resource investigation.
 PDF(6665 KB)
PDF(6665 KB)


 PDF(6665 KB)
PDF(6665 KB)
 PDF(6665 KB)
PDF(6665 KB)