 PDF(1832 KB)
PDF(1832 KB)


基于MODIS数据的2001—2018年黑龙江省林火时空分布
崔阳, 狄海廷, 邢艳秋, 常晓晴, 单炜
南京林业大学学报(自然科学版) ›› 2021, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (1) : 205-211.
 PDF(1832 KB)
PDF(1832 KB)
 PDF(1832 KB)
PDF(1832 KB)
基于MODIS数据的2001—2018年黑龙江省林火时空分布
Spatial and temporal distributions of forest fires in Heilongjiang Province from 2001 to 2018 based on MODIS data
 ,
,
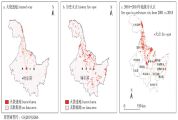
【目的】黑龙江省是中国重要的林业省份之一,也是受林火危害最严重的地区之一。通过遥感数据获取森林火点信息,充分了解近年来黑龙江省林火发生的时空分布格局,探索林火发生规律。【方法】根据黑龙江省2001—2018年MODIS(分辨率成像光谱仪)遥感图像的MCD64A1火烧迹地产品数据集,提取林火火点信息,结合历史火灾记录资料、归一化植被指数NDVI(normalized difference vegetation index)、森林类型、数字高程模型DEM(digital elevation model)等数据,运用地理信息系统空间分析方法和统计分析方法,对黑龙江省的林火时空分布规律进行研究。【结果】2001—2018年,黑龙江省林火次数和过火面积呈现波动性变化,但整体上林火次数呈现下降趋势,其中2002年火灾发生次数最多,2003年过火面积最大,2008年过火面积最小;春、秋两季是林火的多发时期,冬季基本不发生火灾。林火在空间分布上具有异质性,在13个地级行政区中黑河市的森林火灾过火面积最大,其次为大兴安岭地区和绥化市,大庆市发生森林火灾的过火面积最小;过火面积随着林地海拔的升高逐渐呈现减少的趋势。结合森林类型分布情况发现,在针叶林中发生火灾的概率较高,其次为混交林和阔叶林。【结论】采用MCD64A1火烧迹地产品能够较为准确地提取出火灾信息,结合植被类型和高程信息对黑龙江省林火发生的时空规律进行分析,可为区域林火扑救和预警监测提供重要的科学依据。
【Objective】 Heilongjiang Province is one of the most important forestry provinces in China, and it is also one of the areas most seriously damaged by forest fires. In this study, the forest fire point information was obtained from remote sensing data, and the temporal and spatial distribution patterns of forest fire occurrence in Heilongjiang Province in recent years was mapped, so that we could explore the laws of forest fire occurrence. 【Method】 Based on the MCD64A1 data set of fire traces from the Moderate-resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) remote sensing images from 2001 to 2018 in Heilongjiang Province, we extracted the forest fire point information. Then, we combined it with historical fire record data, the normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI), forest type, a digital elevation model (DEM), and other data to study the temporal and spatial distributions of forest fires in Heilongjiang Province. We used the GIS spatial analysis and statistical analysis methods. 【Result】 The number of forest fires and the burned area in Heilongjiang Province fluctuated between 2001 and 2018, overall, the number of forest fires decreased. The number of fires was the highest in 2002, the burned area was the largest in 2003, and the burned area was the smallest in 2008. Spring and autumn were the most frequent periods of forest fires, and there were almost no fires in winter. The spatial distribution of forest fires was heterogeneous. Heihe City had the largest forest fire-burned area out of the 13 prefecture-level administrative regions, followed by Greater Khingan Mountains Prefecture and Suihua City. Daqing City had the smallest forest fire-burned area. The fire-burned area decreased with an increase in altitude. Combined with the distribution of forest types, it was found that the highest probability of fire occurred in coniferous forests, followed by mixed forests and broad-leaved forests. 【Conclusion】 The MCD64A1 data set of fire traces can extract fire information more accurately. By combining it with the vegetation type and elevation information, we identified the temporal and spatial laws of forest fire occurrence in Heilongjiang Province, which provide an important scientific basis for regional forest fire fighting and early warning monitoring.
林火 / 时空分布规律 / 分辨率成像光谱仪 / MCD64A1 / 黑龙江省
forest fire / temporal and spatial distribution / Moderate-resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer(MODIS) / MCD64A1 / Heilongjiang Province
| [1] |
朱教君, 刘足根. 森林干扰生态研究[J]. 应用生态学报, 2004,15(10):1703-1710.
|
| [2] |
胡海清, 魏书精, 魏书威, 等. 气候变暖背景下火干扰对森林生态系统碳循环的影响[J]. 灾害学, 2012,27(4):37-41.
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
Fire significantly affects species composition, structure, and ecosystem processes in boreal forests. Our study objective was to identify the relative effects of climate, vegetation, topography, and human activity on fire occurrence in Chinese boreal forest landscapes. We used historical fire ignition for 1966-2005 and the statistical method of Kernel Density Estimation to derive fire-occurrence density (number of fires/km(2)). The Random Forest models were used to quantify the relative effects of climate, vegetation, topography, and human activity on fire-occurrence density. Our results showed that fire-occurrence density tended to be spatially clustered. Human-caused fire occurrence was highly clustered at the southern part of the region, where human population density is high (comprising about 75% of the area's population). In the north-central areas where elevations are the highest in the region and less densely populated, lightning-caused fires were clustered. Climate factors (e.g., fine fuel and duff moisture content) were important at both regional and landscape scales. Human activity factors (e.g., distance to nearest settlement and road) were secondary to climate as the primary fire occurrence factors. Predictions of fire regimes often assume a strong linkage between climate and fire but usually with less emphasis placed on the effects of local factors such as human activity. We therefore suggest that accurate forecasting of fire regime should include human influences such as those measured by forest proximity to roads and human settlements.
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
萨如拉, 周庆, 刘鑫晔, 等. 1980—2015年内蒙古森林火灾的时空动态[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2019,43(2):137-143.
|
| [8] |
田晓瑞, 舒立福, 王明玉, 等. 大兴安岭林火特征分析[J]. 森林防火, 2008 (2):20-21.
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
张冬有, 邓欧, 李亦秋, 等. 黑龙江省1980—2005年森林火灾时空特征[J]. 林业科学, 2012,48(2):175-179.
|
| [11] |
杨广斌, 唐小明, 宁晋杰, 等. 北京市1986—2006年森林火灾的时空分布规律[J]. 林业科学, 2009,45(7):90-95.
|
| [12] |
刘柯珍, 舒立福, 赵凤君, 等. 基于卫星监测热点的林火分布及发生预报模型[J]. 林业工程学报, 2017,2(4):128-133.
|
| [13] |
李福堂. 基于EOS/MODIS的森林火灾监测模型及应用研究[D]. 武汉:华中科技大学, 2005.
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
贾旭, 高永, 魏宝成, 等. 基于MODIS数据的内蒙古地形因子对火灾分布的影响分析[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2017,39(4):34-39.
|
| [16] |
贾旭, 高永, 齐呼格金, 等. 基于MODIS数据的内蒙古野火时空变化特征[J]. 中国生态农业学报, 2017,25(1):127-135.
|
| [17] |
邓欧, 李亦秋, 冯仲科, 等. 基于空间Logistic 的黑龙江省林火风险模型与火险区划[J]. 农业工程学报, 2012,28(8):200-205.
|
| [18] |
靳全锋, 叶文晶, 沈培福, 等. 浙江2001—2016年露天生物质燃烧排放污染物时空格局[J]. 环境科学学报, 2019,39(1):259-269.
|
| [19] |
金森, 胡海清. 黑龙江省林火规律研究Ⅰ.林火时空动态与分布[J]. 林业科学, 2002,38(1):88-94.
|
| [20] |
郑琼. 黑龙江省森林火灾的时空分布规律及趋势预测[D]. 哈尔滨:东北林业大学, 2013.
|
| [21] |
周小成, 汪小钦. EOS-MODIS数据林火识别算法的验证和改进[J]. 遥感技术与应用, 2006,21(3):206-211.
|
| [22] |
解伏菊, 肖笃宁, 李秀珍. 大兴安岭北坡火烧迹地森林郁闭度恢复及其影响因子[J]. 生态学报, 2007,27(3):784-792.
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
田晓瑞, 殷丽, 舒立福, 等. 2005—2007年大兴安岭林火释放碳量[J]. 应用生态学报, 2009,20(12):2877-2883.
|
| [25] |
王志成. 黑龙江省夏季林火发生规律研究[D]. 2006.
|
| [26] |
杜永胜, 王立夫. 中国森林火灾典型案例1953-2005[M]. 北京: 中国林业出版社, 2007:65-68.
|
| [27] |
邓光葵, 文明. 城乡结合部森林火灾的特点及防治对策[J]. 西南林学院学报, 2001(3):170-179.
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |