
- 国家林草科技领军期刊
- 中国精品科技期刊
- 中国高校百佳科技期刊
- 江苏省新闻出版政府奖期刊奖
- RCCSE林学权威期刊(A+)
- CSCD核心期刊
- Scopus数据库收录期刊
- 中文核心期刊
- SCD核心期刊

南京林业大学学报(自然科学版) ›› 2021, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (6): 31-39.doi: 10.12302/j.issn.1000-2006.202107030
所属专题: 专题报道; 林木 CRISPR/Cas基因编辑专题
• 专题报道(执行主编 施季森 尹佟明 陈金慧) • 上一篇 下一篇
王竹雯( ), 国艳娇, 李爽, 周晨光*(
), 国艳娇, 李爽, 周晨光*( ), 姜立泉, 李伟*(
), 姜立泉, 李伟*( )
)
收稿日期:2021-07-20
接受日期:2021-08-19
出版日期:2021-11-30
发布日期:2021-12-02
基金资助:
WANG Zhuwen( ), GUO Yanjiao, LI Shuang, ZHOU Chenguang*(
), GUO Yanjiao, LI Shuang, ZHOU Chenguang*( ), CHIANG Vincent, LI Wei*(
), CHIANG Vincent, LI Wei*( )
)
Received:2021-07-20
Accepted:2021-08-19
Online:2021-11-30
Published:2021-12-02
摘要: 目的 利用CRISPR/Cas9系统创制毛果杨PtrHBI1功能缺失突变体,初步解析该转录因子在木材形成过程中的功能,为利用基因工程手段培育制浆造纸优良性状的林木新品种提供新思路。方法 以毛果杨(Populus trichocarpa)为研究材料,根据激光显微切割技术捕获的野生型毛果杨不同细胞类型(形成层、木质部和韧皮部)RNA-seq数据,筛选得到1个bHLH家族转录因子PtrHBI1,利用毛果杨木质部原生质体系统对该基因进行亚细胞定位分析,采用原位杂交技术分析PtrHBI1组织特异性表达,采用CRISPR/Cas9技术创制毛果杨ptrhbi1突变体。对ptrhbi1突变体进行生长表型分析,利用石蜡切片对茎段横切面的各细胞类型进行形态分析,利用Klason酸水解法检测突变体木质素含量,使用高效液相色谱测定突变体纤维素和半纤维素含量。结果 亚细胞定位显示PtrHBI1基因定位于细胞核,原位杂交结果表明PtrHBI1主要在形成层和木质部表达。通过CRISPR/Cas9创制的毛果杨ptrhbi1突变体株高显著增加,茎节数和地径在一定时期显著大于野生型。此外,突变体的导管孔径显著增大,纤维细胞数量显著减少。导管细胞的数量和形成层细胞层数与野生型无差异。木材组分分析表明,与野生型植株相比,ptrhbi1植株的纤维素含量增加,木质素总量无显著变化,紫丁香基木质素与愈创木基木质素之质量比(S/G)显著降低。结论 PtrHBI1参与调控毛果杨的生长及次生木质部发育,可能在木材形成过程起着较为重要的调控作用。
中图分类号:
王竹雯,国艳娇,李爽,等. 基于CRISPR/Cas9的毛果杨PtrHBI1基因功能解析[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 45(6): 31-39.
WANG Zhuwen, GUO Yanjiao, LI Shuang, ZHOU Chenguang, CHIANG Vincent, LI Wei. Functional analyses of PtrHBI 1 gene in Populus trichocarpa based on CRISPR/Cas9[J].Journal of Nanjing Forestry University (Natural Science Edition), 2021, 45(6): 31-39.DOI: 10.12302/j.issn.1000-2006.202107030.
表1
所用引物及序列"
| 引物名称 primer name | 序列 sequences | 用途 application |
|---|---|---|
| PtrHBI1-1F | 5'-CACCATGCTGTCTCAAAAACACATCTTT-3' | PtrHBI1基因克隆 cloning of PtrHBI1 gene |
| PtrHBI1-1R | 5'-TCATTCAGGACCATTACTGTAATA-3' | |
| PtrHBI1-2F | 5'-CTAGGGATCCATGCTGTCTCAAAAACACATCT-3' | pUC19-35S-PtrHBI1-GFP瞬时表达载体构建 construction of pUC19-35S-ptrHBI1-GFP transient expression vector |
| PtrHBI1-2R | 5'-CTAGGTCGACATGGAATCCCAAATTTTGAAGG-3' | |
| PtrHBI1-3F | 5'-AGCTGATTAGCCAATTCTATCA-3' | PtrHBI1基因探针 PtrHBI1 gene probe |
| PtrHBI1-3R | 5'-GGTTTACGTAGTTGTTCTCCT-3' | |
| PtrHBI1-4F | 5'GAATTGTAATACGACTCACTATAGGGAGCTGATT AGCCAATTCTATCA-3' | |
| PtrHBI1-4R | 5'GAATTGTAATACGACTCACTATAGGGGGTTTACGT AGTTGTTCTCCT-3' | |
| PtrHBI1-g-F PtrHBI1-g-R | 5'-GATTGAGAAGCAGAGGTAACGGCA-3' 5'-TGCCGTTACCTCTGCTTCTCCAAA-3' | pEgP237载体构建,R端引物亦用于转基因植株鉴定 vector construction of pEgP237,PtrHBI1-g-R also for transgenic identification |
| M13F | 5'-GTAAAACGACGGCCAG-3' | 转基因鉴定 transgenic identification |
| PtrHBI1-5F PtrHBI1-5R | 5'-GAGATAGGATTGATTGGAAGG-3' 5'-AGTCTTCTGATTTTCCTTCGA-3' | 靶位点编辑情况的鉴定 indetification of gene editing |
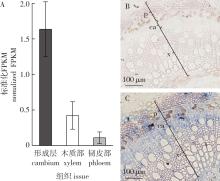
图1
毛果杨PtrHBI1基因的表达模式 A. RNA-seq数据中PtrHBI1基因在不同细胞类型的表达量(标准化FPKM值是指转录本丰度标准化为每千个碱基的转录每百万映射读取的片段数,误差线代表3个生物学重复的SE值)The transcript abundance of PtrHBI1 in RNA-seq data of different cell types (Normalized FPKM indicates normalized transcript abundances as fragments per kilobase of exon model per million mapped fragments. Error bars indicate one SE of three biological replicates); B.PtrHBI1基因的正义探针;C.PtrHBI1基因的反义探针。In situ mRNA localization of PtrHBI1. Digoxigenin-labeled sense PtrHBI1 RNA probe in B and digoxigenin-labeled antisense PtrHBI1 RNA probes in C(p.韧皮部phloem;ca.形成层cambium;x.木质部xylem)。"
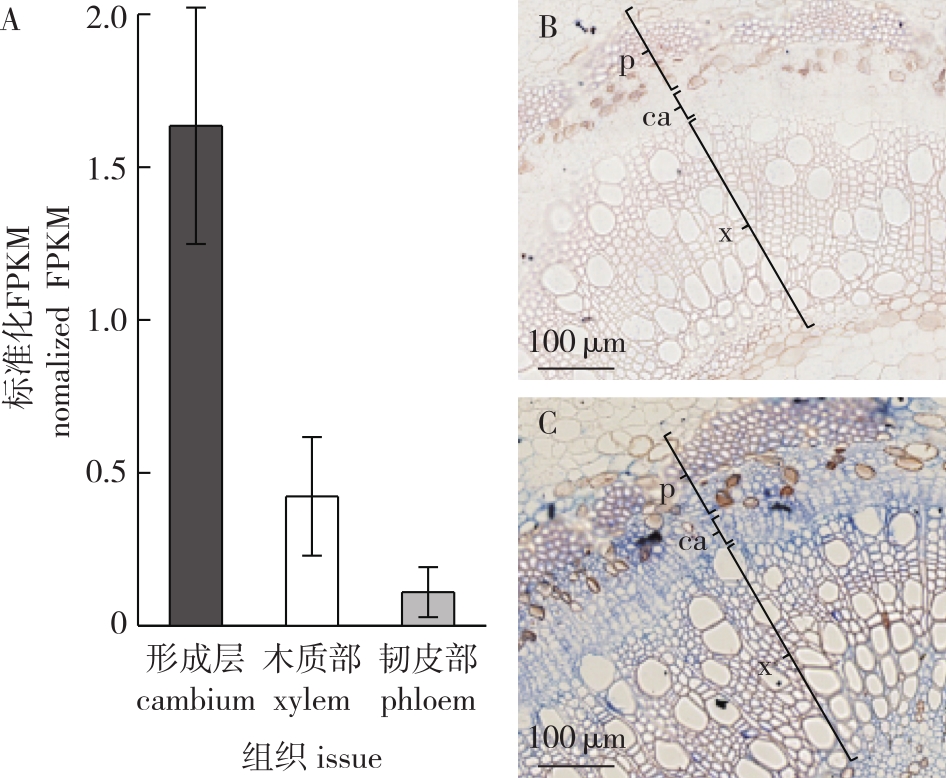

图3
毛果杨转基因植株的获得 A. 愈伤组织分化诱导callus induction;B. 抗性芽诱导shoot induction;C. 抗性植株筛选the screening of the resistant plants;D. 转基因植株的PCR鉴定the PCR detection results(M. DNA marker DL2000; 1. ddH2O为模板的阴性对照negative control with ddH2O as PCR template; 2. pEgP237-U6-PtrHBI1gRNA-35S-Cas9质粒为模板的阳性对照 positive control with plasmid pEgP237-U6-PtrHBI1 gRNA-35S-Cas9 as PCR template; 3. 野生型毛果杨叶片DNA为模板的阴性对照negative control with leaf DNA of wild-type plant as PCR template; 4-5. 抗性植株叶片DNA为模板的样品sample with leaf DNA of kanamycin-resistant plant as PCR template)。"
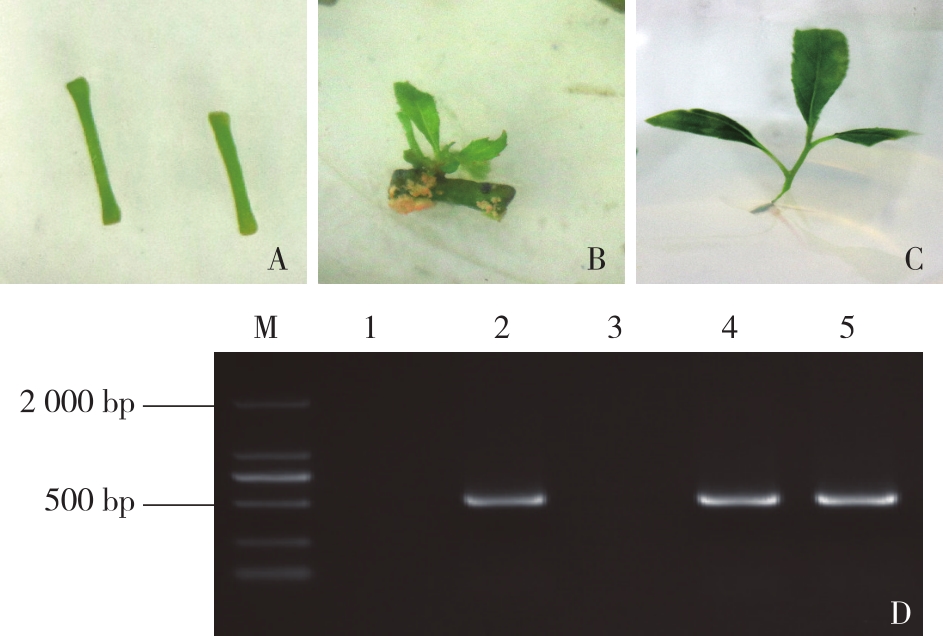
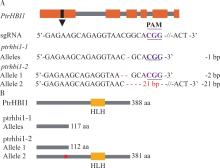
图4
毛果杨PtrHBI1基因编辑情况 A. 等位基因编辑情况(红色“-”表示碱基缺失,“-21 bp-”表示缺失21个碱基)gene editing of alleles (The red short lines “-” represent deletion, “-21 bp-” represent 21 nucleotide deletion);B.被编辑基因的蛋白翻译情况预测(红色块区域表示缺失7个氨基酸) the prediction of amino acid sequence translation (The red short lines represent amino acid changed)。"
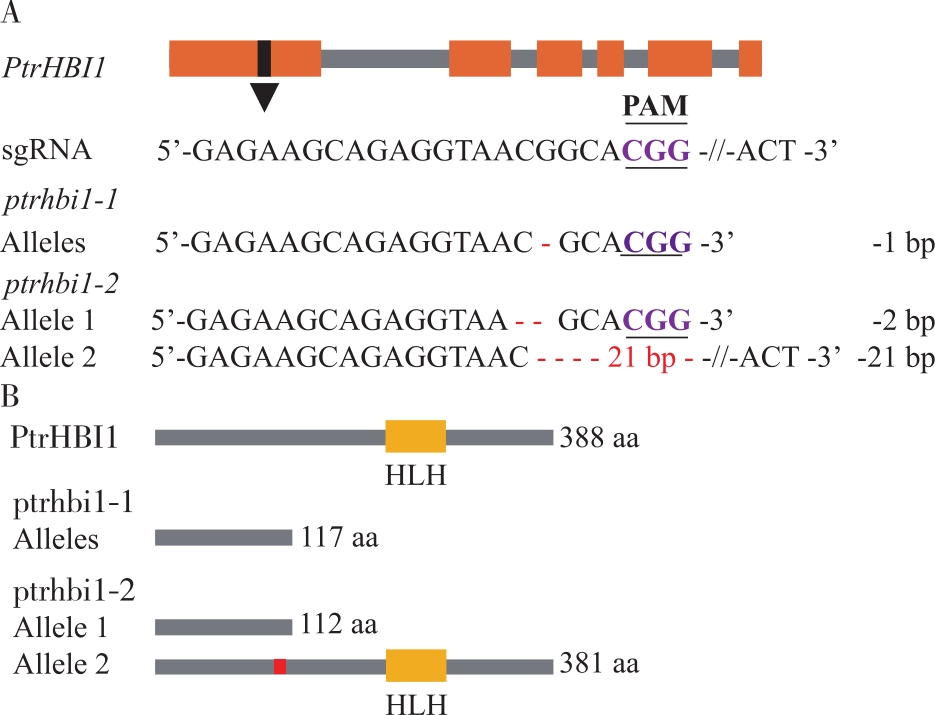
图6
毛果杨野生型与ptrhbi1 突变体植株组织切片表型观察 A. 野生型(WT)和突变体(ptrhbi1)毛果杨各茎节细胞形态观察(比例尺代表200 μm)morphologic observation of stem internodes of WT and ptrhbi1 (Bars=200 μm);B. 形成层细胞形态观察(红色线表示形成层区域,比例尺代表100 μm)morphologic observation of cambium cells (Red line showed cambium areas, Bars=100 μm);C. 单位面积细胞数目统计statistics analysis of number of cambium cell layer;D. 导管孔径大小统计statistics analysis of lumen area of per vessel;E. 形成层细胞层数统计statistics analysis number of cambium cell layer。"
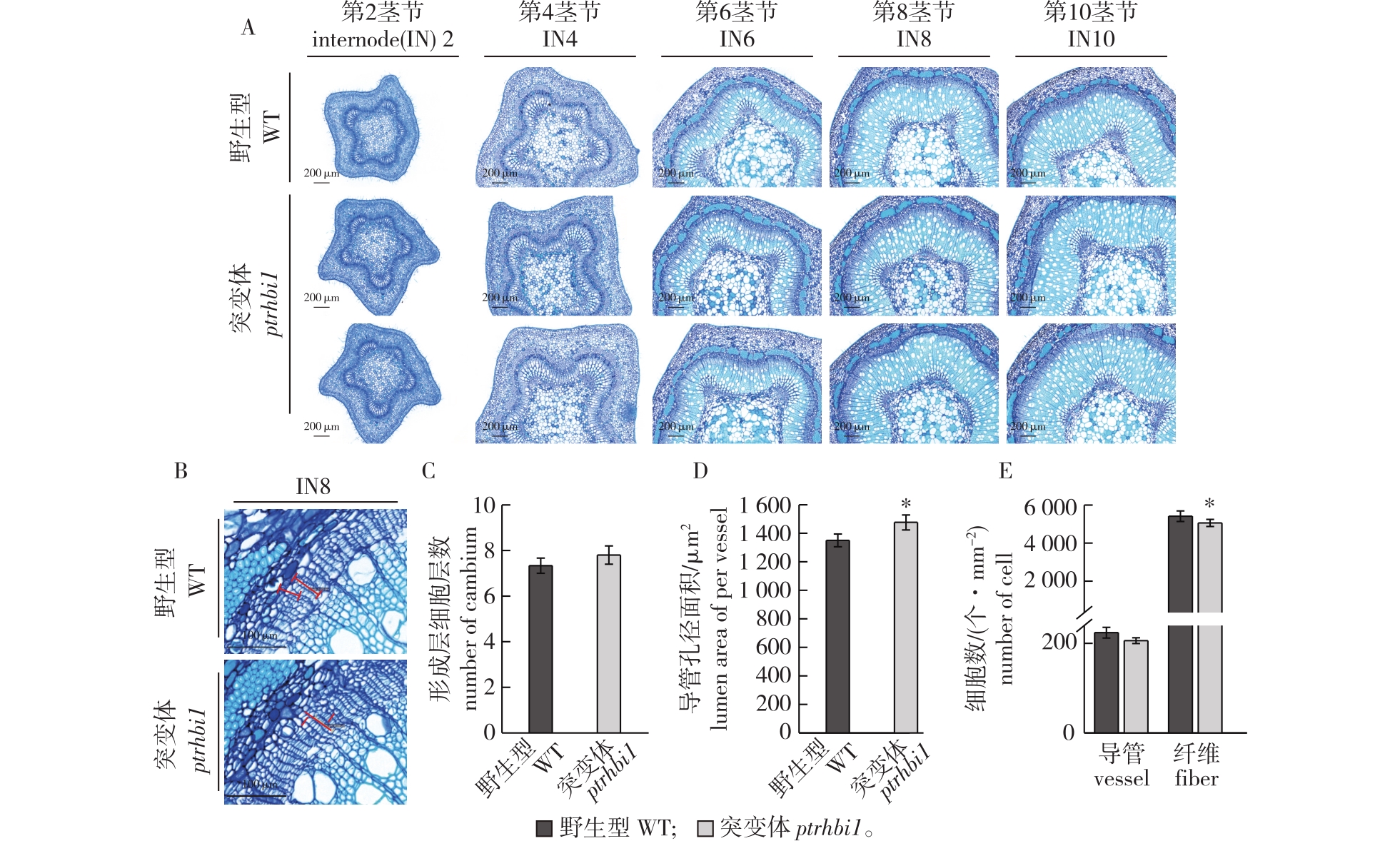
表2
毛果杨野生型与ptrhbi1 突变体植株木材组分占比"
| 样本 sample | 碳水化合物占比carbohydrates rate | 木质素占比lignin rate | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 葡萄糖 glucose | 木糖 xylose | 半乳糖 galactose | 阿拉伯糖 the Arab sugar | 总计 total | 酸不可溶性 木质素 acid insoluble lignin | 酸可溶性 木质素 acid soluble lignin | 总计 total | |
| 野生型 WT | 53.70±0.75 | 12.25±0.31 | 1.25±0.03 | 2.36±0.05 | 69.55±1.10 | 19.40±0.58 | 3.63±0.05 | 23.03±0.62 |
| 突变体 ptrhbi1 | 57.61±0.23** | 11.64±0.08 | 1.04±0.02** | 2.5±0.01* | 72.79±0.17* | 17.39±0.33* | 3.84±0.05* | 21.22±0.28 |
| [1] |
KO J H, KIM H T, HAN K H. Biotechnological improvement of lignocellulosic feedstock for enhanced biofuel productivity and processing[J]. Plant Biotechnol Rep, 2011, 5(1):1-7.DOI: 10.1007/s11816-010-0159-7.
doi: 10.1007/s11816-010-0159-7 |
| [2] | 许会敏, 王莉, 曹德昌, 等. 维管形成层活动周期调控研究进展[J]. 科学通报, 2015, 60(7):619-629. |
|
XU H M, WANG L, CAO D C, et al. Research progress on the regulation of cambium activity periodicity[J]. Chin Sci Bull, 2015, 60(7):619-629.DOI: 10.1360/N972014-01037.
doi: 10.1360/N972014-01037 |
|
| [3] | 文静, 王春涛, 杨永平. 植物木质部次生细胞壁加厚调控的研究进展[J]. 西南林业大学学报, 2021, 41(2):182-188. |
|
WEN J, WANG C T, YANG Y P. Advances in regulation of xylem secondary cell wall thickening in plants[J]. J Southwest For Coll, 2021, 41(2):182-188.DOI: 10.11929/j.swfu.201909077.
doi: 10.11929/j.swfu.201909077 |
|
| [4] |
LIU C, YU H, RAO X L, et al. Abscisic acid regulates secondary cell-wall formation and lignin deposition in Arabidopsis thaliana through phosphorylation of NST1[J]. PNAS, 2021, 118(23): e2106367118.DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2010911118.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.2010911118 |
| [5] |
MARRIOTT P E, GóMEZ L D, MCQUEEN-MASON S J,. Unlocking the potential of lignocellulosic biomass through plant science[J]. New Phytol, 2016, 209(4):1366-1381.DOI: 10.1111/nph.13684.
doi: 10.1111/nph.13684 |
| [6] |
ZHONG R, LEE C, ZHOU J, et al. A battery of transcription factors involved in the regulation of secondary cell wall biosynjournal in Arabidopsis[J]. Plant Cell, 2008, 20(10):2763-2782.DOI: 10.1105/tpc.108.061325.
doi: 10.1105/tpc.108.061325 |
| [7] |
ZHANG J, NIEMINEN K, SERRA J A, et al. The formation of wood and its control[J]. Curr Opin Plant Biol, 2014, 17:56-63.DOI: 10.1016/j.pbi.2013.11.003.
doi: 10.1016/j.pbi.2013.11.003 |
| [8] |
CHEN Y, ZHU P H, WU F, et al. Identification and characterization of the basic helix-loop-helix transcription factor family in Pinus massoniana[J]. Forests, 2020, 11(12):1292.DOI: 10.3390/f11121292.
doi: 10.3390/f11121292 |
| [9] |
ZHANG T, LV W, ZHANG H, et al. Genome-wide analysis of the basic Helix-Loop-Helix (bHLH) transcription factor family in maize[J]. BMC Plant Biol, 2018, 18(1):235.DOI: 10.1186/s12870-018-1441-z.
doi: 10.1186/s12870-018-1441-z |
| [10] |
BAI M Y, FAN M, OH E, et al. A triple helix-loop-helix/basic helix-loop-helix cascade controls cell elongation downstream of multiple hormonal and environmental signaling pathways in Arabidopsis[J]. Plant Cell, 2012, 24(12):4917-4929.DOI: 10.1105/tpc.112.105163.
doi: 10.1105/tpc.112.105163 |
| [11] | 陈儒钢, 巩振辉, 逯明辉, 等. 植物抗逆反应中的转录因子网络研究进展[J]. 农业生物技术学报, 2010, 18(1):126-134. |
|
CHEN R G, GONG Z H, LU M H, et al. Research advance of the transcription factors networks related to plant adverse environmental stress[J]. J Agric Biotechnol, 2010, 18(1):126-134.DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7968.2010.01.020.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7968.2010.01.020 |
|
| [12] |
TOLEDO-ORTIZ G, HUQ E, QUAIL P H. The Arabidopsis basic/helix-loop-helix transcription factor family[J]. Plant Cell, 2003, 15(8):1749-1770.DOI: 10.1105/tpc.013839.
doi: 10.1105/tpc.013839 |
| [13] |
HEIM M A, JAKOBY M, WERBER M, et al. The basic helix-loop-helix transcription factor family in plants:a genome-wide study of protein structure and functional diversity[J]. Mol Biol Evol, 2003, 20(5):735-747.DOI: 10.1093/molbev/msg088.
doi: 10.1093/molbev/msg088 |
| [14] |
LEDENT V, VERVOORT M. The basic helix-loop-helix protein family:comparative genomics and phylogenetic analysis[J]. Genome Res, 2001, 11(5):754-770.DOI: 10.1101/gr.177001.
doi: 10.1101/gr.177001 |
| [15] |
CHU X, LI M, ZHANG S, et al. HBI1-TCP20 interaction positively regulates the CEPs-mediated systemic nitrate acquisition[J]. J Integr Plant Biol, 2021, 63(5):902-912.DOI: 10.1111/jipb.13035.
doi: 10.1111/jipb.13035 |
| [16] |
CAI H, CHAI M, CHEN F, et al. HBI1 Acts downstream of ERECTA and SWR1 in regulating inflorescence architecture through the activation of the brassinosteroid and auxin signaling pathways[J]. New Phytol, 2021, 229(1):414-428.DOI: 10.1111/nph.16840.
doi: 10.1111/nph.16840 |
| [17] |
FERRERO V, VIOLA I L, ARIEL F D, et al. Class I TCP transcription factors target the gibberellin biosynjournal gene GA20ox1 and the growth-promoting genes HBI1 and PRE6 during thermomorphogenic growth in Arabidopsis[J]. Plant Cell Physiol, 2019, 60(8):1633-1645.DOI: 10.1093/pcp/pcz137.
doi: 10.1093/pcp/pcz137 |
| [18] |
WANG S, LI L, XU P, et al. CRY1 interacts directly with HBI1 to regulate its transcriptional activity and photomorphogenesis in Arabidopsis[J]. J Exp Bot, 2018, 69(16):3867-3881.DOI: 10.1093/jxb/ery209.
doi: 10.1093/jxb/ery209 |
| [19] |
FAN M, BAI M Y, KIM J G, et al. The bHLH transcription factor HBI1 mediates the trade-off between growth and pathogen-associated molecular pattern-triggered immunity in Arabidopsis[J]. Plant Cell, 2014, 26(2):828-841.DOI: 10.1105/tpc.113.121111.
doi: 10.1105/tpc.113.121111 |
| [20] |
LI Z, LIU Z B, XING A, et al. Cas9-guide RNA directed genome editing in soybean[J]. Plant Physiol, 2015, 169(2):960-970.DOI: 10.1104/pp.15.00783.
doi: 10.1104/pp.15.00783 |
| [21] |
HSU P D, LANDER E S, ZHANG F. Development and applications of CRISPR-Cas9 for genome engineering[J]. Cell, 2014, 157(6):1262-1278.DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2014.05.010.
doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2014.05.010 |
| [22] |
ALI Z, ABUL-FARAJ A, LI L, et al. Efficient virus-mediated genome editing in plants using the CRISPR/Cas9 system[J]. Mol Plant, 2015, 8(8):1288-1291.DOI: 10.1016/j.molp.2015.02.011.
doi: 10.1016/j.molp.2015.02.011 |
| [23] |
DOUDNA J A, CHARPENTIER E. The new frontier of genome engineering with CRISPR-Cas9[J]. Science, 2014, 346(6213):1258096.DOI: 10.1126/science.1258096.
doi: 10.1126/science.1258096 |
| [24] |
FAN D, LIU T, LI C, et al. Efficient CRISPR/Cas9-mediated targeted mutagenesis in Populus in the first generation[J]. Sci Rep, 2015, 5:12217.DOI: 10.1038/srep12217.
doi: 10.1038/srep12217 |
| [25] |
ZHOU X H, JACOBS T B, XUE L J, et al. Exploiting SNPs for biallelic CRISPR mutations in the outcrossing woody perennial Populus reveals 4-coumarate:CoA ligase specificity and redundancy[J]. New Phytol, 2015, 208(2):298-301.DOI: 10.1111/nph.13470.
doi: 10.1111/nph.13470 |
| [26] |
LIN Y C, LI W, CHEN H, et al. A simple improved-throughput xylem protoplast system for studying wood formation[J]. Nat Protoc, 2014, 9(9):2194-2205.DOI: 10.1038/nprot.2014.147.
doi: 10.1038/nprot.2014.147 |
| [27] |
JAVELLE M, MARCO C F, TIMMERMANS M. In situ hybridization for the precise localization of transcripts in plants[J]. J Vis Exp, 2011(57):e3328.DOI: 10.3791/3328.
doi: 10.3791/3328 |
| [28] |
WANG Z, MAO Y, GUO Y, et al. MYB transcription Factor161 mediates feedback regulation of Secondary wall-associated NAC-Domain1 family genes for wood formation[J]. Plant Physiol, 2020, 184(3):1389-1406.DOI: 10.1104/pp.20.01033.
doi: 10.1104/pp.20.01033 |
| [29] |
LI S, ZHEN C, XU W, et al. Simple,rapid and efficient transformation of genotype Nisqually-1:a basic tool for the first sequenced model tree[J]. Sci Rep, 2017, 7(1):2638.DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-02651-x.
doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-02651-x |
| [30] |
HEIM M A, JAKOBY M, WERBER M, et al. The basic helix-loop-helix transcription factor family in plants:a genome-wide study of protein structure and functional diversity[J]. Mol Biol Evol, 2003, 20(5):735-747.DOI: 10.1093/molbev/msg088.
doi: 10.1093/molbev/msg088 |
| [31] |
LI L, ZHOU Y, CHENG X, et al. Combinatorial modification of multiple lignin traits in trees through multigene cotransformation[J]. PNAS, 2003, 100(8):4939-4944.DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0831166100.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.0831166100 |
| [32] |
SAITO K, WATANABE Y, SHIRAKAWA M, et al. Direct mapping of morphological distribution of syringyl and guaiacyl lignin in the xylem of maple by time-of-flight secondary ion mass spectrometry[J]. Plant J, 2012, 69(3):542-552.DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-313x.2011.04811.x.
doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313x.2011.04811.x |
| [33] |
GUI J, LAM P Y, TOBIMATSU Y, et al. Fibre-specific regulation of lignin biosynjournal improves biomass quality in Populus[J]. New Phytol, 2020, 226(4):1074-1087.DOI: 10.1111/nph.16411.
doi: 10.1111/nph.16411 |
| [34] |
ZHAO K, LI S, YAO W, et al. Characterization of the basic helix-loop-helix gene family and its tissue-differential expression in response to salt stress in poplar[J]. Peer J, 2018, 6:e4502.DOI: 10.7717/peerj.4502.
doi: 10.7717/peerj.4502 |
| [35] |
CHEN F, DIXON R A. Lignin modification improves fermentable sugar yields for biofuel production[J]. Nat Biotechnol, 2007, 25(7):759-761.DOI: 10.1038/nbt1316.
doi: 10.1038/nbt1316 |
| [36] |
FREUDENBERG K. Lignin:its constitution and formation from p-Hydroxycinnamyl alcohols:lignin is duplicated by dehydrogenation of these alcohols;intermediates explain formation and structure[J]. Science, 1965, 148(3670):595-600.DOI: 10.1126/science.148.3670.595.
doi: 10.1126/science.148.3670.595 |
| [37] |
SARKANEN K V. Renewable resources for the production of fuels and chemicals[J]. Science, 1976, 191(4228):773-776.
doi: 10.1126/science.191.4228.773 |
| [38] |
LI L, CHENG X F, LESHKEVICH J, et al. The last step of syringyl monolignol biosynjournal in angiosperms is regulated by a novel gene encoding sinapyl alcohol dehydrogenase[J]. Plant Cell, 2001, 13(7):1567. DOI: 10.1105/tpc.13.7.1567.
doi: 10.1105/tpc.13.7.1567 |
| [39] |
CHIANG V L. From rags to riches[J]. Nat Biotech, 2002, 20(6):557. DOI: 10.1038/nbt0602-557.
doi: 10.1038/nbt0602-557 |
| [40] |
STEWART J J, AKIYAMA T, CHAPPIE C, et al. The effects on lignin structure of overexpression of ferulate 5-hydroxylase in hybrid poplar1[J]. Plant Physio, 2009, 150(2):621-635. DOI: 10.1104/pp.109.137059.
doi: 10.1104/pp.109.137059 |
| [41] | 康向阳. 林木遗传育种研究进展[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 44(3):1-10. |
|
KANG X Y. Research progress of forest genetics and tree breeding[J]. J Nanjing For Univ (Nat Sci Ed), 2020, 44(3):1-10.DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2006.202002033.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2006.202002033 |
| [1] | 高源, 孙佳彤, 周晨光, 姜立泉, 李伟, 李爽. LBD12转录因子调控毛果杨木材形成研究[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2024, 48(1): 29-38. |
| [2] | 王伟, 邱志楠, 李爽, 白向东, 刘桂丰, 姜静. CRISPR/Cas9核糖核蛋白介导的无T-DNA插入的白桦BpGLK1精准突变[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2024, 48(1): 11-17. |
| [3] | 孙佳彤, 国艳娇, 李爽, 周晨光, 姜立泉, 李伟. 基于CRISPR/Cas9的毛果杨bHLH106转录因子的功能研究[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 45(6): 15-23. |
| [4] | 张晨, 臧颖, 许倩, 郑兆娟, 欧阳嘉. 毛果杨苯丙氨酸解氨酶活性比较及肉桂酸制备[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 44(1): 97-104. |
| [5] | 李丹蕾,王峰,陈俏丽,张瑞芝,王佳楠. 美洲黑杨×毛果杨NDR1基因表达对E4锈菌侵染的响应[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 42(01): 21-26. |
| [6] | 王浩然,李爽爽,乐丽娜,匡华琳,黄敏仁,陈英. miR164a及其靶基因PeNAC1相互作用研究[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2016, 40(05): 29-33. |
| [7] | 朱煜,谭梦月,邹爱兰,张文举,戚金亮,杨永华. 拟南芥、水稻和毛果杨中CesA基因的进化和表达分析[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2013, 37(03): 11-16. |
| [8] | 陈英,王浩然,许庆,黄敏仁*. ptr-MIR156a启动子克隆及特征分析[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2011, 35(06): 1-5. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||