 PDF(2190 KB)
PDF(2190 KB)


 PDF(2190 KB)
PDF(2190 KB)
 PDF(2190 KB)
PDF(2190 KB)
乌兰布和沙漠两种植物的分布格局及其变化
Spatial distribution patterns and changes of Haloxylon ammodendron and Artemisia desertorum population in Ulan Buh Desert
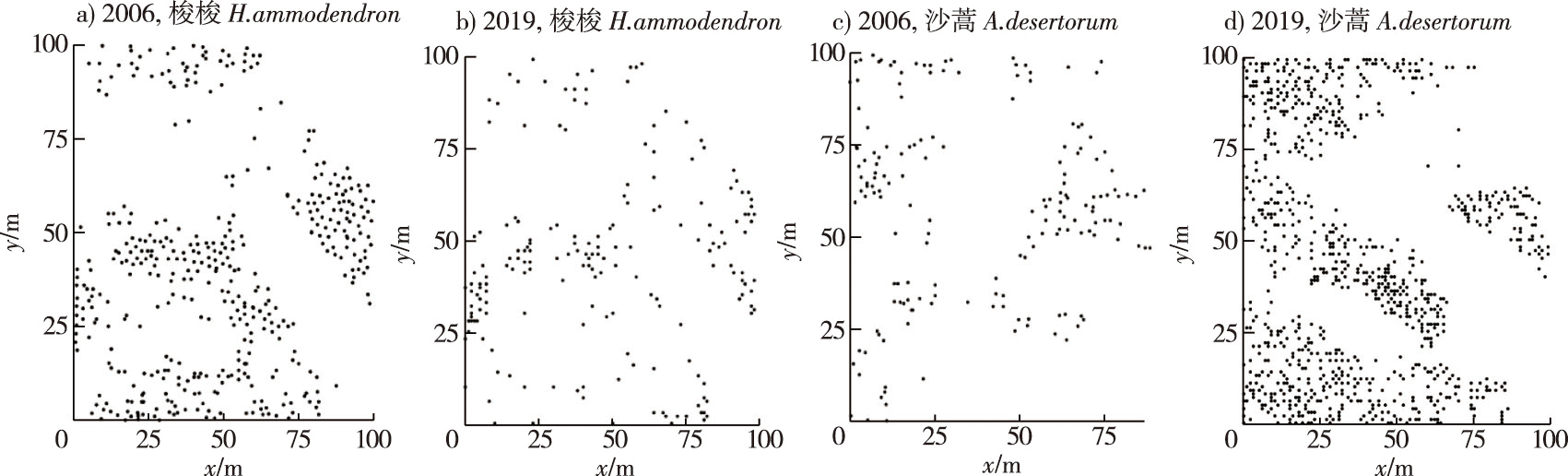
【目的】研究西北干旱地区重要固沙植物梭梭及沙蒿种群空间分布格局和动态,为荒漠化治理与植被恢复提供科学依据。【方法】在乌兰布和沙漠梭梭(Holoxylon ammodendron)+沙蒿(Artemisia desertorum)群落典型分布区域设置1 000 m×1 000 m的样方,于2006和2019年进行2次原位调查,采用点格局分析方法,分析荒漠优势物种的空间分布格局、种间关系及动态变化。【结果】沙蒿灌丛的分布格局由0~20 m尺度的聚集分布,转变为大于10 m尺度上的随机分布,种内关联性呈现减弱的趋势。梭梭灌丛在0~10 m尺度范围内即呈现显著的聚集分布特征。相较于2006年,2019年梭梭的聚集尺度进一步减小,种内关联紧密性有所增强。2006年,梭梭-沙蒿在不同尺度上具有较强的尺度依赖性,在0~18 m尺度内呈现显著的正向作用关系;随着尺度增加,正向作用关系逐渐减弱,表现为相互独立的作用关系。到2019年,正向作用尺度有所减少,在0~15 m即表现为显著的正向作用。【结论】随着时间推移,乌兰布和沙漠梭梭-沙蒿的种间作用尺度有所增强,竞争关系加剧。今后应尽量将梭梭及沙蒿栽种成集群分布而非均匀分布的形式,进而提高植被覆盖率,增强荒漠生态系统功能。
【Objective】Haloxylon ammodendron and Artemisia desertorum are important sand-biding plants in the arid region of the northwest China. Studying the spatial distribution patterns of populations of these two species can help elucidate the population dynamics, which is of great significance to desertification control and vegetation restoration. 【Method】A 1 000 m × 1 000 m quadrat was set in the typical distribution area of H. ammodendron and A. desertorum communities in Ulan Buh Desert, where two in situ surveys were conducted in 2006 and again in 2019. Point pattern analysis was used to analyze the spatial distribution patterns, interspecific relationships, and dynamic changes in dominant desert species. 【Result】The results showed that the distribution pattern of A. desertorum changed from an aggregation distribution at a scale of 0-20 m to a random distribution at a scale of >10 m, and the intra-species correlation showed a weakening trend. The aggregation scale of H. ammodendron decreased further compared to that in 2006, indicating that the intra-species association of H. ammodendron shrubs was enhanced. In 2006, H. ammodendron -A. desertorum had a stronger dependence at different scales, with a significantly positive relationship at the 0-18 m scale. With an increase in scale, this positive relationship weakened and was characterized by an independent relationship. By 2019, the magnitude of the positive effect was reduced, and the positive effect was significant at 0-15 m. 【Conclusion】These results indicate that the inter-specific interaction scale between H. ammodendron and A. desertorum increased with time, and the competition relationship was intensified. If H. ammodendron and A. desertorum are planted in a cluster instead of uniformly distributed, the vegetation coverage rate is expected to be improved, resulting in enhanced function of desert ecosystems.
梭梭 / 沙蒿 / 点格局变化 / 零模型 / 乌兰布和沙漠
Haloxylon ammodendron / Artemisia desertorum / point pattern change / zero model / Ulan Buh Desert
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
赵丽, 王晓江, 刘果厚, 等. 浑善达克沙地榆树种群结构、格局及动态研究[J]. 中国沙漠, 2009, 29(3):508-513.
|
| [3] |
杨洪晓, 张金屯, 吴波, 等. 毛乌素沙地油蒿种群点格局分析[J]. 植物生态学报, 2006, 30(4):563-570.
|
| [4] |
邓文红, 赵欣蕊, 张俊琦, 等. 沙蒿水浸提液化感物质的分离与鉴定[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2019, 41(9):156-163.
|
| [5] |
石蒙沂. 黄河上游沙质滩地模拟飞播试验[J]. 林业科学, 2006, 42(9):39-43.
|
| [6] |
滕玉风, 占玉芳, 马力, 等. 金塔沙漠不同人工植被类型土壤种子库特征[J]. 水土保持通报, 2020, 40(3):163-169.
|
| [7] |
赵明, 王文科, 王周锋, 等. 半干旱区沙地沙蒿生物量及根系分布特征研究[J]. 干旱区地理, 2018, 41(4):786-792.
|
| [8] |
常兆丰, 张大彪, 段小峰, 等. 基于分层投影盖度的荒漠植被相对生态功能测定[J]. 干旱区地理, 2016, 39(4):777-784.
|
| [9] |
苏日格嘎, 王铁娟, 孙海玉, 等. 科尔沁沙地三种沙蒿植株构型特征与防风固沙效应研究[J]. 内蒙古大学学报(自然科学版), 2015, 46(3):270-276.
Surigega,
|
| [10] |
贺学礼, 王银银, 赵丽莉, 等. 荒漠沙蒿根围AM真菌和DSE的空间分布[J]. 生态学报, 2011, 31(3):812-818.
|
| [11] |
李文斌, 李新平. 陕北风沙区不同植被覆盖下的土壤养分特征[J]. 生态学报, 2012, 32(22):6991-6999.
|
| [12] |
王铁娟, 杨持, 吕桂芬, 等. 中国北部六种沙蒿的地理替代规律及其主导生态因子[J]. 生态学报, 2005, 25(5):1012-1018.
|
| [13] |
朱雅娟, 叶学华, 初玉, 等. 降水对鄂尔多斯高原克隆植物分布的影响[J]. 生态学报, 2020, 40(3):952-963.
|
| [14] |
杨力生. 阿拉善盟沙漠治理的几点意见[J]. 中国沙漠, 1982(4):43-45.
|
| [15] |
董光荣, 邹桂香, 李长治, 等. 巴盟河套西部防沙林带防风阻沙效益的初步观测:以磴口县坝楞公社为例[J]. 中国沙漠, 1983, 3(1):13-23.
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
张德魁, 王继和, 马全林, 等. 腾格里沙漠南缘油蒿与沙蒿种群分布格局[J]. 甘肃科技, 2008, 24(3):127-130.
|
| [18] |
张莹花, 刘世增, 刘虎俊, 等. 石羊河中游河岸沙蒿种群的空间格局和关联性分析[J]. 干旱区研究, 2013, 30(2):256-263.
|
| [19] |
地力夏提·包尔汉, 张绘芳, 朱雅丽, 等. 准格尔盆地梭梭天然更新幼苗空间格局与影响因子[J]. 西部林业科学, 2019, 48(1):130-134.
Dilixiati·Baoerhan,
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
张金屯. 植物种群空间分布的点格局分析[J]. 植物生态学报, 1998, 22(4):344-349.
|
| [22] |
李文良, 张小平, 郝朝运, 等. 湘鄂皖连香树种群的年龄结构和点格局分析[J]. 生态学报, 2009, 29(6):3221-3230.
|
| [23] |
吕朝燕. 梭梭自然更新过程的生态学研究[D]. 北京: 中国科学院大学, 2013.
|
| [24] |
韩以晴, 张定海, 张志山. 腾格里沙漠红卫地区固定沙丘上固沙灌木种群空间分布格局与空间关联性研究[J]. 干旱区资源与环境, 2022, 36(3):157-165.
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |