 PDF(2806 KB)
PDF(2806 KB)


基于随机森林协同克里金法的区域森林地上生物量制图——以粤北森林为例
周友锋, 谢秉楼, 李明诗
南京林业大学学报(自然科学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 48 ›› Issue (1) : 169-178.
 PDF(2806 KB)
PDF(2806 KB)
 PDF(2806 KB)
PDF(2806 KB)
基于随机森林协同克里金法的区域森林地上生物量制图——以粤北森林为例
Mapping regional forest aboveground biomass from random forest Co-Kriging approach: a case study from north Guangdong
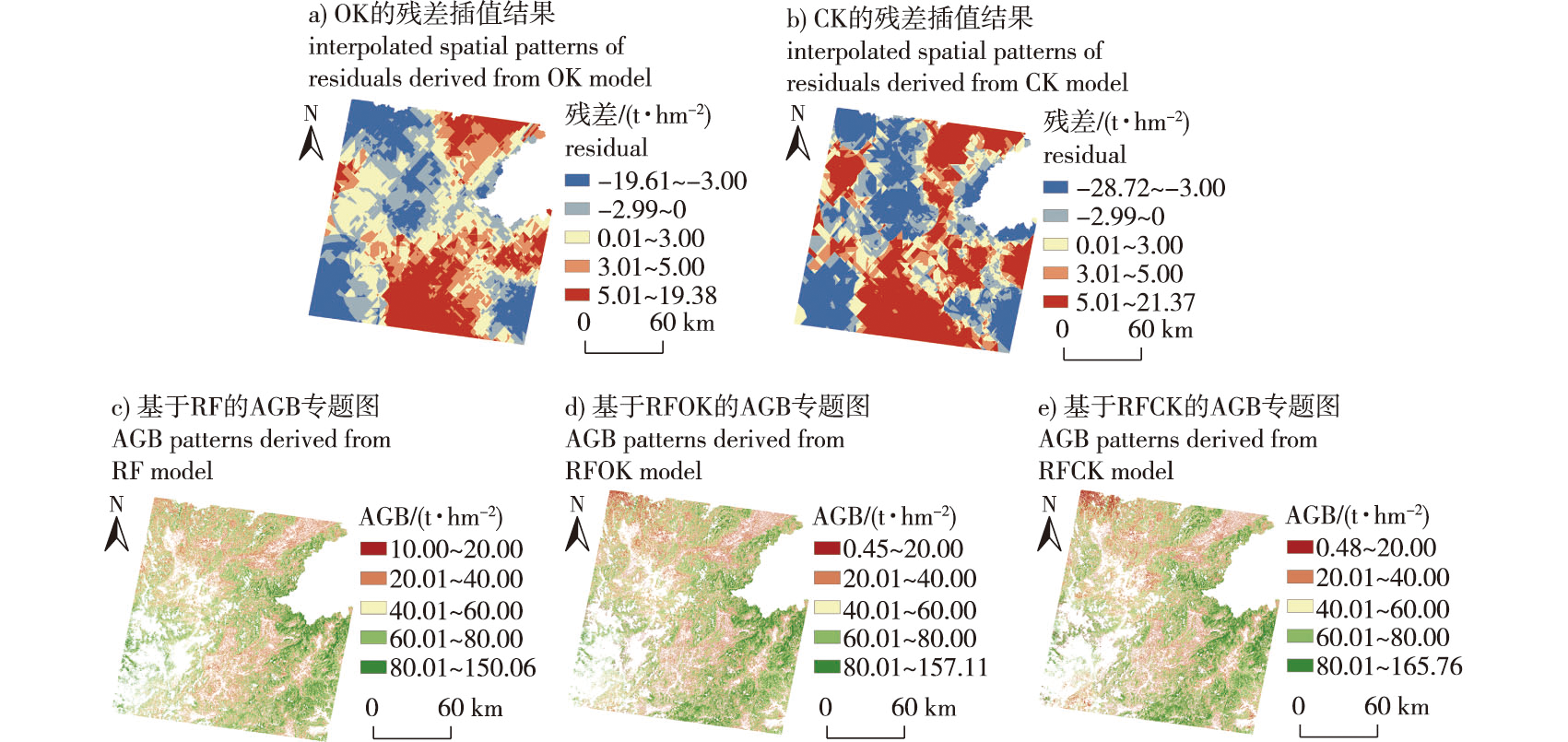
【目的】森林地上生物量(aboveground biomass,AGB)是森林生态系统健康状态和碳汇潜力评估的重要指标,本研究提出了一种快速、准确地获取区域尺度 AGB 信息的制图方法。【方法】基于 Landsat 5 TM、ALOS-1 PALSAR-1、STRM DEM和国家森林资源清查数据,提取光谱特征、纹理指数、后向散射系数和地形因子等特征因子,采用随机森林进行AGB建模。考虑到AGB是典型的具有空间自相关特性的生物物理参量,针对模型残差,使用以高程为协变量的克里金空间插值法分离残差项中的结构化成分,并将其叠加到随机森林模型预测值上形成最终的AGB预测值,从而提高区域尺度的AGB制图精度。【结果】协同克里金法将高程数据作为协变量,在预测AGB残差结构化成分方面的性能优于普通克里金法,协同克里金法与随机森林协同的AGB预测性能明显提升。经独立AGB数据的模型验证表明,随机森林模型预测的AGB与实际观测的AGB间的决定系数 R2为0.46,随机森林结合普通克里金的验证 R2提高到了0.51,而随机森林结合协同克里金模型的验证R2为0.57。相应的均方根误差(RMSE)分别从32.48 t/hm2降低到31.58、29.80 t/hm2,平均绝对误差(MAE)从27.28 t/hm2 降低到26.63、25.12 t/hm2,相对改进指数为0.03和0.08。【结论】总体而言,本研究提出的随机森林协同克里金模型提供了一种更准确、可靠地进行复杂地形区域的亚热带森林AGB制图新方法,所生成的AGB专题图有助于发展针对固碳效能的森林经营方法,为全球气候变化背景下的森林碳增汇和森林可持续经营提供参考。
【Objective】 Forest aboveground biomass (AGB) is an important indicator for evaluating forest ecosystem health status and carbon sink potential. Accurate and quick mapping regional forest AGB has become intensively researched in forest ecosystem status assessment and global climate change studies in recent years. The major objective of this study was to develop a framework for improving the mapping accuracy of AGB in a subtropical forested area with complex terrain. 【Method】 Spectral features, textural indices, backscattering coefficients, and topographical variables were derived from Landsat 5 TM, ALOS-1 PALSAR-1 data and STRM DEM. Next, in tandem with national forest inventory plot measurements, a random forest/Co-Kriging framework that combines the advantages of random forest (RF) and a geostatistical approach was proposed to map AGB in northern Guangdong Province. 【Result】 The experimental results showed that the ordinary Kriging (OK) and Co-Kriging (CK) were able to predict the distribution of the RF-predicted AGB residuals. The predicted structured components of the residuals adding onto the RF predictions could improve the mapping accuracy of AGB to some extent. After the validation of the independent 20% dataset, the determination coefficient between the predictions and the observations increased from 0.46 (RF) to 0.51 (RFOK) and to 0.57 (RFCK). The root mean square error decreased from 32.48 to 31.58 and to 29.80 t/hm2 accordingly. The mean absolute error decreased from 27.28 to 26.63 and to 25.12 t/hm2. Overall, co-Kriging, which considers elevation as a co-variable, was better than ordinary Kriging in predicting AGB residuals. 【Conclusion】 The RFCK framework provides an accurate and reliable method to map subtropical AGB with complex topography. The resulting AGB maps contribute to targeted forest resource management and promote forest carbon sequestration and sustainable forest management under global warming scenarios.
森林地上生物量 / 随机森林 / 协同克里金 / ALOS-1 PALSAR-1 / Landsat 5 TM / 国家森林资源连续清查 / 粤北地区
forest aboveground biomass / random forest / Co-Kriging / ALOS-1 PALSAR-1 / Landsat 5 TM / national forest inventory / north Guangdong Province
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
张志, 田昕, 陈尔学, 等. 森林地上生物量估测方法研究综述[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2011, 33(5):144-150.
|
| [3] |
张少伟, 惠刚盈, 韩宗涛, 等. 基于光学多光谱与SAR遥感特征快速优化的大区域森林地上生物量估测[J]. 遥感技术与应用, 2019, 34(5):925-938.
|
| [4] |
汤旭光, 刘殿伟, 王宗明, 等. 森林地上生物量遥感估算研究进展[J]. 生态学杂志, 2012, 31(5):1311-1318.
|
| [5] |
韩爱惠. 森林生物量及碳储量遥感监测方法研究[D]. 北京: 北京林业大学, 2009.
|
| [6] |
孙雪莲, 舒清态, 欧光龙, 等. 基于随机森林回归模型的思茅松人工林生物量遥感估测[J]. 林业资源管理, 2015(1):71-76.
|
| [7] |
欧光龙, 胥辉. 森林生物量模型研究综述[J]. 西南林业大学学报(自然科学), 2020, 40(1):1-11.
|
| [8] |
张雷, 王琳琳, 张旭东. 随机森林算法基本思想及其在生态学中的应用——以云南松分布模拟为例[J]. 生态学报, 2014, 34(3):650-659.
|
| [9] |
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
许振宇, 李盈昌, 李明阳, 等. 基于Sentinel-1A和Landsat 8数据的区域森林生物量反演[J]. 中南林业科技大学学报, 2020, 40(11):147-155.
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
卢月明, 王亮, 仇阿根, 等. 一种基于主成分分析的协同克里金插值方法[J]. 测绘通报, 2017(11):51-57,63.
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
宋茜, 范文义. 大兴安岭植被生物量的ALOS PALSAR估算[J]. 应用生态学报, 2011, 22(2):303-308.
|
| [27] |
王璟睿, 沈文娟, 李卫正, 等. 基于RapidEye的人工林生物量遥感反演模型性能对比[J]. 西北林学院学报, 2015, 30(6): 196-202.
|
| [28] |
杜虎, 曾馥平, 王克林, 等. 中国南方3种主要人工林生物量和生产力的动态变化[J]. 生态学报, 2014, 34(10):2712-2724.
|
| [29] |
李明诗, 谭莹, 潘洁, 等. 结合光谱、纹理及地形特征的森林生物量建模研究[J]. 遥感信息, 2006(6):6-9,66.
|
| [30] |
徐婷, 曹林, 佘光辉. 基于Landsat 8 OLI的特征变量优化提取及森林生物量反演[J]. 遥感技术与应用, 2015, 30(2):226-234.
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
李云, 张王菲, 崔鋆波, 等. 参数优选支持的光学与SAR数据森林地上生物量反演研究[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2020, 42(10):11-19.
|
| [36] |
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |