
- 国家林草科技领军期刊
- 中国精品科技期刊
- 中国高校百佳科技期刊
- 江苏省新闻出版政府奖期刊奖
- RCCSE林学权威期刊(A+)
- CSCD核心期刊
- Scopus数据库收录期刊
- 中文核心期刊
- SCD核心期刊

南京林业大学学报(自然科学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 48 ›› Issue (1): 18-28.doi: 10.12302/j.issn.1000-2006.202207018
所属专题: 基因编辑与分子设计育种专题
• 专题报道Ⅰ:基因编辑与分子设计育种专题(执行主编 施季森 尹佟明) • 上一篇 下一篇
收稿日期:2022-07-10
修回日期:2022-08-31
出版日期:2024-01-30
发布日期:2024-01-24
基金资助:
YANG Yunli( ), CAO Li, WANG Yang, GU Chenrui, CHEN Kun, LIU Guifeng(
), CAO Li, WANG Yang, GU Chenrui, CHEN Kun, LIU Guifeng( )
)
Received:2022-07-10
Revised:2022-08-31
Online:2024-01-30
Published:2024-01-24
摘要:
【目的】为培育更多的彩叶树种,以满足人们对城市园林绿化美景的追求,采用分子设计育种手段创制黄叶裂叶桦(Betula pendula ‘Dalecarlica’)。【方法】以裂叶桦茎段为材料,通过农杆菌介导法将前期构建的35S::BpGLK1-RNAi载体导入其基因组中,进而对获得的抗性转基因株系进行DNA水平及mRNA的检测,同时测定裂叶桦BpGLK1干扰表达株系的叶色、光合色素及光合参数、株高生长、基因表达特性。【结果】实验共获得8个抗除草剂再生转化株系,分子检测表明,BpGLK1干扰序列分别整合于8个转基因株系基因组中,且这些转基因株系中的BpGLK1相对表达量均呈下调表达。对移栽田间的1年生转基因株系叶色、叶色参数和叶绿素相对含量调查发现,8个转基因株系中RE1—RE5为黄叶株系,RE6—RE8为绿叶株系;相对于WT及绿叶株系,黄叶株系叶色参数L*及b*显著升高,叶绿素a及叶绿素b含量降低,但叶绿素a与b的比值呈上升趋势。转基因株系与野生型(WT)株系相比净光合速率(Pn)没有显著差异。株高分析显示,4个转基因株系显著高于WT株系;3个株系与WT株系差异不显著。基于RNA-Seq找到的显著下调的差异基因BpCOL、BpLCHⅡ、BpPDS和BpFKBP的qRT-PCR分析显示,上述4个基因在RE1—RE3中均呈显著下调表达趋势。【结论】导入的GLK1干扰靶序列能够降低转基因裂叶桦BpGLK1基因表达量,并获得了在园林绿化中具有潜在应用价值的黄叶裂叶桦。
中图分类号:
杨蕴力,曹俐,王阳,等. BpGLK1基因干扰表达对裂叶桦叶色及生长的影响[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2024, 48(1): 18-28.
YANG Yunli, CAO Li, WANG Yang, GU Chenrui, CHEN Kun, LIU Guifeng. Effects of BpGLK1 interference expression on leaf color and growth of Betula pendula ‘Dalecarlica’[J].Journal of Nanjing Forestry University (Natural Science Edition), 2024, 48(1): 18-28.DOI: 10.12302/j.issn.1000-2006.202207018.
表1
qRT-PCR扩增引物序列"
| 引物名称 primer name | 引物序列(5'-3') primer sequence(5'-3') |
|---|---|
| GLK_RNAi_Cis_F | CATGCCATGGGCACAGAAGGTTTGTGCAAG |
| GLK_RNAi_Cis_R | TTGGCGCGCCCCATACATCTGCCTTCTCTGG |
| GLK_RNAi_Anti_F | GCTCTAGAGCACAGAAGGTTTGTGCAAG |
| GLK_RNAi_Anti_R | CGCGGATCCCCATACATCTGCCTTCTCTGG |
| Bar-F | TTAGATCTCGGTGACGGGCA |
| Bar-R | CGGTCTGCACCATCGTCAAC |
表2
差异基因qRT-PCR扩增引物序列"
| 引物名称 primer name | 引物序列(5'-3') primer sequence(5'-3') |
|---|---|
| BpCOL-F' | GTTGCTGAGCTATGCACGAC |
| BpCOL-R' | CTACCTAAACAATCCGCATC |
| BpLCHⅡ-F' | AGTGATATTCTCGATCTCATCTAACAC |
| BpLCHⅡ-R' | AAGCAGCCATTGGTTTGAAAG |
| BpPDS-F' | ATGAGTCTCTGCCTCGTCTC |
| BpPDS-R' | CTGCGTCGGAAGCTTCGAGG |
| BpFKBP-F' | ATGGCTTCCATCTTCGGCTC |
| BpFKBP-R' | GCTGGAAGCTATCCAGTCTG |
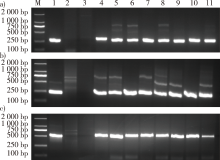
图2
转基因裂叶桦PCR扩增电泳图谱 a. BpGLK1正向靶序列PCR扩增 the forward target sequence of BpGLK1 detected by PCR;b. BpGLK1反向互补序列PCR扩增 the reverse complementary sequence of BpGLK1 detected by PCR;c.Bar基因PCR检测 detection of resistance gene Bar。M.DNA maker DL2000;1.阳性质粒 pFGC5941-BpGLK1 plasmid;2.水 water;3.WT株系 wild type;4—11.RE1—RE8。"
表3
RNA-seq测序质量评估"
| 样本株系 line sample | 总高质量序列数 clean reads number | 总碱基数 clean bases number | 高质量序列比/% clean reads rate | clean Q30 bases rate/% | 总序列数 total teads | 比对序列数 mapped reads | 比对序列占比/% mapping rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WT-2 | 39 924 512 | 5 988 676 800 | 97.78 | 93.39 | 39 924 512 | 37 088 384 | 92.90 |
| WT-3 | 42 201 930 | 6 330 289 500 | 97.18 | 93.50 | 42 201 930 | 39 028 012 | 92.48 |
| RE1-2 | 39 945 148 | 5 991 772 200 | 97.47 | 93.48 | 39 945 148 | 36 893 214 | 92.36 |
| RE1-3 | 40 224 716 | 6 033 707 400 | 97.32 | 93.68 | 40 224 716 | 37 287 119 | 92.70 |
| RE2-1 | 39 919 844 | 5 987 976 600 | 97.40 | 93.44 | 39 919 844 | 36 833 970 | 92.27 |
| RE2-2 | 39 735 726 | 5 960 358 900 | 97.36 | 93.44 | 39 735 726 | 36 608 938 | 92.13 |
| RE3-1 | 40 146 146 | 6 021 921 900 | 97.77 | 93.56 | 40 146 146 | 36 960 182 | 92.06 |
| RE3-2 | 43 059 882 | 6 458 982 300 | 97.75 | 93.67 | 43 059 882 | 39 603 300 | 91.97 |
表4
转基因株系与WT的差异表达基因GO分类"
| 编号 No. | GO分类号 GO code | GO生物过程 biological process |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | GO:0042742 | 细菌防御反应 defense response to bacterium |
| 2 | GO:0006952 | 防御反应 defense response |
| 3 | GO:0006950 | 对压力的反应 response to stress |
| 4 | GO:0006796 | 含磷化合物代谢过程 phosphate-containing compound metabolic process |
| 5 | GO:0006793 | 磷代谢过程 phosphorus metabolic process |
| 6 | GO:0044237 | 细胞代谢过程 cellular metabolic process |
| 7 | GO:0008152 | 代谢过程 metabolic process |
| 8 | GO:0009987 | 细胞过程 cellular process |
| 9 | GO:1901576 | 有机物生物合成过程 organic substance biosynthetic process |
| 10 | GO:0009058 | 生物合成过程 biosynthetic process |
| 11 | GO:0071704 | 有机物代谢过程 organic substance metabolic process |
| 12 | GO:0044238 | 初级代谢过程 primary metabolic process |
| 13 | GO:0043170 | 大分子代谢过程 macromolecule metabolic process |
表5
相对WT株系转基因裂叶桦的4个显著下调差异基因比对结果"
| 基因 gene | 编号 code | 比对基因 compared gene |
|---|---|---|
| BpCOL | Bpev01.c0088.g0068 | 栓皮栎(Quercus suber)锌指蛋白(zinc finger protein) CONSTANS-LIKE 16-like (LOC112018537) |
| BpPDS | Bpev01.c0172.g0006 | 英国胡桃(Juglans regia (English walnut))15顺式植物烯脱饱和酶,叶绿体/色塑性(15-cis-phytoene desaturase, chloroplastic/chromoplastic)(LOC109007079) |
| BpLCHⅡ | Bpev01.c0362.g0012 | 白栎(Quercus lobata)LHCII 1型叶绿素a-b结合蛋白(chlorophyll a-b binding protein of LHCII type 1)(LOC115955462) |
| BpFKBP | Bpev01.c1427.g0002 | 英国胡桃(Juglans regia (English walnut))肽基脯氨酰顺反异构酶FKBP17-2(peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase FKBP17-2),chloroplastic-like (LOC108982577) |
| Bpev01.c1427.g0004 | 野生黑核桃×英国胡桃(Juglans microcarpa×J. sregia)肽基脯氨酰顺反异构酶FKBP17-2,叶绿体(peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase FKBP17-2, chloroplastic)(LOC121243416) |
| [1] | VALOBRA C P, JAMES D J. In vitro shoot regeneration from leaf discs of Betula pendula ‘Dalecarlica’ EM 85[J]. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult, 1990, 21(1):51-54.DOI: 10.1007/BF00034491. |
| [2] | MU H Z, LIN L, LIU G F, et al. Transcriptomic analysis of incised leaf-shape determination in birch[J]. Gene, 2013, 531(2):263-269.DOI: 10.1016/j.gene.2013.08.091. |
| [3] | BIAN X Y, QU C, ZHANG M M, et al. Transcriptome analysis provides new insights into leaf shape variation in birch[J]. Trees, 2019, 33(5):1265-1281.DOI: 10.1007/s00468-019-01856-z. |
| [4] | BILSBOROUGH G D, RUNIONS A, BARKOULAS M, et al. Model for the regulation of Arabidopsis thaliana leaf margin development[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2011, 108(8):3424-3429.DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1015162108. |
| [5] | 任凤伟. 辽宁省裂叶垂枝桦适宜栽培区研究初报[J]. 防护林科技, 2016(3):25-26,29. |
| REN F W. Suitable cultivation area for Betula pendula in Liaoning Province[J]. Prot For Sci Technol, 2016(3):25-26, 29.DOI: 10.13601/j.issn.1005-5215.2016.03.009. | |
| [6] | 渠畅, 边秀艳, 姜静, 等. 裂叶桦和欧洲白桦叶片形态特征及相关基因表达特性比较[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2017, 39(8):9-16. |
| QU C, BIAN X Y, JIANG J, et al. Leaf morphological characteristics and related gene expression characteristic analysis in Betula pendula ‘Dalecarlica’and Betula pendula[J]. J Beijing For Univ, 2017, 39(8):9-16.DOI: 10.13332/j.1000-1522.20160200. | |
| [7] | 扈延伍. 裂叶垂枝桦的引种与栽培繁殖技术探讨[J]. 绿色科技, 2018(1):182-183,186. |
| HU Y W. Discussion on introduction,cultivation and propagation techniques of Betula platyphylla[J]. J Green Sci Technol, 2018(1):182-183, 186.DOI: 10.16663/j.cnki.lskj.2018.01.079. | |
| [8] | 刘俊芳, 张佳, 李贺, 等. 植物GOLDEN2-Like转录因子研究进展[J]. 分子植物育种, 2017, 15(10):3949-3956. |
| LIU J F, ZHANG J, LI H, et al. Research progress of plant GOLDEN2-like transcription factor[J]. Mol Plant Breed, 2017, 15(10):3949-3956.DOI: 10.13271/j.mpb.015.003949. | |
| [9] | 袁俊杰. 水稻高光效基因NRPC2的生物学功能研究[D]. 金华: 浙江师范大学, 2019. |
| YUAN J J. Study on the biological function of high photosynthetic gene NRPC2 in rice[D]. Jinhua: Zhejiang Normal University, 2019.DOI:10.27464/d.cnki.gzsfu.2019.000177. | |
| [10] | WATERS M T, MOYLAN E C, LANGDALE J A. GLK transcription factors regulate chloroplast development in a cell-autonomous manner[J]. Plant J, 2008, 56(3):432-444.DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2008.03616.x. |
| [11] | WATERS M T, WANG P, KORKARIC M, et al. GLK transcription factors coordinate expression of the photosynthetic apparatus in Arabidopsis[J]. Plant Cell, 2009, 21(4):1109-1128.DOI: 10.1105/tpc.108.065250. |
| [12] | GANG H X, LI R H, ZHAO Y M, et al. Loss of GLK1 transcription factor function reveals new insights in chlorophyll biosynthesis and chloroplast development[J]. J Exp Bot, 2019, 70(12):3125-3138.DOI: 10.1093/jxb/erz128. |
| [13] | GANG H X, LIU G F, CHEN S, et al. Physiological and transcriptome analysis of a yellow-green leaf mutant in birch (Betula platyphylla × B. pendula)[J]. Forests, 2019, 10(2):120.DOI: 10.3390/f10020120. |
| [14] | LI Y D, GU C R, GANG H X, et al. Generation of a golden leaf triploid poplar by repressing the expression of GLK genes[J]. For Pese, 2021, 1(1):3.DOI: 10.48130/fr-2021-0003. |
| [15] | 杨光. 白桦BpGH3.5基因的功能研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 东北林业大学, 2015. |
| YANG G. Function research of BpGH3.5 in Betula platyphylla × B. pendula[D]. Harbin:Northeast Forestry University, 2015.DOI:10.27009/d.cnki.gdblu.2015.000071. | |
| [16] | 任烁淇, 刘冰洋, 李雪莹, 等. 白桦黄叶突变株叶色变化规律及苗高生长特性分析[J]. 植物研究, 2018, 38(6):852-859. |
| REN S Q, LIU B Y, LI X Y, et al. Analysis of leaf color variation and height growth characteristics of yellow-green leaf mutant in birch[J]. Bull Bot Res, 2018, 38(6):852-859.DOI: 10.7525/j.issn.1673-5102.2018.06.008. | |
| [17] | 程贵文, 龚洪恩, 颜送宝, 等. 油茶叶绿素提取方法的比较研究[J]. 湖北林业科技, 2017, 46(6):11-13,58. |
| CHENG G W, GONG H E, YAN S B, et al. Comparison of chlorophyll extraction methods in Camellia oleifera[J]. Hubei For Sci Technol, 2017, 46(6):11-13,58. | |
| [18] | 杨蕴力. 裂叶桦转BpGLK基因的研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 东北林业大学, 2021. |
| YANGW/YL. Research on the genetic transformation of BpGLK in Betula pendula’Dalecarlica’[D]. Harbin:Northeast Forestry University, 2021.DOI:10.27009/d.cnki.gdblu.2021.000536. | |
| [19] | 刘佳琦, 宋逸欣, 成星川, 等. 转BpGLK1基因白桦叶色变异规律及生长特性分析[J]. 江西农业学报, 2021, 33(8):17-23. |
| LIU J Q, SONG Y X, CHENG X C, et al. Analysis of leaf color variation and growth characteristics of transgenic BpGLK1 brich[J]. Acta Agric Jiangxi, 2021, 33(8):17-23.DOI: 10.19386/j.cnki.jxnyxb.2021.08.004. | |
| [20] | 李志亮, 黄丛林, 刘晓彬, 等. 转基因植物及其安全性的研究进展[J]. 北方园艺, 2020(8):129-135. |
| LI Z L, HUANG C L, LIU X B, et al. Research progress of genetically modified plants and their bio-safety[J]. North Hortic, 2020(8):129-135.DOI: 10.11937/bfyy.20193411. | |
| [21] | 田世龙, 马庆, 王阳, 等. 紫叶桦与裂叶桦杂交子代的种子活力及叶片性状分离[J]. 林业科学研究, 2019, 32(3):40-48. |
| TIAN S L, MA Q, WANG Y, et al. Segregation of seed vigor and leaf traits in hybrid progenies of Betula pendula‘Purple rain’ and Betula pendula‘Dplecprlicp’[J]. For Res, 2019, 32(3):40-48.DOI: 10.13275/j.cnki.lykxyj.2019.03.006. | |
| [22] | LI R H, CHEN S, LIU G F, et al. Characterization and Identification of a woody lesion mimic mutant lmd,showing defence response and resistance to Alternaria alternate in birch[J]. Sci Rep, 2017, 7(1):11308.DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-11748-2. |
| [23] | 刘金文. 拟南芥核糖核酸酶YbeY参与叶绿体rRNA加工的功能研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 东北林业大学, 2014. |
| LIU J W. Mechanism of chloroplast rRNA processing mediated by endoribonuclease YbeY in arbidopsis thaliana[D]. Harbin:Northeast Forestry University, 2014. | |
| [24] | VAUGHN K C, WILSON K G, REIBACH P H. Ultrastructure and biochemistry of two mutants in Hosta (Liliaceae)[J]. Cytobios, 1980, 27(106):71-80. |
| [25] | ZHOU X S, WU D X, SHEN S Q, et al. High photosynthetic efficiency of a rice (Oryza sativa L.) xantha mutant[J]. Photosynthetica, 2006, 44(2):316-319.DOI: 10.1007/s11099-006-0025-6. |
| [26] | LI W, TANG S, ZHANG S, et al. Gene mapping and functional analysis of the novel leaf color gene SiYGL1 in foxtail millet[Setaria italica (L.) P.Beauv][J]. Physiol Plant, 2016, 157(1):24-37.DOI: 10.1111/ppl.12405. |
| [27] | FITTER D W, MARTIN D J, COPLEY M J, et al. GLK gene pairs regulate chloroplast development in diverse plant species[J]. Plant J, 2002, 31(6):713-727.DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-313x.2002.01390.x. |
| [28] | POWELL A L T, NGUYEN C V, HILL T, et al. Uniform ripening encodes a Golden 2-like transcription factor regulating tomato fruit chloroplast development[J]. Science, 2012, 336(6089):1711-1715.DOI: 10.1126/science.1222218. |
| [29] | ROSSINI L, CRIBBL, MARTIN D J, et al. The maize golden2 gene defines a novel class of transcriptional regulators in plants[J]. Plant Cell, 2001, 13(5):1231-1244.DOI: 10.1105/tpc.13.5.1231. |
| [30] | YASUMURA Y, MOYLAN E C, LANGDALE J A. A conserved transcription factor mediates nuclear control of organelle biogenesis in anciently diverged land plants[J]. Plant Cell, 2005, 17(7):1894-1907.DOI: 10.1105/tpc.105.033191. |
| [31] | 冮慧欣. 白桦黄叶突变体的鉴定及BpGLKl功能研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 东北林业大学, 2019. |
| GANG H X. Identification of a clorina mutant in Betula platyphylla× B. Pendula and function research of BpGLK1[D]. Harbin:Northeast Forestry University, 2019.DOI:10.27009/d.cnki.gdblu.2019.000022. | |
| [32] | OHMIYA A, ODA-YAMAMIZO C, KISHIMOTO S. Overexpression of CONSTANS-like 16 enhances chlorophyll accumulation in petunia corollas[J]. Plant Sci, 2019, 280:90-96.DOI: 10.1016/j.plantsci.2018.11.013. |
| [33] | LI Q H, YANG S P, YU Y N, et al. Comprehensive transcriptome-based characterization of differentially expressed genes involved in carotenoid biosynthesis of different ripening stages of Capsicum[J]. Sci Hortic, 2021, 288:110311.DOI: 10.1016/j.scienta.2021.110311. |
| [34] | DU W K, HU F R, YUAN S X, et al. The identification of key candidate genes mediating yellow seedling lethality in a Lilium regale mutant[J]. Mol Biol Rep, 2020, 47(4):2487-2499.DOI: 10.1007/s11033-020-05323-8. |
| [35] | 程涛. 拟南芥结合Zea的捕光蛋白Zea-LHCⅡ的结构生物学研究[D]. 北京: 中国科学院大学, 2017. |
| CHENG T. Structural andbiological studies onZea-LHCⅡ,a light catching protein binding to Zea in Arabidopsis thaliana[D]. Beijing: University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2017. |
| [1] | 吴翼, 刘勇, 周晓杰, 王开勇, 王文霄. 土壤碱性改良剂处理下银红槭叶色变化及其与叶片矿质元素的关系[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2025, 49(2): 115-122. |
| [2] | 胡衍平, 刘卫东, 张珉, 陈明皋, 程勇, 魏志恒, 庞文胜, 吴际友. 山乌桕家系叶片叶色参数和色素含量及其解剖结构研究[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2025, 49(2): 123-133. |
| [3] | 徐薪璐, 孔淑鑫, 吕卓, 江帅君, 赵婉琪, 林树燕. 靓竹叶色表型叶片形态、结构与光合特性相关性研究[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2025, 49(1): 145-154. |
| [4] | 曹俐, 金冬雪, 姜静, 李天芳. 转BpGLK白桦土壤酶活及根际土壤细菌、真菌群落组成分析[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2024, 48(6): 129-137. |
| [5] | 顾宸瑞, 袁启航, 姜静, 穆怀志, 刘桂丰. 基于转录组测序的关联分析定位裂叶桦叶形调控基因[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2024, 48(1): 39-46. |
| [6] | 魏静, 谭星, 王昌盛, 闫瑞, 李林珂, 宁月, 刘芸. 引种美国红枫在两种紫色土区的生长和光合特性比较[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2024, 48(1): 97-105. |
| [7] | 王剑超, 邱文敏, 金康鸣, 陆铸畴, 韩小娇, 卓仁英, 刘晓光, 何正权. 伴矿景天WRKY基因家族鉴定及镉胁迫响应分析[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2023, 47(2): 49-60. |
| [8] | 崔祺, 吴昀, 李东泽, 吴凡, 韩蕊莲, 黄均华, 胡绍庆. 彩叶桂叶片发育过程中叶色表型与色素成分变化[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2023, 47(2): 79-86. |
| [9] | 王阳, 王伟, 姜静, 顾宸瑞, 杨蕴力. 转基因小黑杨根际土壤微生物群落特征研究[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2023, 47(1): 199-208. |
| [10] | 王占军, 吴子琦, 王朝霞, 欧祖兰, 李杰, 蔡倩文, 徐忠东, 张照亮. 3个茶树品种WOX基因家族的进化及密码子偏好性比较[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 46(2): 71-80. |
| [11] | 徐展宏, 朱莹, 金慧颖, 孙操稳, 方升佐. 不同叶色青钱柳叶片色素、多酚含量及光合特性的差异[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 46(2): 103-110. |
| [12] | 路买林, 陈梦娇, 张嘉嘉, 赵建霞, 朱景乐, 杜红岩. ‘红叶’杜仲叶色转变过程中叶片生理指标变化[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 45(1): 86-92. |
| [13] | 沈星诚, 周婷, 范俊俊, 徐立安, 张往祥. 日本红枫春季叶片色彩评价[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 44(6): 213-220. |
| [14] | 叶查龙, 颜斌, 申婷婷, 宁坤, 李慧玉. 转BpmiR156基因白桦株系的耐盐性分析[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 44(6): 147-151. |
| [15] | 夏溪, 奉树成, 张春英. 新型分子生物学技术在花卉定向育种中的应用进展[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 43(6): 173-180. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||