 PDF(1688 KB)
PDF(1688 KB)


施肥对毛竹林产量影响的Meta分析
陆启帆, 林上平, 刘胜辉, 郑翔, 毕毓芳, 肖子璋, 姜姜, 王安可, 杜旭华
南京林业大学学报(自然科学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 48 ›› Issue (1) : 88-96.
 PDF(1688 KB)
PDF(1688 KB)
 PDF(1688 KB)
PDF(1688 KB)
施肥对毛竹林产量影响的Meta分析
Meta-analysis of the effect of fertilization on the yield of Phyllostachys edulis forest
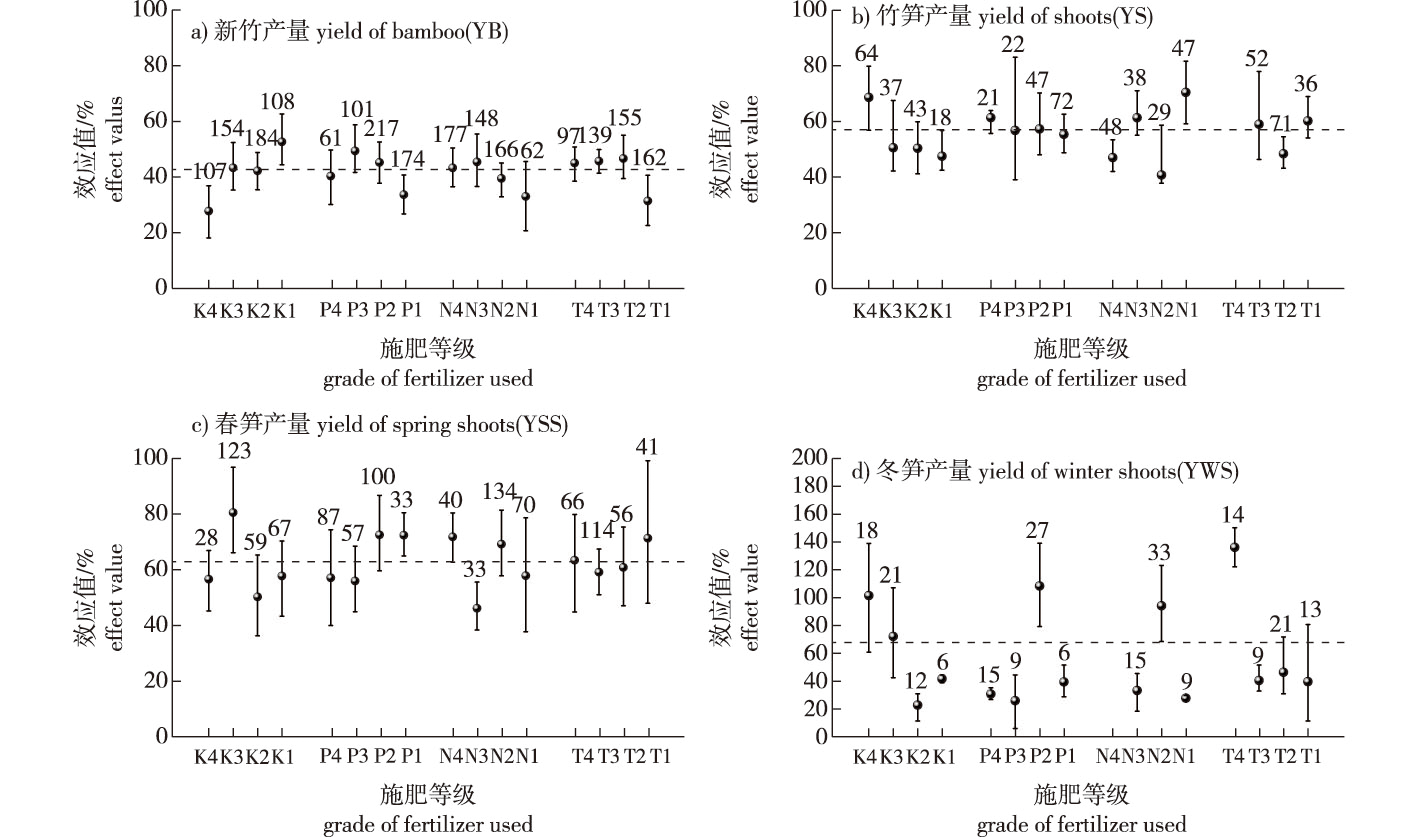
【目的】施肥及其配比是决定毛竹(Phyllostachys edulis)林产量的重要因素,但当前毛竹林的最佳施肥方案仍存在争议。笔者综合汇总分析已有文献,用Meta分析比较施肥总量和元素配比对产量及其构成因子的影响,提出相对普适的毛竹林施肥方案。【方法】基于Meta分析,搜集汇总当前3种重要数据库中有关于“主题[毛竹(moso bamboo/Phyllostachys edulis)]和(and) 主题[施肥(apply fertilizer/fertilization)]和 (and) 主题[产量(yield)]”的文献,再对收录数据划级分类,系统探究施肥总量、氮肥占比、磷肥占比、钾肥占比对毛竹林产量及其构成因子的影响。【结果】施肥使新竹产量(YB)、竹笋产量(YS,包括春笋产量和冬笋产量)、春笋产量(YSS)、冬笋产量(YWS)、新竹胸径(DB)、新竹高度(HB)、成竹数(NB)、出笋数(NS)、春笋出笋数(NSS)、春笋退笋数(NRSS)分别提升了42.76%、57.01%、62.88%、67.78%、7.22%、8.17%、35.84%、40.35%、38.35%、33.38%。磷肥占比与YB呈正相关,而与YSS和YWS呈负相关,钾肥占比则与YB呈负相关,与YSS和YWS呈正相关。【结论】材用毛竹林的施肥策略建议为施肥总量不超过337.5 kg/hm2,不低于228.7 kg/hm2,其中氮肥占比不超过62.5%,不低于50.9%,磷肥占比为14.0%~32.7%,钾肥占比低于16.4%。笋用毛竹林的施肥策略建议为施肥总量不超过228.7 kg/hm2,氮肥占比在37.8%~62.5%之间,磷肥占比低于22.3%,钾肥占比高于24.9%。笋材两用毛竹林施肥量应在228.7~337.5 kg/hm2之间,氮肥占比在50.9%~62.5%之间,磷肥占比应在14.0%~22.3%之间,钾肥占比则应控制在16.4%~24.9%之间。
【Objective】 The fertilization regime and its composition are crucial in determining the yield of Phyllostachys edulis (moso bamboo) forests. There is ongoing debate over the optimal fertilization strategy for these forests. This study aims to synthesize existing literature through a Meta-analysis to compare the impacts of total fertilization amounts and nutrient ratios on yield and its contributing factors, ultimately proposing a more universally applicable fertilization plan for moso bamboo forests. 【Method】 In this Meta-analysis, relevant data concerning moso bamboo, fertilizer application, and yield were collected and aggregated from various databases. The data underwent categorization and analysis to systematically explore the effects of total fertilization, and the proportions of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium fertilizers, on the yield of Moso bamboo forests and their contributing factors. 【Result】 Fertilization was found to significantly enhance various metrics: yield of new bamboo (YB) by 42.76%, shoot yield (YS), including both spring and winter shoot yields, by 57.01%, spring shoot yield (YSS) by 62.88%, winter shoot yield (YWS) by 67.78%, diameter of new bamboo (DB) by 7.22%, height of new bamboo (HB) by 8.17%, the number of mature bamboos (NB) by 35.84%, the number of shoots (NS) by 40.35%, the number of spring shoots (NSS) by 38.35%, and the number of retrogressed spring shoots (NRSS) by 33.38%. A positive correlation was observed between the proportion of phosphorus fertilizer and YB, but a negative correlation with YSS and YWS. In contrast, the proportion of potassium fertilizer showed a negative correlation with YB and a positive correlation with YSS and YWS. 【Conclusion】 For timber-producing bamboo forests, the recommended total fertilization amount should range from 228.7 to 337.5 kg/hm2, with nitrogen fertilizer comprising 50.9%-62.5%, phosphorus between 14.0% and 32.7%, and potassium lower than 16.4%. For shoot-producing forests, the total fertilization should not exceed 228.7 kg/hm2, with nitrogen proportions between 37.8% and 62.5%, phosphorus below 22.3%, and potassium above 24.9%. In dual-purpose forests, fertilization amounts should be maintained between 228.7 and 337.5 kg/hm2, with nitrogen at 50.9%-62.5%, phosphorus at 14.0%-22.3%, and potassium controlled between 16.4% and 24.9%.
新竹产量 / 竹笋产量 / 产量构成因子 / 施肥总量 / 养分配比 / Meta分析 / 毛竹
yield of bamboo / yield of shoots / yield components / total fertilization / nutrient proportion / Meta-analysis / Phyllostachys edulis (moso bamboo)
| [1] |
耿伯介, 王正平. 中国植物志:第9卷第1分册[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1996: 275.
|
| [2] |
李玉敏, 冯鹏飞. 基于第九次全国森林资源清查的中国竹资源分析[J]. 世界竹藤通讯, 2019, 17(6): 45-48.
|
| [3] |
张洋洋, 邓智文, 荣俊冬, 等. 毛竹林施肥研究进展[J]. 世界竹藤通讯, 2019, 17(5): 58-62.
|
| [4] |
储成才, 王毅, 王二涛. 植物氮磷钾养分高效利用研究现状与展望[J]. 中国科学:生命科学, 2021, 51(10): 1415-1423.
|
| [5] |
郑风英, 李欣欣, 李士坤, 等. 带状采伐下施肥对毛竹生理特性的影响[J]. 竹子学报, 2021, 40(2): 22-28.
|
| [6] |
李榕, 于娜, 毕海明, 等. 毛竹林带状采伐抚育技术研究现状[J]. 竹子学报, 2021, 40(2): 84-88.
|
| [7] |
王勤, 孙孟瑶, 遆建航, 等. 垦复结合施肥对毛竹林生长及土壤理化特性的影响[J]. 西北林学院学报, 2020, 35(4): 13-17.
|
| [8] |
高培军, 邱永华, 周紫球, 等. 氮素施肥对毛竹生产力与光合能力的影响[J]. 浙江农林大学学报, 2014, 31(5): 697-703.
|
| [9] |
刘巧云. 低产毛竹林改造及竹刺瘿螨的防治[J]. 林业科学, 2003( 增刊1): 159-163.
|
| [10] |
洪顺山. 毛竹配方施肥研究初报[J]. 竹子研究汇刊, 1987(1): 35-41.
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
李静文, 刘晓颖, 李士坤, 等. 氮磷钾配比施肥对毛竹出笋及叶片生理特性的影响[J]. 西南农业学报, 2020, 33(12): 2885-2890.
|
| [13] |
张洋洋, 凡莉莉, 黄霞, 等. 毛竹林带状采伐后垦复施肥对新竹生长及土壤养分含量的影响[J]. 热带作物学报, 2021, 42(4): 1047-1054.
|
| [14] |
郭晓敏, 陈广生, 牛德奎, 等. 平衡施肥对毛竹笋产量的影响效应研究[J]. 江西农业大学学报(自然科学版), 2003(1): 48-53.
|
| [15] |
陈本学, 刘广路, 蔡春菊, 等. 不同施肥方式对毛竹林碳储量及土壤理化性质的影响[J]. 四川农业大学学报, 2018, 36(3): 323-328.
|
| [16] |
严伍明, 杨明亮, 胡瑞牯. 毛竹笋材两用林配方施肥试验效果初报[J]. 竹子研究汇刊, 1997, 16(4): 53-55.
|
| [17] |
胡冬南, 陈立新, 李发凯, 等. 配方施肥对毛竹笋材的影响[J]. 江西农业大学学报(自然科学), 2004, 26(2): 196-199.
|
| [18] |
彭少麟, 唐小焱. Meta分析及其在生态学上的应用[J]. 生态学杂志, 1998(5): 75-80.
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
才璐, 罗珠珠, 王林林, 等. 施肥对苜蓿土壤水分、养分和产量的影响:基于定位试验数据的Meta分析[J]. 草业科学, 2021, 38(1): 160-170.
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
彭丹莉, 柳丹, 晏闻博, 等. 基于丰产目的下毛竹生长调控技术研究进展[J]. 浙江林业科技, 2015, 35(1): 85-89.
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
张飞英, 刘亚群, 柏明娥. 长期不同施肥方式对毛竹林土壤酸化过程的影响[J]. 浙江林业科技, 2017, 37(2): 60-64.
|
| [29] |
李翀, 周国模, 施拥军, 等. 不同经营措施对毛竹林生态系统净碳汇能力的影响[J]. 林业科学, 2017, 53(2): 1-9.
|
| [30] |
王宏, 金晓春, 金爱武, 等. 施肥对毛竹生长量和秆形的影响[J]. 浙江农林大学学报, 2011, 28(5): 741-746.
|
| [31] |
连华萍. 配方施肥对毛竹林新竹生长及经济效益的影响[J]. 林业科技开发, 2015, 29(2): 44-48.
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
巨晓棠, 谷保静. 我国农田氮肥施用现状、问题及趋势[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2014, 20(4): 783-795.
|
| [35] |
刘琦蕊, 漆良华, 胡璇, 等. 氮肥对毛竹林土壤硝化和反硝化作用的影响[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2017, 41(1): 82-88.
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
范合琴, 杨冰美, 连延浩, 等. 氮肥对豆茬冬小麦氮素利用及产量的影响[J]. 麦类作物学报, 2021, 41(11): 1383-1391.
|
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
胡亮, 王婷, 郭晓敏. 平衡施肥对毛竹产量的影响[J]. 安徽农业科学, 2009, 37(30): 15019-15020.
|
| [40] |
郭世乾, 崔增团, 师伟杰, 等. 氮、磷、钾及其配施对制种玉米养分吸收利用的影响[J]. 干旱地区农业研究, 2020, 38(2): 221-226.
|
| [41] |
郭雯, 漆良华, 雷刚, 等. 毛竹及其变种叶片化学计量与养分重吸收效率[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 45(1): 79-85.
|
| [42] |
|
| [43] |
张海燕, 董顺旭, 解备涛, 等. 钾肥用量对瘠薄地甘薯产量和钾肥利用率的影响[J]. 核农学报, 2020, 34(10): 2299-2306.
|
| [44] |
|
| [45] |
杨杰, 郑蓉, 温晓芸, 等. 土壤类型对毛竹林氮素流失的影响[J]. 竹子学报, 2020, 39(4): 55-63.
|
| [46] |
|
| [47] |
|
| [48] |
吴可, 谢慧敏, 刘文奇, 等. 氮、磷、钾肥对南方双季稻区水稻产量及产量构成因子的影响[J]. 作物杂志, 2021(4): 178-183.
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |