 PDF(4637 KB)
PDF(4637 KB)


 PDF(4637 KB)
PDF(4637 KB)
 PDF(4637 KB)
PDF(4637 KB)
基于保护政策影响的抚仙湖流域景观格局变化及生态系统服务价值响应
Protection policy impacts on landscape pattern changes and ecosystem service value responses in Fuxian Lake basin
【目的】 云南省抚仙湖流域作为我国西南地区和珠江流域重要的生态屏障,是我国“两屏三带”生态安全格局的重要组成部分。抚仙湖流域景观格局和生态系统服务价值(ESV)的变化受到“四退三还”保护政策的影响,定量研究其发展演变规律,为流域景观的保护与规划提供参考。【方法】 选取2006—2021年“四退三还”保护政策实施前后抚仙湖流域的4期遥感影像进行景观分类,计算土地利用动态度、转移矩阵、景观格局指数,并基于当量因子法评估生态系统服务价值(ESV),运用SPSS对流域的ESV与景观格局指数进行相关性分析。【结果】 ①“四退三还”政策实施前,抚仙湖流域林地面积大量减少,建设用地持续扩展,水体面积减少;景观格局复杂化、破碎化,连通性减弱,同时流域ESV明显下降。“四退三还”政策实施后,抚仙湖流域林地面积显著增加,建设用地扩张速度明显减缓,水体缩减速度降低;景观格局破碎化程度降低,连通性增强;流域ESV显著增加。②抚仙湖流域ESV与景观格局之间存在明显联系,流域ESV总量与景观格局指数蔓延度(CONTAGE)显著正相关,与香浓多样性指数(SHDI)和香浓均匀度指数(SHEI)相关性较高且呈负相关。各单项生态系统服务价值中,供给服务与最大斑块指数(LPI)显著负相关;调节服务和支持服务与CONTAGE显著正相关,与SHDI和SHEI显著负相关;文化服务与CONTAGE显著正相关。【结论】 景观类型的剧烈变化引起景观类型之间的相互转移以及景观多样性、连通度等的变化,并改变了景观生态系统的结构和功能,同时也影响生态系统服务价值。未来研究中可聚焦其机制,为抚仙湖流域下一步的保护与管理提供参考。
【Objective】 Changes in landscape patterns and ecosystem service values (ESVs) in the Fuxian Lake basin are affected by the “Four Retreats and Three Returns” protection policy. Quantitatively understanding such changes can provide a reference for the protection of watershed landscapes. 【Method】 Four sets of remote sensing images taken from 2006 to 2021 (before and after the implementation of the “Four Retreats and Three Returns” protection policy) were selected for landscape classification, and the land use dynamics, transfer matrix and landscape pattern indices were calculated. The ESVs were evaluated using the equivalent factor method and the SPSS software package was used to analyze the correlations between the ESVs in the watershed and the landscape pattern indices. 【Result】 The results indicated that the forested and water system areas in the Fuxian Lake basin were small, while the construction land area was expanding before the implementation of the “Four Retreats and Three Returns” protection policy. The landscape pattern was also complicated and fragmented, with weak connectivity and low ESVs. After the policy was implemented, the forested area increased significantly, the expansion of construction land slowed significantly, and the rate of water system reduction decreased. The degree of fragmentation of the landscape pattern also decreased and the connectivity was enhanced. The ESVs in the basin increased significantly. (2) The ESVs in the Fuxian Lake basin were connected with the landscape pattern, and the total basin ESV was significantly positively correlated with CONTAGE and negatively correlated with SHDI and SHEI. Among the individual ESVs, supply services were significantly negatively correlated with LPI, regulation and support services were significantly positively correlated with CONTAGE and significantly negatively correlated with SHDI and SHEI, and cultural services were significantly positively correlated with CONTAGE. 【Conclusion】 Future studies should focus on the mechanism behind these changes and provide a reference for the next step in protecting and managing the Fuxian Lake basin.
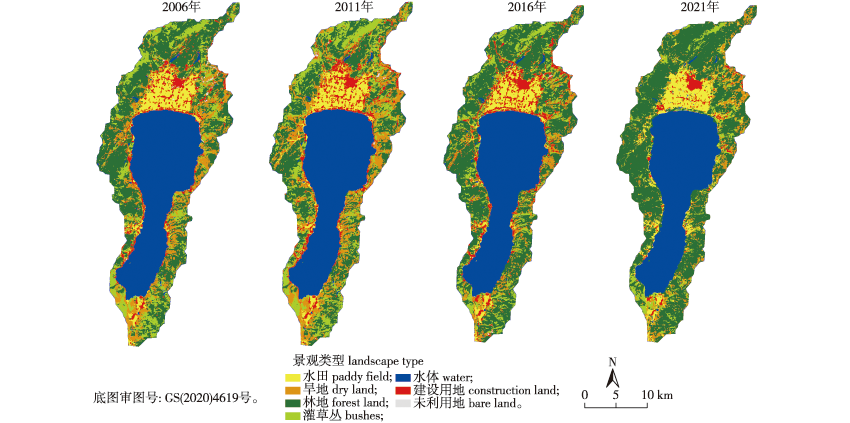
生态系统服务价值(ESV) / 景观格局 / “四退三还”政策 / 云南抚仙湖流域
ecosystem service value(ESV) / landscape pattern / ‘Four Retreats and Three Refunds’ policy / Fuxian Lake basin of Yunnan Province
| [1] |
郭玉静, 王妍, 郑毅, 等. 滇西北高原湖泊剑湖流域景观时空演变特征[J]. 浙江农林大学学报, 2018, 35(4):695-704.
|
| [2] |
谢高地, 张彩霞, 张雷明, 等. 基于单位面积价值当量因子的生态系统服务价值化方法改进[J]. 自然资源学报, 2015, 30(8):1243-1254.
|
| [3] |
柳迪子, 杜守帅, 王晨旭. 旅游型乡村景观格局变化及生态系统服务价值响应:以江苏省无锡市太湖国家旅游度假区为例[J]. 水土保持通报, 2021, 41(5):264-275,286.
|
| [4] |
朱颖, 王杉, 冯育青. 近30年太湖流域湿地生态系统服务价值对景观格局变化的响应:基于“退田还湖”工程的实施[J]. 中国园林, 2022, 38(1):88-93.
|
| [5] |
樊凯, 张建生, 裴文娟, 等. 云南省三大高原湖泊流域土地利用景观格局及其稳定性分析[J]. 西南农业学报, 2018, 31(8):1706-1711.
|
| [6] |
马小霞. 新时代中国高原湖泊流域保护治理的几点思考[J]. 中国国土资源经济, 2021, 34(7):14-19.
|
| [7] |
鲁宏旺, 胡文敏, 佘济云, 等. 生态退杨对洞庭湖湿地景观格局变化影响研究[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 44(3): 171-178.
|
| [8] |
陈文波, 肖笃宁, 李秀珍. 景观指数分类、应用及构建研究[J]. 应用生态学报, 2002, 13(1):121-125.
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
杨婉清, 杨鹏, 孙晓, 等. 北京市景观格局演变及其对多种生态系统服务的影响[J]. 生态学报, 2022, 42(16):6487-6498.
|
| [12] |
王双, 刘永强. 浙江省土地景观格局演变及其生态服务价值效应分析[J]. 上海国土资源, 2021, 42(3):63-70.
|
| [13] |
王圳峰, 王欣珂, 谢香群, 等. 基于GWR模型的福建省绿色空间景观格局演变影响因素及其空间差异[J]. 西北林学院学报, 2022, 37(5):242-250.
|
| [14] |
王春晓, 黄舒语, 苗菁, 等. 珠三角基塘景观格局演变特征及驱动因素研究:以佛山顺德区为例[J]. 中国园林, 2022, 38(6):75-80.
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
侯鹏, 高吉喜, 陈妍, 等. 中国生态保护政策发展历程及其演进特征[J]. 生态学报, 2021, 41(4):1656-1667.
|
| [19] |
林琰, 董加云. 森林生态保护政策中多元利益共生的实现路径[J]. 林业经济问题, 2021, 41(3):271-277.
|
| [20] |
牛远, 胡小贞, 王琳杰, 等. 抚仙湖流域山水林田湖草生态保护修复思路与实践[J]. 环境工程技术学报, 2019, 9(5):482-490.
|
| [21] |
尹娟, 资本飞, 阳利永, 等. 抚仙湖流域生态用地时空演变及其驱动因素[J]. 水土保持通报, 2020, 40(6):228-235,331.
|
| [22] |
赵筱青, 李思楠, 谭琨, 等. 基于功能空间分类的抚仙湖流域“3类空间”时空格局变化[J]. 水土保持研究, 2019, 26(4):299-305,313.
|
| [23] |
李思楠, 赵筱青, 谭琨, 等. 基于GIS的抚仙湖流域土地利用时空变化研究[J]. 人民长江, 2019, 50(6):63-69,87.
|
| [24] |
李石华, 周峻松, 王金亮. 1974—2014年抚仙湖流域土地利用/覆盖时空变化与驱动力分析[J]. 国土资源遥感, 2017, 29(4):132-139.
|
| [25] |
刘娇, 张超, 余哲修, 等. 基于Landsat影像的抚仙湖流域土地利用变化及预测研究[J]. 西南林业大学学报(自然科学), 2020, 40(3):131-138.
|
| [26] |
杨娅楠, 王金亮, 陈光杰, 等. 抚仙湖流域土地利用格局与水质变化关系[J]. 国土资源遥感, 2016, 28(1):159-165.
|
| [27] |
赵筱青, 苗培培, 普军伟, 等. 抚仙湖流域土地利用变化及其生态系统生产总值影响[J]. 水土保持研究, 2020, 27(2):291-299.
|
| [28] |
孔维琳, 王余舟, 向伶, 等. 抚仙湖流域植被景观格局分析[J]. 云南大学学报(自然科学版), 2012, 34(4):468-475.
|
| [29] |
王秀兰, 包玉海. 土地利用动态变化研究方法探讨[J]. 地理科学进展, 1999, 18(1):81-87.
|
| [30] |
杨静, 庄家尧, 张金池. 基于RS和GIS的徐州市20年间土地利用变化研究[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2013, 37(2): 85-91.
|
| [31] |
朱会义, 李秀彬. 关于区域土地利用变化指数模型方法的讨论[J]. 地理学报, 2003, 58(5):643-650.
|
| [32] |
岑晓腾. 土地利用景观格局与生态系统服务价值的关联分析及优化研究:以杭州湾南岸区域为例[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2016.
|
| [33] |
谢高地, 鲁春霞, 冷允法, 等. 青藏高原生态资产的价值评估[J]. 自然资源学报, 2003, 18(2):189-196.
|
| [34] |
王朋冲, 于强, 裴燕如, 等. 翁牛特旗景观格局尺度效应分析[J]. 农业机械学报, 2020, 51(5):223-231,181.
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |