 PDF(2719 KB)
PDF(2719 KB)


西南地区不同下垫面雷电活动特征与森林雷击火的关系
李岩松, 杨艳蓉, 张文艺, 张乐英, 黄傲, 张贻荣
南京林业大学学报(自然科学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 48 ›› Issue (3) : 219-228.
 PDF(2719 KB)
PDF(2719 KB)
 PDF(2719 KB)
PDF(2719 KB)
西南地区不同下垫面雷电活动特征与森林雷击火的关系
Relationship between characteristics of lightning activity on different underlying surface and forest lightning fire in southwest China
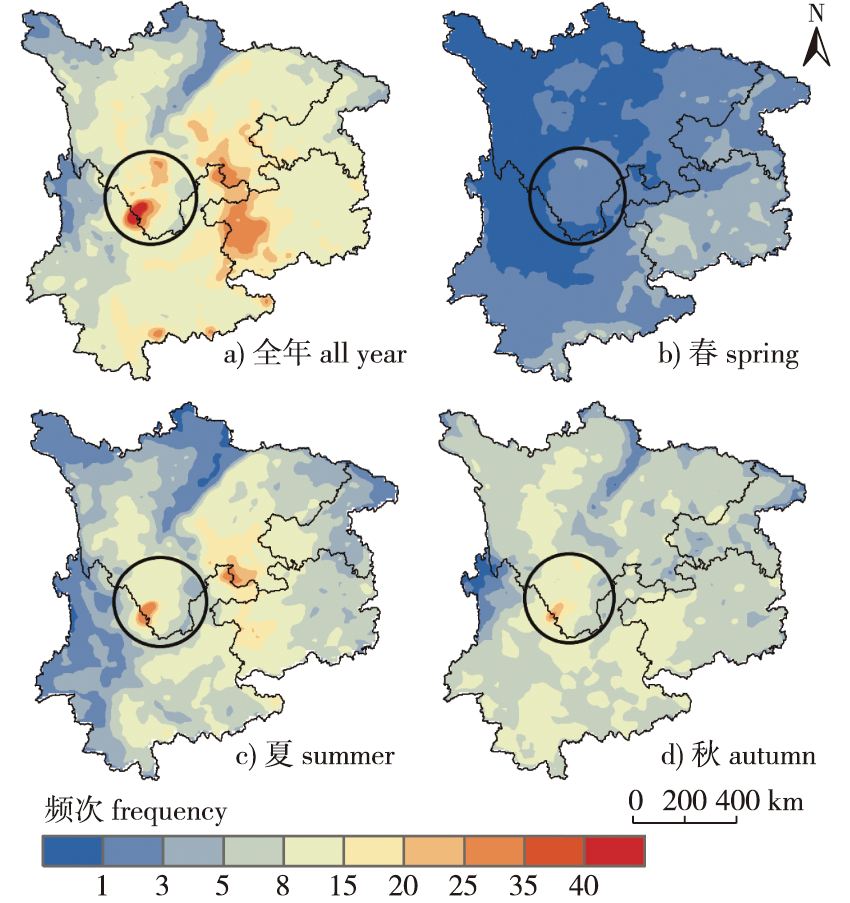
【目的】 西南地区是我国第二大天然林区,该地生态系统脆弱,森林雷击火灾频发。通过遥感、探测资料分析不同地表覆盖类型、不同海拔下垫面的雷电活动特征,探究雷电活动对森林雷击火的影响。【方法】 根据2005—2017年全球闪电定位系统(WWLLN)闪电数据、MCD12Q1土地覆盖数据、SRTM(shuttle radar topography mission)海拔数据以及相应森林雷击火个例,结合Theil-Sen趋势分析、Mann-Kendall趋势检验、相对密度差分析,对我国西南地区雷电活动随下垫面类型、海拔的变化特征及其与森林雷击火的关系进行研究。【结果】 ① 2005—2017年西南地区云地闪频次以每年8.75%的速率增加。四川和云南交界的攀枝花附近区域是最高值核心区。② 海拔500~1 000 m、稀树草原类下垫面年均云地闪频次最多。以相对密度差表征雷电活跃程度,从季节上看,春季最活跃;从昼夜变化尺度上看,昼间最活跃。表现活跃的下垫面集中在海拔0~1 000 m段,以及农用地/自然植被拼接、稀树草原类和城区为主的地表类型。③ 云地闪在不同下垫面均呈增长趋势,其增长面积占比为西南地区的93.48%。其中,海拔3 500 m以上和草地类型下垫面的增长趋势最显著,从海拔和地表类型来看,显著的面积占比均超过80%。④ 年云地闪频次越高,发生森林雷击火的概率越大。海拔0~1 000 m森林雷击火发生与云地闪活动的下垫面特点一致,海拔1 000 m以上雷击火主要受高云地闪频次影响。【结论】 西南地区雷电活动与下垫面的海拔、地表类型关系密切,且这一关系随不同时间尺度而变化。作为森林雷击火的起因,结合下垫面特征分析雷电活动,探究森林雷击火,可以为西南山地天然林保护提供科学支撑。
【Objective】 Southwest China is the second largest natural forest region in China, where the ecosystem is fragile and forest lightning fire disasters occur frequently. According to the causal relationship between lightning and forest lightning fire, the characteristics of lightning activities on underlying surfaces with different land cover types and different altitudes, and the influence of lightning activity on forest lightning fire is explored. 【Method】 Based on WWLLN lightning data, land cover data MCD12Q1, altitude data SRTM and corresponding lightning forest fires from 2005 to 2017, combined with Theil-Sen trend analysis, Mann-Kendall trend test, relative density difference analysis. The variation characteristics of lightning activity with underlying surface type and altitude in southwest China and its relationship with forest lightning fire were studied.【Result】 (1) From 2005 to 2017, the cloud-to-ground lightning frequency in southwest China increased at a rate of 8.75% per year. The area near Panzhihua at the border of Sichuan and Yunnan maintains the core area of the highest value in years and seasons. (2) The annual cloud-to-ground lightning frequency was the highest in the underlying surface of savanna at an altitude of 500-1 000 m. The degree of lightning activity is characterized by the relative density difference. It is most active in spring and most active in daytime on a daily scale. The active surface types are concentrated in the 0-1 000 m elevation, Agricultural land/natural vegetation Mosaic, savanna type and urban type. (3) Cloud-to-ground lightning showed an increasing trend in different underlying surfaces, and its area accounted for 93.48% in southwest China. Among them, the growth trend of underlying surface of above 3 500 m altitude and grassland type is the most significant, and the significant area accounts for more than 80% from the elevation and surface type respectively. (4) The higher the annual cloud-to-ground lightning frequency, the greater the probability of lightning fire. The occurrence of forest lightning fire at 0-1 000 m altitude is consistent with the characteristics of the underlying surface of cloud-to-ground lightning distribution, and the lightning fire above 1 000 m altitude is mainly affected by high cloud-to-ground lightning frequency. 【Conclusion】 The lightning activity in southwest China is closely related to the underlying surface altitude and surface type, and the relationship varies with different time scales. As the cause of forest lightning fire, the analysis of lightning activity and forest lightning fire combined with the characteristics of underlying surface can provide scientific support for the protection of natural forest in southwest mountainous area.
森林雷击火 / 云地闪 / 海拔 / 地表覆盖类型 / 西南地区
lightning caused forest fire / cloud-to-ground lightning / altitude / land cover type / southwest China
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
赵生昊, 杨磊. 基于MODIS数据的地表覆盖种类与地闪分布特征关系研究[J]. 气象科技, 2016, 44(5): 822-827.
|
| [8] |
吴量, 郭媛, 向清才. 河池市闪电活动与下垫面植被类型关系分析[J]. 气象研究与应用, 2019, 40(1): 62-64.
|
| [9] |
卢友发, 吴世安. 河南省闪电活动与复杂下垫面之间的相关性分析[J]. 信阳师范学院学报(自然科学版), 2017, 30(1): 87-91.
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
李政, 肖稳安, 李家启, 等. 区域海拔高度变化对闪电特征影响的初步分析[J]. 湖北大学学报(自然科学版), 2011, 33(2): 197-201.
|
| [13] |
王凯, 周丽雅, 鞠晓雨, 等. 2011—2019年中国长江三角洲区域闪电时空分布特征[J]. 气象与环境学报, 2021, 37(4): 100-106.
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
尹赛男, 王东昶, 单延龙, 等. 黑龙江省3种主要火源引发森林火灾的次数和面积时空分布特征[J]. 林业科学, 2021, 7(6): 115-124.
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
何诚, 舒立福, 刘柯珍. 大兴安岭地区夏季森林火灾环境因子特征分析[J]. 西南林业大学学报(自然科学), 2021, 41(3): 87-93.
|
| [22] |
杨少斌, 曹萌, 祝鑫海, 等. 2001—2019年内蒙古大兴安岭北部原始林区森林火灾发生规律研究[J]. 灾害学, 2022, 37 (3): 122-128.
|
| [23] |
杜野. 内蒙古北部原始林区的雷击火分布规律研究[J]. 森林防火, 2017(4): 28-31.
|
| [24] |
靖娟利, 和彩霞, 王永锋, 等. 西南地区1902-2018年干旱时空演变特征分析[J]. 水土保持研究, 2022, 29(3): 220-227.
|
| [25] |
田晓瑞, 舒立福, 赵凤君, 等. 气候变化对中国森林火险的影响[J]. 林业科学, 2017, 53(3): 159-169.
|
| [26] |
刘晔, 李鹏, 许玥, 等. 中国西南干旱河谷植物群落的数量分类和排序分析[J]. 生物多样性, 2016, 24(4): 378-388.
|
| [27] |
杨艳蓉, 侯召朕, 张增信. 2001—2018年西南地区NDVI变化特征及影响因素[J]. 水土保持通报, 2021, 41(2): 337-344.
|
| [28] |
舒洋, 孙子瑜, 张恒. 世界森林雷击火研究现状和展望[J]. 世界林业研究, 2022, 35(2):34-40.
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
马金福, 冯志伟. 雷击地闪密度与雷暴日数的关系分析[J]. 气象科学, 2009, 29(5): 674-678.
|
| [31] |
李洪广, 周旭, 肖杨, 等. 基于SRP模型的西南喀斯特山区生态脆弱性时空变化特征[J]. 生态科学, 2021, 40(3): 238-246.
|
| [32] |
杨宗凯, 刘平英, 胡颖, 等. 云南省雷电活动分布特征及对农村地区的影响分析[J]. 中国农业资源与区划, 2018, 39(9): 262-267.
|
| [33] |
杨水泉, 熊晓洪. 利用LIS/OTD格点资料分析西南地区闪电活动的气候分布特征[J]. 广西气象, 2006(S3): 60-66.
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
王学良, 张科杰, 余田野, 等. 湖北地区云地闪电频次及雷电流幅值时间分布特征[J]. 电瓷避雷器, 2017(3): 1-9.
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
王义耕, 刘洁, 王介君, 等. 卫星观测的西南地区闪电的时空分布[J]. 大气科学学报, 2010, 33(4): 489-495.
|
| [38] |
成鹏伟, 周筠珺, 赵鹏国, 等. 北京与成都城市下垫面闪电时空分布特征对比研究[J]. 成都信息工程大学学报, 2018, 33(3): 326-334.
|
| [39] |
许洪泽, 周梅. ADTD异常对闪电定位资料影响分析[J]. 气象科技进展, 2018, 8(1): 33-37.
|
| [40] |
邓雨荣, 李涵, 朱时阳, 等. 基于卫星资料的全球闪电定位系统探测效率评估[J]. 气象科学, 2015, 35(5): 599-604.
|
| [41] |
|
| [42] |
|
| [43] |
|
| [44] |
岳超, 罗彩访, 舒立福, 等. 全球变化背景下野火研究进展[J]. 生态学报, 2020, 40(2): 385-401.
|
| [45] |
孙龙, 窦旭, 胡同欣. 林火对森林生态系统碳氮磷生态化学计量特征影响研究进展[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 45(2): 1-9.
|
| [46] |
张宏民, 乔艺骞, 唐珑坪, 等. 模拟雷击明火点燃松针燃料的实验研究[J]. 工程热物理学报, 2022, 43(3): 840-845.
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |