 PDF(1762 KB)
PDF(1762 KB)


不同载体菌肥对紫穗槐生长和光合特性及土壤养分的影响
杨皓, 刘超, 庄家尧, 张树同, 张文韬, 毛国豪
南京林业大学学报(自然科学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 48 ›› Issue (3) : 81-89.
 PDF(1762 KB)
PDF(1762 KB)
 PDF(1762 KB)
PDF(1762 KB)
不同载体菌肥对紫穗槐生长和光合特性及土壤养分的影响
Effects of different carrier bacterial fertilizers on growth, photosynthetic characteristics and soil nutrients of Amorpha fruticosa
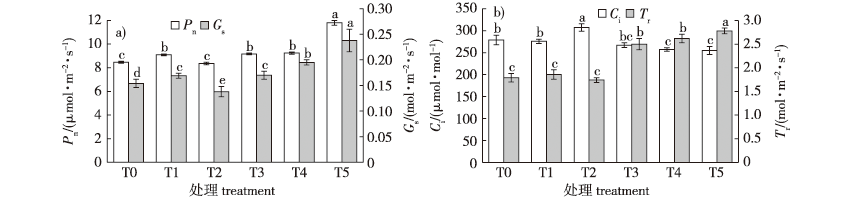
【目的】 探究接种不同载体基质制备的粘质沙雷氏菌(Serratia marcescens N1.14,X-45)菌肥对植物生长、光合特性和土壤pH及速效养分的影响,筛选能有效替代泥炭的菌肥载体,为微生物肥料的研发提供参考。【方法】 以紫穗槐(Amorpha fruticosa)幼苗为对象,分别施用泥炭载体菌肥(处理T0,CK)、单一秸秆载体菌肥(处理T1)、单一麦麸载体菌肥(处理T2)、秸秆与麦麸(体积比1∶1)载体菌肥(处理T3)、秸秆和麦麸与棉籽壳(体积比1∶1∶1)载体菌肥处理组(处理T4)、秸秆和麦麸与豆饼(体积比1∶1∶1)栽体菌肥(处理T5),对比分析不同载体菌肥的施用对紫穗槐生长特性、光合特性以及土壤养分的影响。【结果】 与CK(T0)相比:①T2、T3、T4、T5处理下紫穗槐生长状况均显著提升,以T3处理最为显著;②T1、T3、T4、T5处理对紫穗槐叶片的各项光合特性指标参数均有不同程度改善效应,其中气体交换参数以T5处理改善效果最为显著,叶绿素含量以T3处理改善效果最为明显。复合菌肥载体比单一菌肥对佳士科技光合特性的改善效果更好;③T3、T4、T5处理下紫穗槐土壤养分含量有所提高。【结论】 秸秆与麦麸处理、秸秆和麦麸与豆饼处理的促生菌肥可促进紫穗槐生长发育并提高其光合效率、优化土壤营养环境、提高土壤肥力,能有效替代泥炭载体菌肥发挥效能。
【Objective】 This study explored the effects of Serratia marcescens N1.14, X-45 bacterial fertilizer inoculated with different carrier substrates on the growth, photosynthetic characteristics, soil pH and available nutrients of Amorpha fruticosa. Based on this, bacterial fertilizer carriers that can effectively replace rare resource peat were determined in order to provide a theoretical basis for the development of microbial fertilizers.【Method】 Taking A. fruticosa seedlings as the object, the peat bacterial fertilizer (T0, CK), straw bacterial fertilizer (T1), wheat bran bacterial fertilizer (T2), straw and wheat bran as carrier bacterial fertilizer (volume ratio = 1∶1, T3), straw wheat bran and cotton seed hull as carrier bacterial fertilizer (volume ratio = 1∶1∶1, T4), and straw wheat bran and soybean cake as carrier bacterial fertilizer (volume ratio = 1∶1∶1, T5) were applied. Through comparative analysis, the effects of the application of different carrier bacterial fertilizer on the growth characteristics, photosynthetic characteristics and soil nutrients of A. fruticosa were explored, and treatment groups that can replace peat bacterial fertilizer were selected.【Result】 Compared with CK, there were three key findings. First, the growth statuses of T2, T3, T4, and T5 were significantly improved, especially T3. Second, the photosynthetic characteristic parameters of Amorpha fruticosa leaves under T1, T3, T4, and T5 improved to varying degrees. Among the gas exchange parameters, T5 had the most significant improvement effect, and T3 had the most obvious improvement effect on chlorophyll content. At the same time, the improvement effect of compound carrier bacterial fertilizer was better than that of single bacterial fertilizer. Third, the soil nutrient content of A. fruticosa under T3, T4, and T5 treatments increased.【Conclusion】 The straw, wheat bran and soybean cake as carrier bacterial fertilizers can promote the growth and development of A. fruticosa, improve photosynthetic characteristics, optimize the soil nutrient environment, improve soil fertility, and effectively replace peat carrier bacterial fertilizer.
微生物菌肥 / 紫穗槐 / 生长特性 / 光合特性 / 土壤养分
microbial fertilizer / Amorpha fruticosa / growth characteristics / photosynthetic characteristics / soil nutrient
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
王景超, 于晓菲, 商姗姗. 我国微生物肥料研究现状及其在作物上的应用进展[J]. 农业与技术, 2022, 42(1):34-37.
|
| [3] |
王应兰. 解磷微生物细菌的筛选、鉴定及其制备肥料的研究[D]. 贵阳: 贵州大学, 2020.
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
李永兴, 匡柏健, 李久蒂. 不同载体对微生物菌剂质量的影响[J]. 土壤肥料, 1999(6):25-27.
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
万永霞. 紫穗槐的价值及其繁殖[J]. 特种经济动植物, 2004, 7(1):31.
|
| [9] |
孟剑侠. 丛枝菌根真菌对紫穗槐固氮能力的影响[D]. 哈尔滨: 黑龙江大学, 2009.
|
| [10] |
韩华雯. 几种新型植物根际促生菌肥载体筛选及研究[D]. 兰州: 甘肃农业大学, 2013.
|
| [11] |
陈福明, 陈顺伟. 混合液法测定叶绿素含量的研究[J]. 浙江林业科技, 1984, 4(1):19-23,36.
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
何海洋, 彭方仁, 张瑞, 等. 不同品种美国山核桃嫁接苗光合特性比较[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2015, 39(4):19-25.
|
| [14] |
季艳红, 潘平平, 窦全琴, 等. 不同泥炭替代基质对薄壳山核桃幼苗生长及叶绿素荧光特性的影响[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 46(1):145-155.
|
| [15] |
邹锦丰, 周传志. 微生物肥料研究进展及发展前景[J]. 现代农业科技, 2021(22):142-144.
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
卢培娜. 菌肥与腐熟秸秆对盐碱地燕麦土壤微生态环境的调控机制[D]. 呼和浩特: 内蒙古农业大学, 2021.
|
| [20] |
段志慧. 水培下复合微生物菌剂对香蕉根系诱导抗枯萎病的影响[D]. 南京: 南京农业大学, 2020.
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
蔡琪琪, 王堽, 董寅壮, 等. 不同中性盐胁迫对甜菜幼苗光合作用和抗氧化酶系统的影响[J]. 作物杂志, 2022(1):130-136.
|
| [23] |
兰艳, 伍鑫, 王锦, 等. 施氮量对绿米稻叶绿素含量及光合特性的影响[J]. 云南农业大学学报(自然科学), 2021, 36(4):566-572.
|
| [24] |
潘小怡. 小麦压青和生物菌肥对连作花生土壤理化性质和产量形成的影响[D]. 泰安: 山东农业大学, 2021.
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
罗永忠, 成自勇. 水分胁迫对紫花苜蓿叶水势、蒸腾速率和气孔导度的影响[J]. 草地学报, 2011, 19(2):215-221.
|
| [27] |
杨玉玲, 刘文兆, 王俊, 等. 配施钾肥、有机肥对旱地春玉米光合生理特性和产量的影响[J]. 西北农业学报, 2009, 18(3):116-121.
|
| [28] |
苑丽彩. 不同肥料配施对设施番茄生长、品质、病虫害和产量的影响[D]. 新乡: 河南科技学院, 2016.
|
| [29] |
王鹰翔. 不同土壤菌配置对紫穗槐幼苗生理生态学特性的影响[D]. 南京: 南京林业大学, 2017.
|
| [30] |
王涛, 雷锦桂, 黄语燕, 等. 绣球菌渣复合基质对黄瓜幼苗素质及产量的影响[J]. 核农学报, 2020, 34(1):177-185.
|
| [31] |
姚乔花, 程永龙, 王姣敏, 等. FM-生物菌肥在设施温室马铃薯微型薯生产中的应用[J]. 中国果菜, 2021, 41(12):60-65.
|
| [32] |
丁伟, 辛睿滢. 莠去津土壤残留生物修复菌肥作用原理与田间应用[J]. 植物保护, 2021, 47(3):83-88.
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
褚义红. 不同微生物菌肥对温室生菜生长、品质、产量及氮素积累的影响[D]. 呼和浩特: 内蒙古农业大学, 2014.
|
| [36] |
陈娜丽. 固定化固氮菌的制备及其性能的研究[D]. 兰州: 西北师范大学, 2003.
|
| [37] |
赵玥. 芽孢杆菌的筛选及在复合菌肥中应用研究[D]. 长春: 吉林农业大学, 2020.
|
| [38] |
王爱斌, 宋慧芳, 张流洋, 等. 生物肥和菌肥对蓝莓苗生长及土壤养分的影响[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 44(6):63-70.
|
| [39] |
李海云, 姚拓, 韩华雯, 等. 不同载体及菌肥浸提液对苏丹草种子萌发的影响[J]. 草原与草坪, 2018, 38(5):28-34,42.
|
| [40] |
成思轩, 于嘉欣, 肖析蒙, 等. 一种微生物菌肥对雷竹笋生长、土壤养分及微生物的影响[J]. 安徽农学通报, 2021, 27(1):106-109.
|
| [41] |
施燕华. 添加巨大芽孢杆菌对于干旱胁迫下紫花苜蓿幼苗生长影响的研究[D]. 扬州: 扬州大学, 2022.
|
| [42] |
涂保华, 符菁, 赵远, 等. 基于光合菌剂的复合微生物菌肥对土壤速效养分含量及微生物群落结构多样性的影响[J]. 西南农业学报, 2019, 32(12):2878-2884.
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |