 PDF(1798 KB)
PDF(1798 KB)


 PDF(1798 KB)
PDF(1798 KB)
 PDF(1798 KB)
PDF(1798 KB)
植物干旱和盐胁迫响应相关miRNA研究进展
Advancements in the research of miRNAs associated with plant drought and salt stress responses
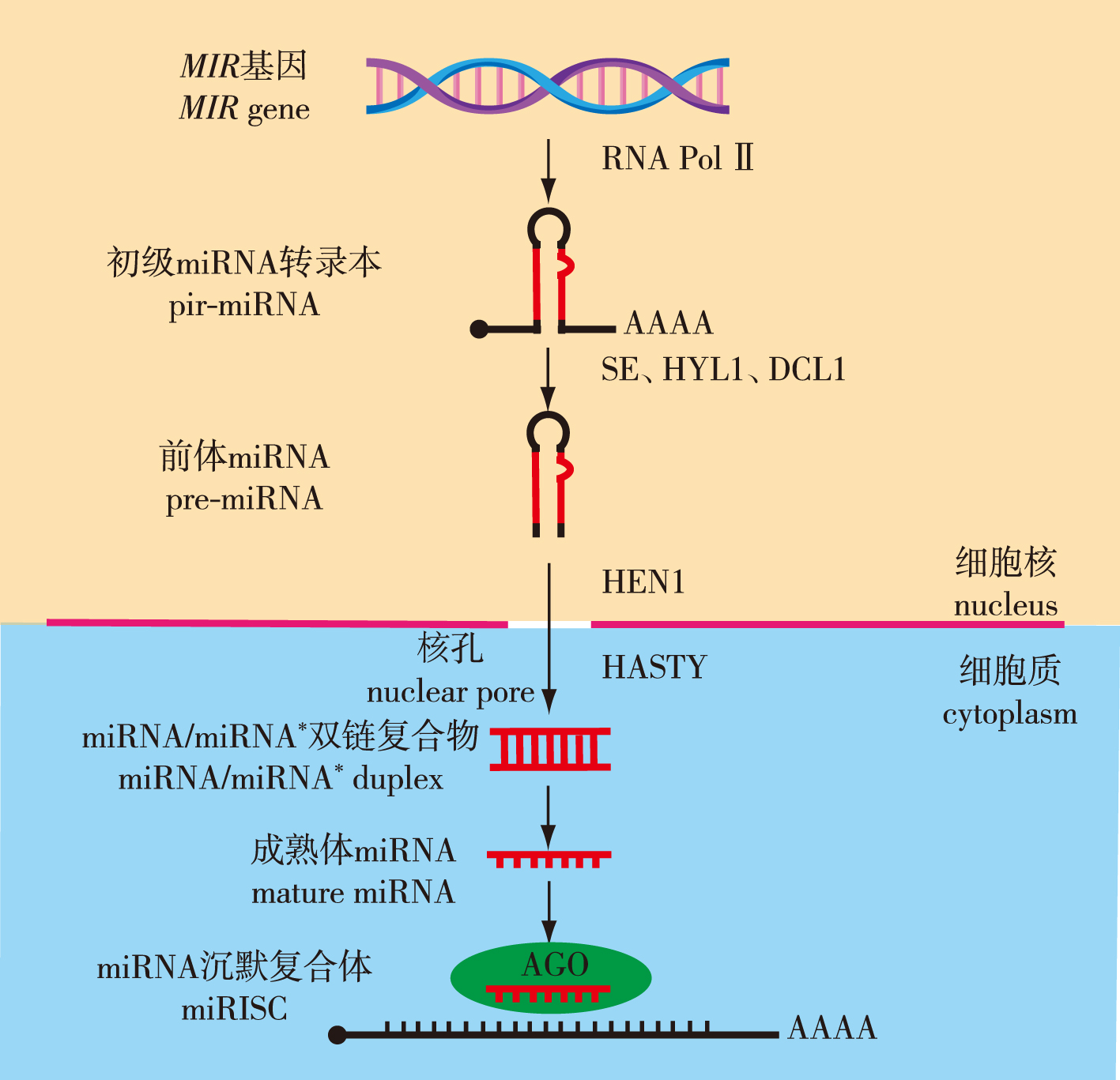
非编码RNA(non-coding RNA,ncRNA)是一类由生物基因组转录产生但不编码蛋白质的遗传信息分子,作为表观遗传学研究的主要内容,曾一度被视为基因组中的“暗物质”或“转录噪音”。最广为人知的微小RNA (microRNA,miRNA)是在进化上高度保守的一类长20~24个核苷酸的短链非编码小分子RNA,通过与靶位点碱基互补配对切割降解靶基因转录本或抑制其翻译,从而实现对生物体生长发育等过程的调控。随着小RNA测序和降解组测序等miRNA研究手段的发展,越来越多的miRNA及其生物学功能在动植物中被相继报道,揭示了miRNA在逆境响应过程中的重要调控作用。笔者较为系统地论述了植物miRNA的特征、合成过程、作用方式及其在抗旱耐盐方面的研究进展,以期揭示植物抗旱耐盐的miRNA调控机理,为创制抗旱耐盐新种质提供依据。
China is a maritime power with a long coastline and abundant coastal resources. However, this long costline brings vast areas of saline-alkali land. Additionally, global warming has led to more frequent seasonal drought. Under such extreme conditions, the survival rate of most plants is very low. Therefore, research on the molecular mechanisms of drought resistance and salt tolerance is particularly important. Improving the survival rate of plants in arid and saline-alkali areas can bring significant ecological benefits and economic value. Non-coding RNA (ncRNA) is a class of genetic information molecules transcribed from the genome that do not encode proteins. As a major focus of epigenetic research, ncRNAs were once considered the “dark matter” or “transcriptional noise” of the genome. The most well-known type of ncRNA is microRNA (miRNA), a highly conserved class of short non-coding small RNA molecules that are 20-24 nucleotides in length. They regulate the growth and development of organisms by cleaving and degrading target gene transcripts or inhibiting the translation of target genes through complementary base pairing with target sites. With the development of miRNA research methods such as small RNA sequencing and degradome sequencing, an increasing number of miRNAs and their target genes has been reported in animals and plants. Their biological synthesis, processing, maturation, and functional effects have been elucidated. Plant miRNAs complementarily pair with their target genes mostly in the open reading frame, with a full or nearly full complementarity to the target sequences. These characteristics stimulated the rapid development in plant miRNA research, and a large amount of research has revealed important regulatory roles of miRNAs in plant growth, development, and stress responses. This article provides a systematic review of the features, synthesis process, mode of action, and research progress of plant miRNAs in drought and salt resistance. We summarizes the main techniques and strategies for plant miRNA research in recent years, discuss the existing problems and prospects, and reveals the regulatory mechanisms of miRNA in plant drought and salt resistance, providing a basis for generating new varieties of drought and salt resistance.
非编码RNA / 盐胁迫 / 干旱胁迫 / 小RNA测序 / 降解组
non-coding RNA / salt stress / drought stress / small RNA-Seq / degradome
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
|
| [40] |
|
| [41] |
|
| [42] |
|
| [43] |
|
| [44] |
董淼, 黄越, 陈文铎, 等. 降解组测序技术在植物miRNA研究中的应用[J]. 植物学报, 2013, 48(3):344-353.
|
| [45] |
|
| [46] |
|
| [47] |
|
| [48] |
|
| [49] |
|
| [50] |
|
| [51] |
|
| [52] |
|
| [53] |
|
| [54] |
|
| [55] |
郑文清, 张倩, 杜亮. 短串联靶标模拟技术及其在植物miRNA功能研究中的应用[J]. 生物技术通报, 2020, 36(12):256-264.
|
| [56] |
|
| [57] |
|
| [58] |
|
| [59] |
|
| [60] |
|
| [61] |
|
| [62] |
|
| [63] |
|
| [64] |
|
| [65] |
|
| [66] |
|
| [67] |
|
| [68] |
|
| [69] |
|
| [70] |
黎家, 李传友. 新中国成立70年来植物激素研究进展[J]. 中国科学:生命科学, 2019, 49(10):1227-1281.
|
| [71] |
|
| [72] |
|
| [73] |
|
| [74] |
|
| [75] |
|
| [76] |
|
| [77] |
|
| [78] |
|
| [79] |
|
| [80] |
|
| [81] |
|
| [82] |
|
| [83] |
|
| [84] |
|
| [85] |
|
| [86] |
|
| [87] |
|
| [88] |
|
| [89] |
|
| [90] |
|
| [91] |
|
| [92] |
|
| [93] |
|
| [94] |
|
| [95] |
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |