 PDF(2626 KB)
PDF(2626 KB)


极端气候对美国白蛾在我国潜在适生区分布的影响预测
薛明宇, 郝德君, 赵旭东, 耿薏舒, 胡天义, 解春霞
南京林业大学学报(自然科学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 48 ›› Issue (5) : 197-203.
 PDF(2626 KB)
PDF(2626 KB)
 PDF(2626 KB)
PDF(2626 KB)
极端气候对美国白蛾在我国潜在适生区分布的影响预测
Effects of extreme climate on the distribution and potential habitat of Hyphantria cunea in China
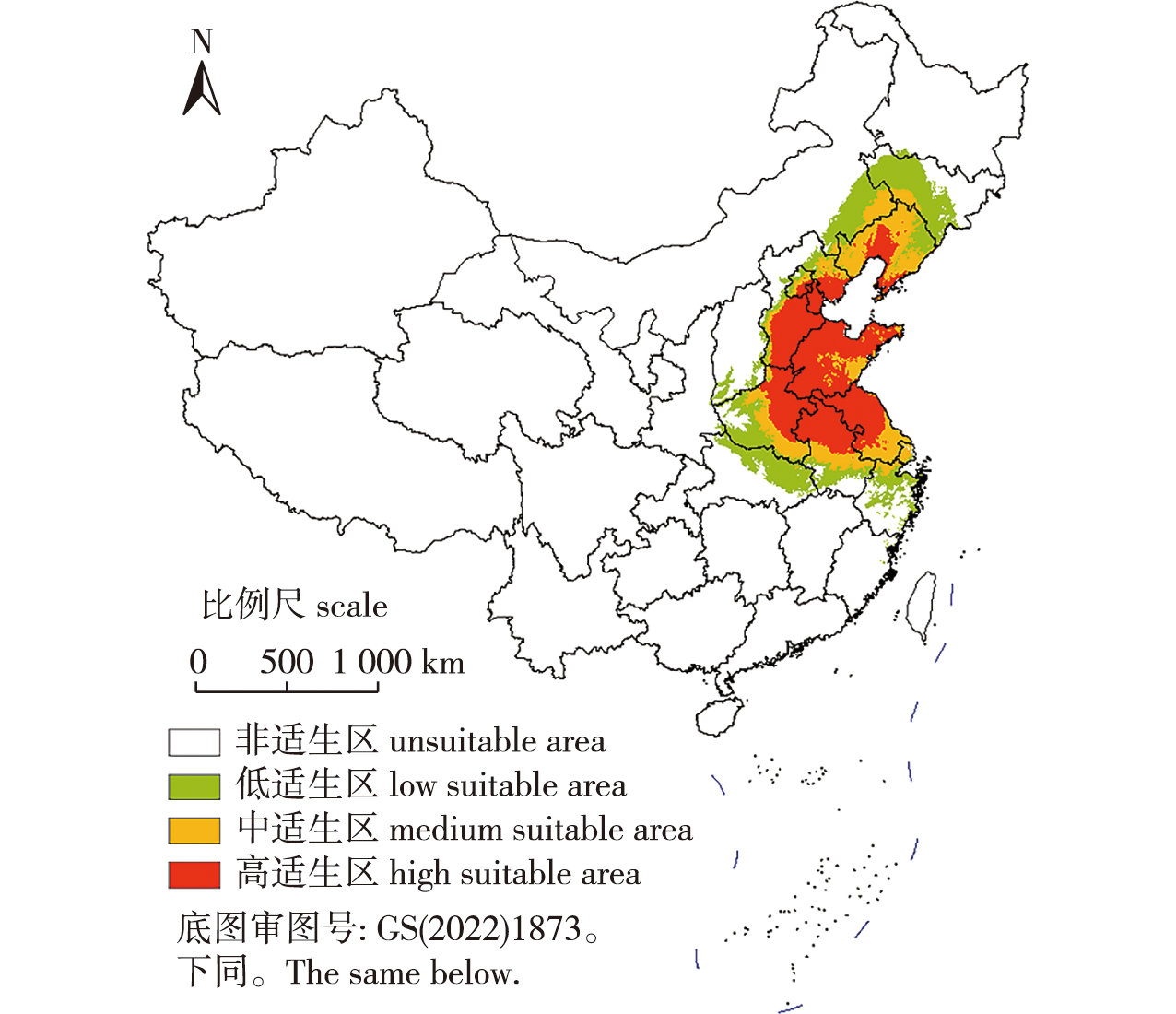
【目的】预测极端气候条件下美国白蛾在我国的潜在适生区分布,为有效防控美国白蛾扩散及对潜在适生区美国白蛾的监测预警提供依据。【方法】收集美国白蛾分布数据,获取当代和未来的低温室气体排放和高温室气体排放情境下的生物气候变量数据、极端气候指数数据,利用ArcGIS和DIVA-GIS对数据进行处理,筛选出相关系数<0.8且对美国白蛾潜在分布概率贡献大的气候变量,将其代入MaxEnt进行运算,获得美国白蛾当代、2021—2040、2041—2060、2061—2080年的潜在适生区,并根据适生区重心的相对位置判断适生区的空间变化。【结果】日最大降水量、暖日持续指数、冷夜日数占比、最湿季度平均气温是影响美国白蛾分布的重要气候变量。当前环境下美国白蛾的潜在适生区主要分布在华北东部、东北南部、黄淮、江淮、江南东部、江汉北部。无论何种情境,美国白蛾未来将向西南方向扩散,到达川渝一带,并在两广交界处有零散分布。【结论】极端降水是影响美国白蛾分布的重要因素,美国白蛾适宜生活在气候特征较为稳定的地区。基于极端气候指数预测表明,美国白蛾未来60年在我国呈现向西南方向扩散的风险。
【Objective】This study aims to predict the potential habitat of Hyphantria cunea under extreme climate conditions in China. 【Method】The occurrence data of H. cunea were obtained. Contemporary and future bioclimatic variables and extreme climate index data were processed using ArcGIS and DIVA-GIS. Environmental variables with low correlation coefficients and high contribution rates were selected. These variables were input into MaxEnt to calculate the potential habitats of H. cunea for the contemporary period, 2021 to 2040, 2041 to 2060, and 2061 to 2080. The spatial changes in the habitats were expressed by the relative positions of the centroids of the habitats. 【Result】The maximum daily precipitation, warm spell duration index, percentage of nights when the minimum temperature is below the 10th percentile, and mean temperature of the wettest quarter were important variables affecting the distribution of H. cunea. The potential habitat of H. cunea was currently mainly distributed in eastern, northern, and northeastern China, as well as the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River. In the future, H. cunea might spread to southwest China, reaching Sichuan and Chongqing, with scattered distributions in Guangdong and Guangxi. 【Conclusion】The extreme precipitation is an important factor affecting the distribution of H. cunea. H. cunea is adapted to areas with stable climates. Predictions based on the extreme climate index indicate a risk that H. cunea will spread to southwest China in the future.
美国白蛾 / MaxEnt / 潜在适生区 / 极端气候 / 空间分布 / 气候情景
Hyphantria cunea / MaxEnt / potential habitat / extreme climate / spatial distribution / climate scenarios
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
李慧, 郝德君, 徐天, 等. 高温胁迫对植食性昆虫影响研究进展[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 46(6):215-224.
|
| [4] |
贾志怡, 陈聪, 马宇萱, 等. 温度对香樟齿喙象生长发育的影响[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 44(4):131-136.
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
赵旭东, 耿薏舒, 郝德君, 等. 美国白蛾防控技术的研究进展及展望[J]. 中国森林病虫, 2022, 41(5):44-52.
|
| [9] |
孔雪华, 杨洛滨, 韩世德, 等. 高温对美国白蛾生长发育的影响研究[J]. 山东林业科技, 2009, 39(6):35-37.
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
纪烨琳, 苏喜友, 于治军. 基于随机森林模型的美国白蛾在中国的潜在生境预测[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 43(6):121-128.
|
| [15] |
国家林业和草原局公告(2021年第7号)(2021年美国白蛾疫区)[EB/OL].
NFGA. National Forestry and Grassland Administration Announcement [2021] No.7:The affected areas of Hyphantria. cunea in 2021 (2021-03-30) [2022-12-25] http://www.forestry.gov.cn/main/6206/20220407/094424748508406.html.
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
李淑清. 甜菜夜蛾的生长发育与温湿度的关系[J]. 华中农业大学学报, 2002, 21(4):352-355.
|
| [18] |
罗礼智, 程云霞, 唐继洪, 等. 温湿度是影响草地螟发生为害规律的关键因子[J]. 植物保护, 2016, 42(4):1-8.
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
问锦曾, 王海鸿, 胡平, 等. 降雨对防治美国白蛾药效的影响[J]. 中国植保导刊, 2008, 28(3):41-43.
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
孔锋, 方建, 乔枫雪, 等. 透视中国小时极端降水强度和频次的时空变化特征[J]. 长江流域资源与环境, 2019, 28(12):3051-3067.
|
| [23] |
薛媛, 薛晓萍. 极端降水与干旱同步频发的研究进展[J]. 海洋气象学报, 2022, 42(1):61-73.
|
| [24] |
卢珊, 胡泽勇, 王百朋, 等. 近56年中国极端降水事件的时空变化格局[J]. 高原气象, 2020, 39(4):683-693.
|
| [25] |
胡冬春, 徐富强, 刘旭, 等. 昆虫生长阻滞肽研究进展[J]. 江苏农业学报, 2023, 39(4):1072-1079.
|
| [26] |
叶江霞, 王敬文, 张明莎, 等. 基于空间矩阵模型及0-1测度的美国白蛾风险格局分析[J]. 林业科学, 2021, 57(1):140-152.
|
| [27] |
董欣, 倪相. 西南地区不同海拔极端降水时空变化特征[J]. 西南大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 44(9):110-121.
|
| [28] |
吉戴婧琪, 元媛, 韩剑桥. 中国极端降水事件的时空变化及趋势预测[J]. 中国农村水利水电, 2022(10):74-80.
|
| [29] |
李德斌, 卢修亮, 何姍, 等. 东北地区美国白蛾灾害扩散过程和趋势分析[J]. 中国森林病虫, 2023, 42(2):9-15.
|
| [30] |
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |