 PDF(2570 KB)
PDF(2570 KB)


滇东南地区蚂蚁物种分布格局研究
杨林, 诸慧琴, 徐正会, 张新民, 周雪英, 许国莲, 刘霞
南京林业大学学报(自然科学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 48 ›› Issue (5) : 204-210.
 PDF(2570 KB)
PDF(2570 KB)
 PDF(2570 KB)
PDF(2570 KB)
滇东南地区蚂蚁物种分布格局研究
Distribution patterns of ant species in southeastern Yunnan Province
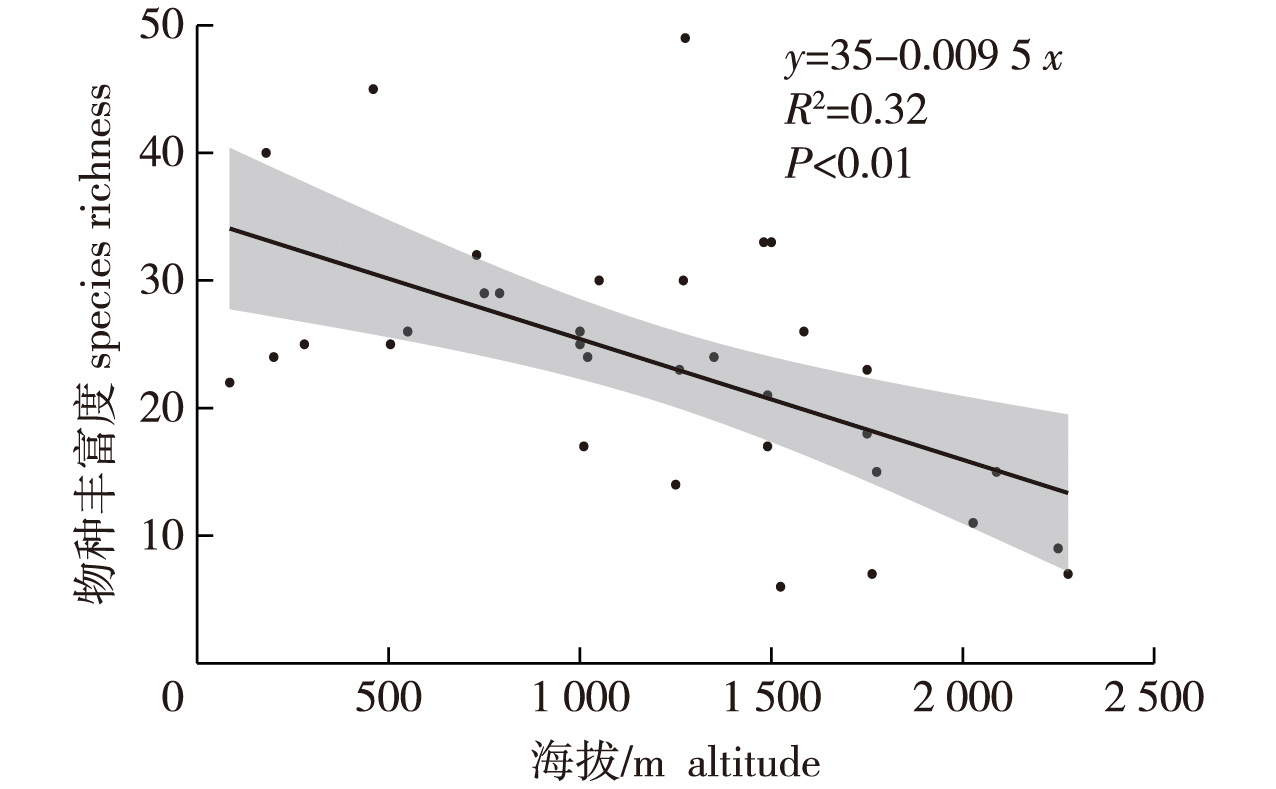
【目的】研究滇东南地区蚂蚁物种的栖息生境、垂直分布、觅食场所和筑巢场所等分布格局和规律,为该区生物多样性编目和保护提供科学依据。【方法】采用样地调查法对滇东南地区蚂蚁物种分布格局进行调查研究,运用采获频数法进行数据统计,并用SPSS 26软件作海拔与蚂蚁物种丰富度间的Pearson相关性分析。【结果】在滇东南地区5个垂直带共发现蚂蚁9亚科64属197种。大多数蚂蚁可在多类植被中栖息,舒尔盘腹蚁(Aphaenogaster schurri)、喜马毛蚁(Lasius himalayanus)等少数蚂蚁只在单类植被中栖息。在13类栖息生境中,处于中低海拔的季风常绿阔叶林蚂蚁物种最丰富(87种),处于高海拔的高山栎林物种数最少(8种)。多数蚂蚁物种生态适应幅度狭窄,垂直分布高差小于500 m;爪哇扁头猛蚁(Ectomomyrmex javana)、黄足尼兰蚁(Nylanderia flavipes)等少数种蚂蚁生态适应幅度宽阔,垂直分布高差大于2 000 m。大多数蚂蚁的觅食和筑巢场所不尽相同,大阪举腹蚁(Crematogaster osakensis)、掘穴蚁(Formica cunicularia)、黑腹臭蚁(Dolichoderus taprobanae)等少数物种选择在多个场所中觅食和筑巢,其中选择在地表、土壤内觅食和筑巢的物种最丰富。相关分析显示,海拔与蚂蚁物种丰富度呈极显著负相关(P<0.01)。【结论】滇东南地区蚂蚁资源较丰富,物种分布格局主要与海拔、植被类型和蚂蚁的适应能力有关。中低海拔区域气候湿热,植被类型丰富,具有充足的食物资源和筑巢场所,物种较丰富;高海拔区域气候寒冷,植被单一,蚂蚁栖息生境较差,物种稀少。蚂蚁的功能特征决定了它的生存能力,大多数物种对环境的选择较为严苛,不同物种分布格局差异明显。
【Objective】The study aimed to investigate the patterns and laws of ant species distribution, including the habitat, vertical distribution, foraging patterns and nesting sites in southeastern Yunnan Province, provide a scientific basis for biodiversity cataloging and protection in this area.【Method】The distribution patterns of ant species in southeastern Yunnan Province were investigated using the plot-sampling method, and the data were counted using the harvesting frequency method. The Pearson correlation between the altitude and species richness of the ants was analyzed using the SPSS 26 software. 【Result】 A total of 197 species of ants, belonging to 64 genera and nine subfamilies under the Formicidae family, were recorded from five vertical zones in southeastern Yunnan Province. The majority of ant species inhabited different vegetation zones; however, a few ants, including Aphaenogaster schurri and Lasius himalayanus, inhabited only a single vegetation type. Of the 13 habitats, the ants (87 species) were most abundant in the middle-and low-altitude monsoon evergreen broadleaf forest, and least abundant (eight species) in the high-altitude Quercus semicarpifolia forest. The majority of ant species had a narrow ecological adaptation range, and the height difference in vertical distribution was less than 500 m. A few species of ants, including Ectomomyrmex javana, Nylanderia flavipes, and others exhibited a wide ecological adaptation range, and the height difference in vertical distribution was greater than 2 000 m. There were differences in the foraging zones and nesting sites of the majority of ant species. A few species, including Crematogaster osakensis, Formica cunicularia and Dolichoderus taprobanae, foraged and nested in multiple sites, and the species that foraged on the ground and nested in the soil were the most abundant. Correlation analysis revealed that the altitude and species richness were significantly negatively correlated at 0.01 level of significance. 【Conclusion】There are abundant resource for ant populations in southeastern Yunnan Province, and the distribution patterns of ant species in the region are primarily related to the altitude, types of vegetation, and adaptability. The species richness was found to be high in the middle-and low-altitude areas, which have a hot and humid climate, rich vegetation types, and sufficient food resources and nesting sites; however, the ants in the high-altitude areas inhabited fewer habitats and their species richness was low due to the cold climate and single type of vegetation. The study revealed that the functional characteristics of the ants determine their viability. The majority of ant species exhibited a strict environmental selection, and there were obvious differences in the distribution patterns of different species.
蚁科物种 / 垂直分布 / 栖息生境 / 觅食场所 / 筑巢场所
Formicidae species / vertical distribution / habitat / foraging place / nesting site
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
徐正会. 西双版纳自然保护区蚁科昆虫生物多样性研究[M]. 昆明: 云南科技出版社, 2002.
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
李巧, 卢志兴, 张威, 等. 金沙江干热河谷人工林地表的蚂蚁群落[J]. 林业科学, 2015, 51(8):134-142.
|
| [5] |
长有德, 贺达汉. 中国西北地区蚂蚁区系特征[J]. 动物学报, 2002, 48(3):322-332.
|
| [6] |
郭萧, 徐正会, 杨俊伍, 等. 滇西北云岭东坡蚂蚁物种多样性研究[J]. 林业科学研究, 2007, 20(5):660-667.
|
| [7] |
黄钊, 徐正会, 刘霞, 等. 滇东北地区的蚂蚁物种多样性[J]. 生态学杂志, 2019, 38(12):3697-3705.
|
| [8] |
诸慧琴, 徐正会, 和玉成, 等. 滇东南地区蚂蚁群落结构研究[J]. 湖北农业科学, 2020, 59(5):113-120.
|
| [9] |
诸慧琴, 徐正会, 张新民, 等. 滇东南地区的蚂蚁物种多样性[J]. 环境昆虫学报, 2019, 41(3):533-544.
|
| [10] |
郭宁妍, 钱昱含, 徐正会, 等. 滇西南地区蚂蚁物种多样性研究[J]. 西南农业学报, 2021, 34(8):1728-1739.
|
| [11] |
郭宁妍, 房华, 徐正会, 等. 滇西南地区蚁科昆虫区系分析[J]. 云南农业大学学报(自然科学), 2022, 37(5):729-742.
|
| [12] |
郭宁妍, 钱昱含, 徐正会, 等. 滇西南地区蚂蚁物种分布格局研究[J]. 云南农业大学学报(自然科学), 2022, 37(1):10-23.
|
| [13] |
莫福燕, 徐正会, 宋扬, 等. 喜马拉雅山亚东段蚂蚁群落研究[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2015, 39(3):85-90.
|
| [14] |
徐正会, 褚姣娇, 张成林, 等. 藏东南工布自然保护区的蚂蚁种类及分布格局[J]. 四川动物, 2011, 30(1):118-123.
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
吴坚, 王常禄. 中国蚂蚁[M]. 北京: 中国林业出版社, 1995.
|
| [17] |
罗成龙, 徐正会, 熊忠平, 等. 四川王朗自然保护区及邻近地区蚂蚁物种的分布格局[J]. 浙江农林大学学报, 2019, 36(4):638-645.
|
| [18] |
徐正会, 曾光, 柳太勇, 等. 西双版纳地区不同植被亚型蚁科昆虫群落研究[J]. 动物学研究, 1999, 20(2):118-125.
|
| [19] |
陈超, 熊忠平, 徐正会, 等. 青藏高原东北坡蚂蚁物种的分布格局[J]. 林业科学研究, 2022, 35(3):131-140.
|
| [20] |
沈梦伟, 陈圣宾, 毕孟杰, 等. 中国蚂蚁丰富度地理分布格局及其与环境因子的关系[J]. 生态学报, 2016, 36(23):7732-7739.
|
| [21] |
翟奖, 李彪, 徐正会, 等. 新疆天山东部与邻近地区蚂蚁种类及其分布规律[J]. 森林与环境学报, 2021, 41(4):431-438.
|
| [22] |
陈又清. 蚂蚁群落与栖境关系研究进展及新趋势[J]. 环境昆虫学报, 2017, 39(4):735-740.
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |