 PDF(2686 KB)
PDF(2686 KB)


南京5种木本植物早春花期物候对城市热岛效应的响应研究
史俐莎, 文书生, 黄小婉, 韩茜, 史正阳
南京林业大学学报(自然科学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 48 ›› Issue (5) : 228-234.
 PDF(2686 KB)
PDF(2686 KB)
 PDF(2686 KB)
PDF(2686 KB)
南京5种木本植物早春花期物候对城市热岛效应的响应研究
The flowering phenology response of five early spring woody plants to the urban heat island effect in Nanjing
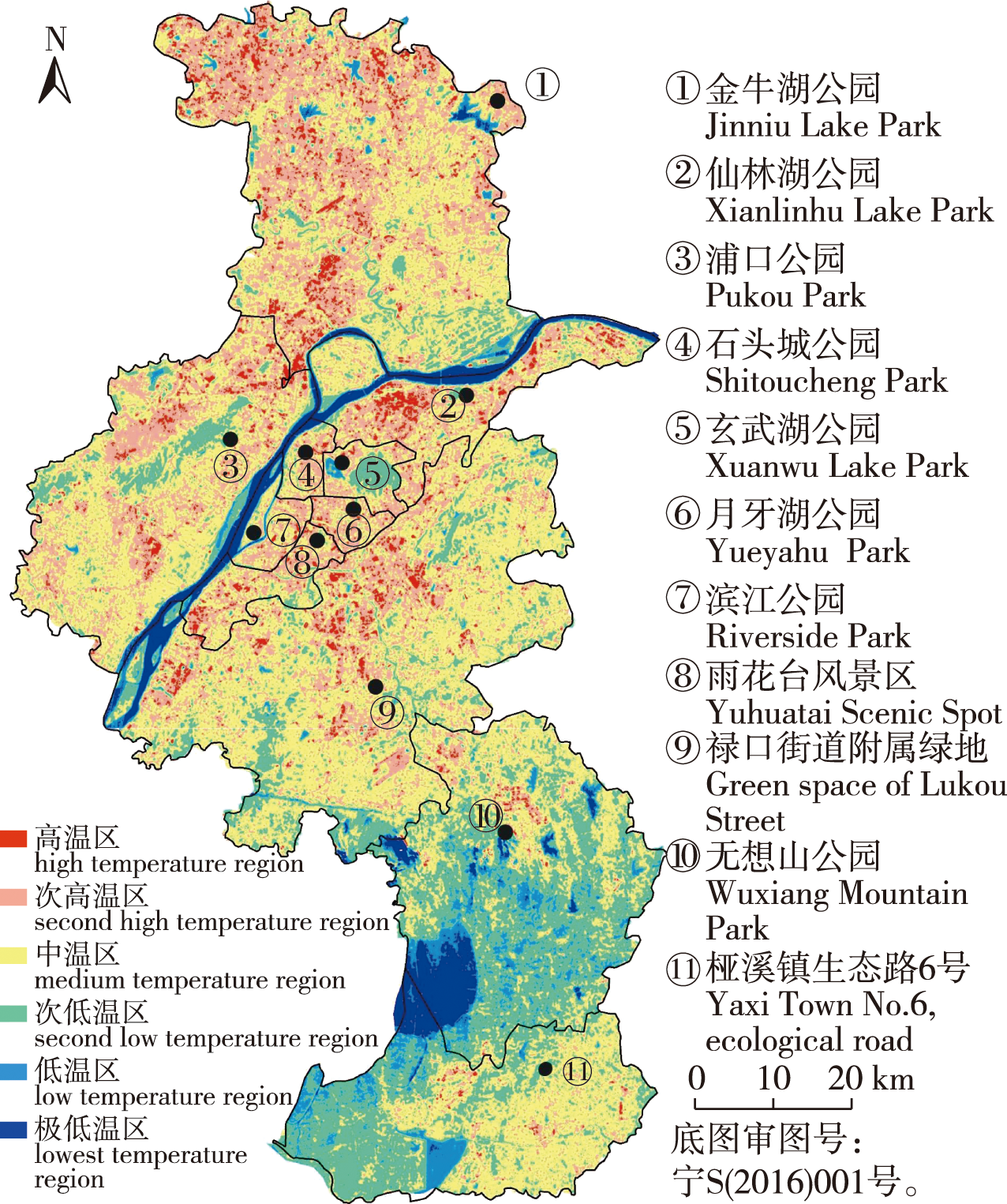
【目的】植物物候作为城市生态系统的指示器,能够直观反映城市化进程下生态系统的变化。本研究结合地表温度数据,探究南京市5种常见观花木本植物的花期物候对热岛效应的响应规律,为明晰我国华东地区植被物候对热岛效应的响应机制提供依据。【方法】基于Landsat 8遥感数据反演南京市地表温度,采用热岛比例指数(URI)表征热岛强度,结合花期物候观测数据,定量研究城市热岛效应对植物花期物候的影响。【结果】南京市城市热岛效应明显,热岛强度从大到小排序为:中心城区> 近郊区> 远郊区。5种植物对热岛效应的敏感度存在明显差异,白玉兰 (Yulania denudata)对城市热岛效应的响应最敏感,花期可提前4~11 d,花期持续时间最多缩短50%;巨紫荆 (Cercis gigantea)、垂丝海棠 (Malus halliana)、东京樱花 (Prunus yedoensis)受影响程度相近;红花檵木 (Loropetalum chinense var. rubrum)受影响程度最小,花期提前2~4 d,花期持续时间缩短约19%。【结论】热岛效应对植物花期的起止时间和持续时间皆存在显著影响,随着热岛效应的增强,植物始花期、盛花期和末花期均出现提前和缩短趋势,在未来的研究中,可探讨其他植被类型对城市热岛的响应,以进一步揭示植物物候对城市气候变化的响应规律。
【Objective】As an indicator of urban ecosystems, plant phenology can visually reflect the changes of ecosystem under the process of urbanization. In this study, we investigated the response pattern of flowering phenology of five common flowering woody species to the heat island effect in Nanjing, and provided data supplement for the response mechanism of vegetation phenology to the heat island effect in East China. 【Method】Based on Landsat 8 remote sensing data to invert the surface temperature of Nanjing, the urban heat island radio index (URI) was used to characterize the heat island intensity, and the combined with the flowering phenology observation data to quantitatively study the effect of urban heat island effect on the flowering phenology of plants.【Result】Nanjing showed a significant urban heat island effect. Heat island intensity ranking: central city > suburban area > remote suburban area. The sensitivity of the same plant to the heat island effect differed at different points. Among the five plants, Yulania denudata was the most affected by the heat island effect, with the flowering period advanced by four to 11 days and the flowering period duration shortened by up to 50%; Cercis gigantea, Malus halliana and Prunus yedoensis were affected to a similar extent and were at a medium level; Loropetalum chinense var. rubrum was the least affected, with the flowering period advanced by about two to four days and the flowering period duration shortened by about 19%. 【Conclusion】The heat island effect has a significant effect on the onset and duration of flowering periods of plants, and as the heat island effect increases, the onset, bloom and last flowering periods of plants tend to be earlier and shorter.
热岛效应 / 花期物候 / 热岛比例指数 / Landsat8 / 地表温度 / 南京市
urban heat island effect / flowering phenology / urban heat island radio (URI) index / Landsat8 / surface temperature / Nanjing City
| [1] |
彭保发, 石忆邵, 王贺封, 等. 城市热岛效应的影响机理及其作用规律:以上海市为例[J]. 地理学报, 2013, 68(11):1461-1471.
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
陶泽兴, 葛全胜, 徐韵佳, 等. 西安和宝鸡木本植物花期物候变化及温度敏感度对比[J]. 生态学报, 2020, 40(11):3666-3676.
|
| [7] |
陆佩玲. 中国木本植物物候对气候变化的响应研究[D]. 北京: 北京林业大学, 2006.
|
| [8] |
车少静, 智利辉, 冯立辉. 气候变暖对石家庄冬小麦主要生育期的影响及对策[J]. 中国农业气象, 2005, 26(3):180-183.
|
| [9] |
陈芳, 马英芳, 申红艳, 等. 长江源区近44年气候变化的若干统计分析[J]. 气象科技, 2007, 35(3):340-344.
|
| [10] |
韩超, 郑景云, 葛全胜. 中国华北地区近40年物候春季变化[J]. 中国农业气象, 2007, 28(2):113-117.
|
| [11] |
刘宇翔, 杨英宝, 胡佳, 等. 基于长时序MODIS数据的中国城市昼夜热岛强度时空特征[J]. 地球信息科学学报, 2022, 24(5):981-995.
|
| [12] |
古丽拜合热姆·艾合麦提, 昝梅. 新疆天山北坡经济带主要城市群热岛效应对植被物候的影响[J]. 生态与农村环境学报, 2022, 38(7):872-881.
Gulbakram·Ahmed,
|
| [13] |
吴瑞芬, 霍治国, 曹艳芳, 等. 内蒙古典型草本植物春季物候变化及其对气候变暖的响应[J]. 生态学杂志, 2009, 28(8):1470-1475.
|
| [14] |
王琳, 郑育桃, 伍艳芳, 等. 气象因子对芳香植物始花期的影响[J]. 经济林研究, 2017, 35(2):194-199.
|
| [15] |
张福春. 气候变化对中国木本植物物候的可能影响[J]. 地理学报, 1995, 50(5): 402-410.
|
| [16] |
王言鑫, 张增信, 杨艳蓉, 等. 南京市77种常见木本植物花期特征分析[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2014, 38(5):118-122.
|
| [17] |
蒋菊芳, 王鹤龄, 魏育国, 等. 河西走廊东部不同类型植物物候对气候变化的响应[J]. 中国农业气象, 2011, 32(4):543-549.
|
| [18] |
王静, 常青, 柳冬良. 早春草本植物开花物候期对城市化进程的响应:以北京市为例[J]. 生态学报, 2014, 34(22):6701-6710.
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
胡召玲, 戴慧, 侯飞, 等. 中国东北城乡植被物候时空变化及其对地表温度的响应[J]. 生态学报, 2020, 40(12):4137-4145.
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
孟丹, 刘芯蕊, 张聪聪. 北京市植物物候对热岛效应的响应[J]. 生态学杂志, 2021, 40(3):844-854.
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
徐涵秋, 陈本清. 不同时相的遥感热红外图像在研究城市热岛变化中的处理方法[J]. 遥感技术与应用, 2003, 18(3):129-133,185.
|
| [25] |
刘增超, 李家科, 蒋丹烈. 基于URI指数的海绵城市热岛效应评价方法构建与应用[J]. 水资源与水工程学报, 2018, 29(4):53-58.
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
姚晓洁, 王霞, 姚侠妹. 基于RS技术的皖北城市阜阳市主城区热环境效应分析[J]. 生态学杂志, 2021, 40(10):3290-3303.
|
| [28] |
沈志. 物候学在生态监测中的应用[J]. 干旱环境监测, 1991, 5(1):50-52,64.
|
| [29] |
奥勇, 王周航, 赵永华, 等. 不同城市化水平下绿地景观要素对温度的影响:以关中平原城市群为例[J]. 生态学杂志, 2023, 42(11):2721-2729.
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
李杨. 城市热岛效应评价方法的研究[D]. 重庆: 重庆大学, 2014.
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
赖小红, 李名扬, 刘聪, 等. 植物物候对重庆主城区热岛效应的响应[J]. 生态学报, 2019, 39(19):7025-7034.
|
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
|
| [40] |
|
| [41] |
张德顺, 刘鸣. 上海木本植物早春花期对城市热岛效应的时空响应[J]. 中国园林, 2017, 33(1):72-77.
|
| [42] |
|
| [43] |
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |