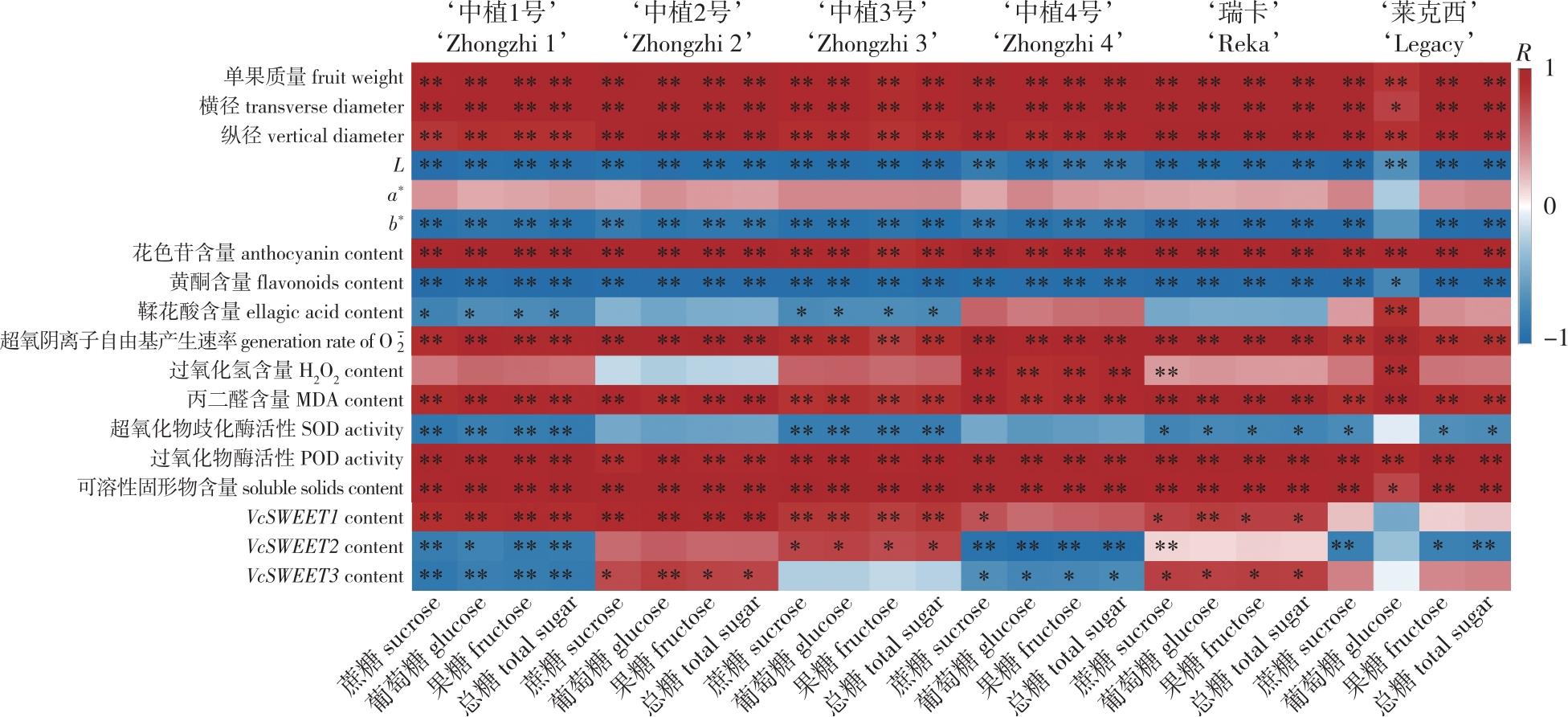
【目的】分析蓝莓(Vaccinum spp.)果实发育过程中糖及其他品质指标的变化特点,探讨蓝莓果实发育过程中糖类物质积累的潜在机制,为品质改良提供理论依据。【方法】以6个蓝莓品种不同发育阶段的果实为研究对象,对其外观参数、抗氧化指标、品质指标、糖转运蛋白基因的表达,以及糖的组分和含量进行测定,并采用Pearson模型进行各指标间的相关性分析。【结果】随着果实的发育,各品种果实逐渐增大,颜色逐渐加深,在紫果期(S3),6个蓝莓品种中,‘莱克西’的单果质量和横径最大,‘中植2号’最小;在紫果期(S3)‘莱克西’的颜色指标L值最大,a*和b*值最小。随着果实的发育, 的产生速率和丙二醛(MDA)含量逐渐上升,H2O2含量(除‘中植4号’外)和超氧化物歧化酶(SOD)活性均先降后升,过氧化物酶(POD)活性逐渐增加;可溶性固形物和花色苷含量逐渐上升,黄酮含量逐渐下降,鞣花酸含量先降后升,其中‘中植4号’紫果期的可溶性固形物和花色苷含量最高;3个VcSWEETs基因的表达具有明显的品种特异性和发育阶段依赖性;蔗糖、葡萄糖、果糖和总糖含量持续增加,其中葡萄糖含量在各阶段均较低,在S3时期,除‘中植1号’外总糖质量分数均大于200 mg/g。【结论】随着果实的发育,糖含量逐渐增加,S3时期‘莱克西’的总糖含量最高,其次是‘中植2号’和‘中植4号’;果实的增大、花色苷含量和POD活性的增加,以及VcSWEET1基因的上调表达均有利于糖积累。
【Objective】The purpose of this study is to understand the changes in sugar and other quality indexes during fruit development, to explore the potential mechanism of carbohydrate accumulation during blueberry (Vaccinium spp.) fruit development, and to establish a theoretical foundation for blueberry quality enhancement.【Method】Fruits of six blueberry cultivars at different developmental stages were used as the test materials. The morphological traits (size and color), antioxidant system-related parameters, fruit quality indexes, the expression levels of VcSWEETs genes, and sugar composition and content were determined. The correlation analysis among these parameters was performed using the Pearson correlation model.【Result】With the development of the fruit, the fruits of each cultivar gradually increased in size and deepened in color, of which the ‘Legacy’ cultivar had the largest fruit weight and transverse diameter, and ‘Zhongzhi 2’ had the smallest during the purple fruit stage (S3). In the S3 period, ‘Legacy’ showed peak L value with minimal a* and b* values. The generation rate of and MDA content steadily increased, while H2O2 content (excluding ‘Zhongzhi 4’) and SOD activity decreased first and then increased, and POD activity gradually increased. Total soluble solids (TSS) and anthocyanin contents gradually increased, flavonoid content gradually decreased, and ellagic acid content initially decreased and then increased. Among them, ‘Zhongzhi 4’ had the highest TSS and anthocyanin content during the S3 period. The expression patterns of three VcSWEETs genes exhibited distinct cultivar specificity and developmental stage dependence. Sucrose, glucose, fructose, and total sugar accumulated continuously, though glucose maintained basal levels. In the S3 period, the total sugar contents of all cultivars were more than 200 mg/g, except for ‘Zhongzhi 1’.【Conclusion】Sugar content increased continually during fruit development, with sucrose and fructose concentrations predominating over glucose. ‘Legacy’ had the greatest total sugar content during the S3 period, followed by ‘Zhongzhi 2’ and ‘Zhongzhi 4’. The expansion of the fruit, the rise in anthocyanin content and POD activity, and the up-regulated expression of the VcSWEET1 gene were significantly correlated with sugar accumulation patterns.
 PDF(3072 KB)
PDF(3072 KB)


 PDF(3072 KB)
PDF(3072 KB)
 PDF(3072 KB)
PDF(3072 KB)