
- 国家林草科技领军期刊
- 中国精品科技期刊
- 中国高校百佳科技期刊
- 江苏省新闻出版政府奖期刊奖
- RCCSE林学权威期刊(A+)
- CSCD核心期刊
- Scopus数据库收录期刊
- 中文核心期刊
- SCD核心期刊

南京林业大学学报(自然科学版) ›› 2021, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (6): 15-23.doi: 10.12302/j.issn.1000-2006.202107031
所属专题: 专题报道; 林木 CRISPR/Cas基因编辑专题
• 专题报道(执行主编 施季森 尹佟明 陈金慧) • 上一篇 下一篇
孙佳彤( ), 国艳娇, 李爽, 周晨光*(
), 国艳娇, 李爽, 周晨光*( ), 姜立泉, 李伟*(
), 姜立泉, 李伟*( )
)
收稿日期:2021-07-20
接受日期:2021-08-25
出版日期:2021-11-30
发布日期:2021-12-02
基金资助:
SUN Jiatong( ), GUO Yanjiao, LI Shuang, ZHOU Chenguang*(
), GUO Yanjiao, LI Shuang, ZHOU Chenguang*( ), CHIANG Vincent, LI Wei*(
), CHIANG Vincent, LI Wei*( )
)
Received:2021-07-20
Accepted:2021-08-25
Online:2021-11-30
Published:2021-12-02
摘要: 目的 采用CRISPR/Cas9基因编辑系统创制毛果杨(Populus trichocarpa)bHLH106(Basic Helix-Loop-Helix 106)基因的突变体,分析植株的表型特征,初步揭示PtrbHLH106基因在毛果杨木材形成过程中的功能。方法 基于前期对毛果杨野生型(WT)茎干的不同细胞类型(形成层、木质部和韧皮部细胞)RNA-seq数据,克隆得到一个在形成层及木质部较高表达的bHLH基因PtrbHLH106。采用CRISPR/Cas9基因编辑技术创制毛果杨PtrbHLH106的功能缺失突变体。对生长60、90、120 d的毛果杨ptrbhlh106突变体和WT植株进行表型观察;对生长120 d的植株各茎节进行石蜡切片,利用甲苯胺蓝染色观察并进行细胞统计分析。结果 获得毛果杨ptrbhlh106突变体;与WT相比,突变体植株的株高、地径无明显差异;在整个测量的生长周期中,第8茎节长度有缩短的趋势,茎节数量有增加的趋势;形成层细胞层数有增加的趋势但差异不显著,导管细胞孔径显著增大,纤维细胞数量显著减少。结论 ptrbhlh106突变体与WT植株在导管孔径和纤维细胞数量上存在差异,初步证明PtrbHLH106基因参与了调控毛果杨次生木质部的发育。
中图分类号:
孙佳彤,国艳娇,李爽,等. 基于CRISPR/Cas9的毛果杨bHLH106转录因子的功能研究[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 45(6): 15-23.
SUN Jiatong, GUO Yanjiao, LI Shuang, ZHOU Chenguang, CHIANG Vincent, LI Wei. A functional study of bHLH106 transcription factor based on CRISPR/Cas9 in Populus trichocarpa[J].Journal of Nanjing Forestry University (Natural Science Edition), 2021, 45(6): 15-23.DOI: 10.12302/j.issn.1000-2006.202107031.
表1
所用引物及序列"
| 引物名称 primer name | 引物序列 sequences | 用途 application |
|---|---|---|
| F | 5'-CACCATGCAGCCTGAAAACTGTCAGGAG-3' | PtrbHLH106基因克隆 cloning of PtrbHLH106 gene |
| R | 5'-CATAGCCATTCAACGTCCAAAGAT-3' | |
| T7-bHLH106-stem-loop | 5'-TAATACGACTCACTATAGGTTCCATTCTCGGTAAGAAAC GTTTAAGAGCTATGCTGGAAACAGCATAGCAAGTTTAAATAAGG-3' | 体外检测的gRNA转录模板 gRNA transcription template for in vitro detection |
| pUC19-F | 5'-CTAGGGATCCCTTCACTTGCGGGTCATCTC-3' | 体外检测中的模板DNA the template DNA for in vitro detection |
| pUC19-R | 5'-CTAGGTCGACGACTTGTTTGTGTAGATCCAAG-3' | |
| gRNA-F | 5'-GATTGTTCCATTCTCGGTAAGAAAC-3' | pEgP237载体构建,R端引物亦用于转基因植株鉴定 vector construction of pEgP237, gRNA-R also for transgenic identification |
| gRNA-R | 5'-GTTTCTTACCGAGAATGGAACCAAA-3' | |
| M13F | 5'-GTAAAACGACGGCCAG-3' | 转基因鉴定 transgenic identification |
| PtrbHLH106-F | 5'-ACTTGCGGGTCATCTCCCTT-3' | 靶位点编辑情况的鉴定 identification of gene editing |
| PtrbHLH106-R | 5'-GCCTGCAACACCTAAAAATATT-3' |

图3
毛果杨转基因植株的获得 A. 愈伤组织分化诱导callus induction;B. 抗性芽诱导shoot induction;C. 抗性植株筛选screaning of the resistant plants;D. 转基因植株的PCR鉴定the PCR detection results(M. DNA marker DL 2000。 1. ddH2O为模板的阴性对照negative control with ddH2O as PCR template; 2. pEgP237-U6-PtrbHLH106 gRNA-35S-Cas9质粒为模板的阳性对照positive control with plasmid pEgP237-U6-PtrbHLH106 gRNA-35S-Cas9 as PCR template; 3. 野生型毛果杨叶片DNA为模板的阴性对照negative control with leaf DNA of wild-type plant as PCR template; 4~6. 抗性植株叶片DNA为模板的样品sample with leaf DNA of kanamycin-resistant plant as PCR template)。"
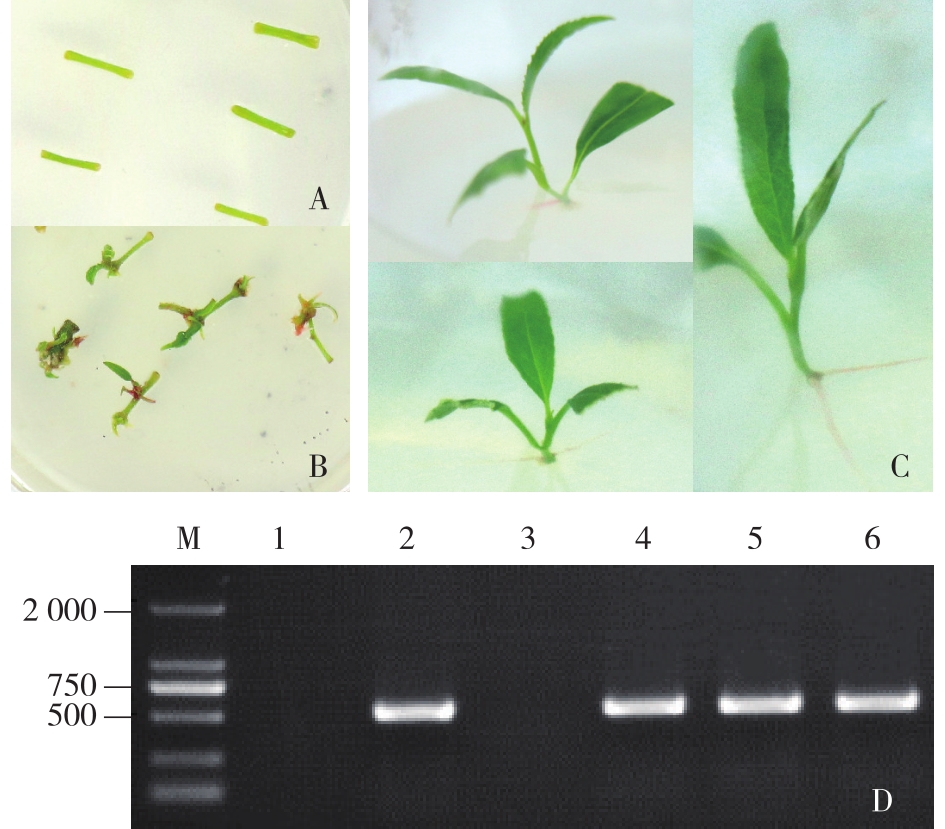

图4
毛果杨PtrbHLH106基因编辑情况 A. 等位基因编辑情况(红色字母表示碱基插入,红色“-”表示碱基缺失,“-16 bp-”表示缺失16个碱基)gene editing of alleles (The red letters represent insertion; the red short lines “-” represent deletion; “-16 bp-” represents 16 nucleotide deletion);B. 被编辑基因的蛋白翻译情况预测(红色块区域代表氨基酸改变) the prediction of amino acid sequence translation (The red short lines represent amino acid changed)。"
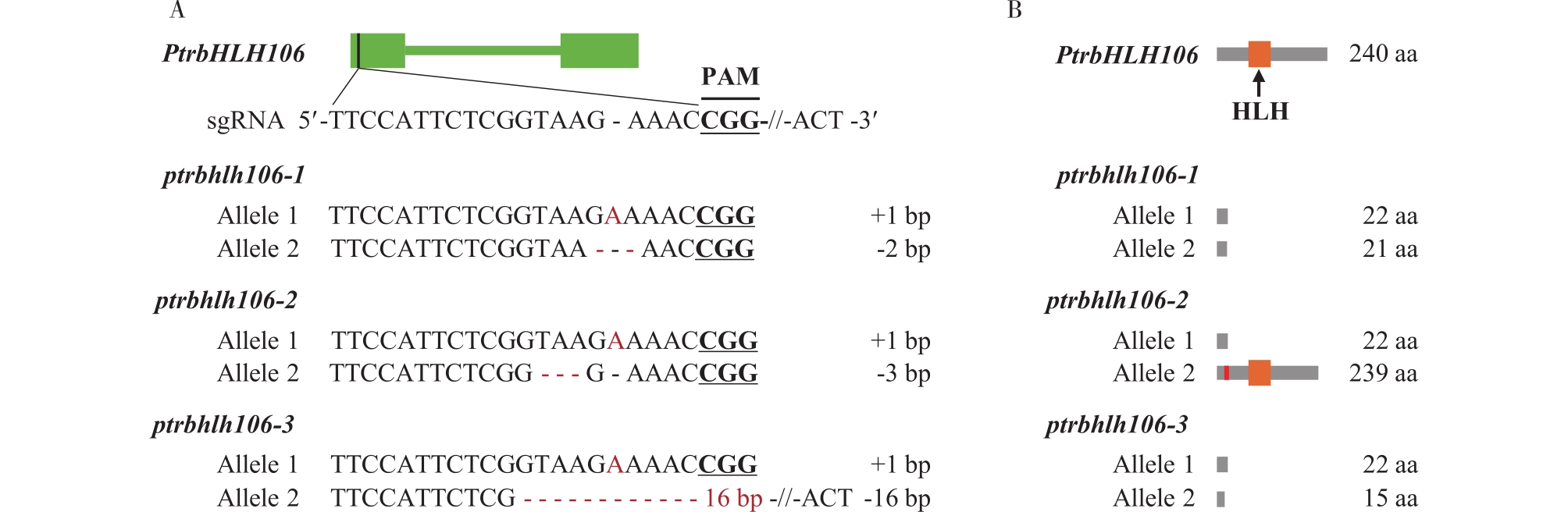
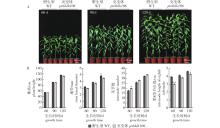
图5
毛果杨野生型与ptrbhlh106突变体表型分析 误差线代表由3个生物学重复计算的标准误,*表示通过t检验,突变体与野生型植物各株系之间存在显著差异,*.P<0.05,**.P<0.01)。下同。Statistical analysis of growth index of wild-type(WT) and ptrbhlh106 plants. Error bars represent SE values of three independent experiments. Asterisks indicate significant differences between each line of the mutants and wild-type plants by Student’s t test. The same below."
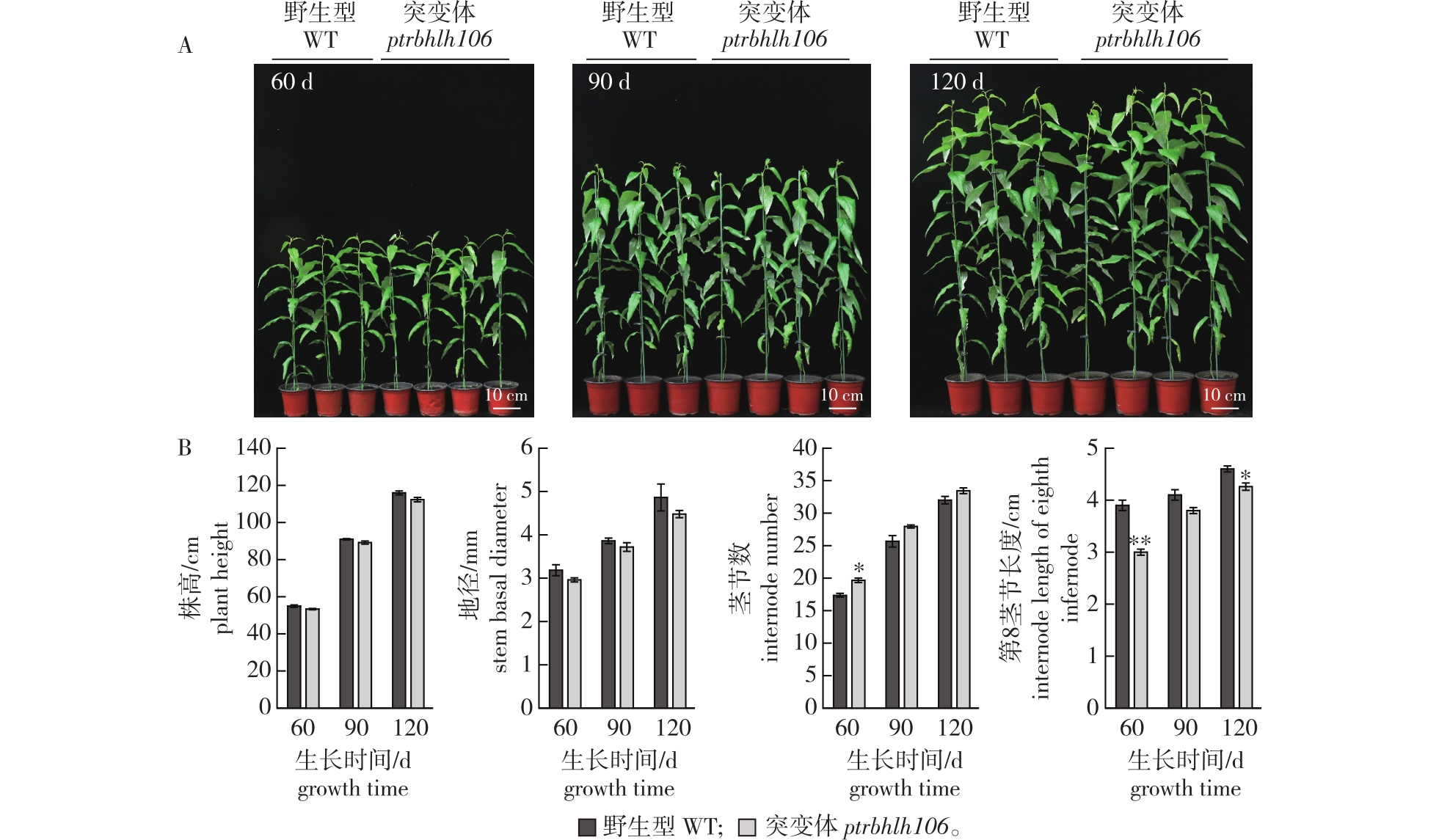
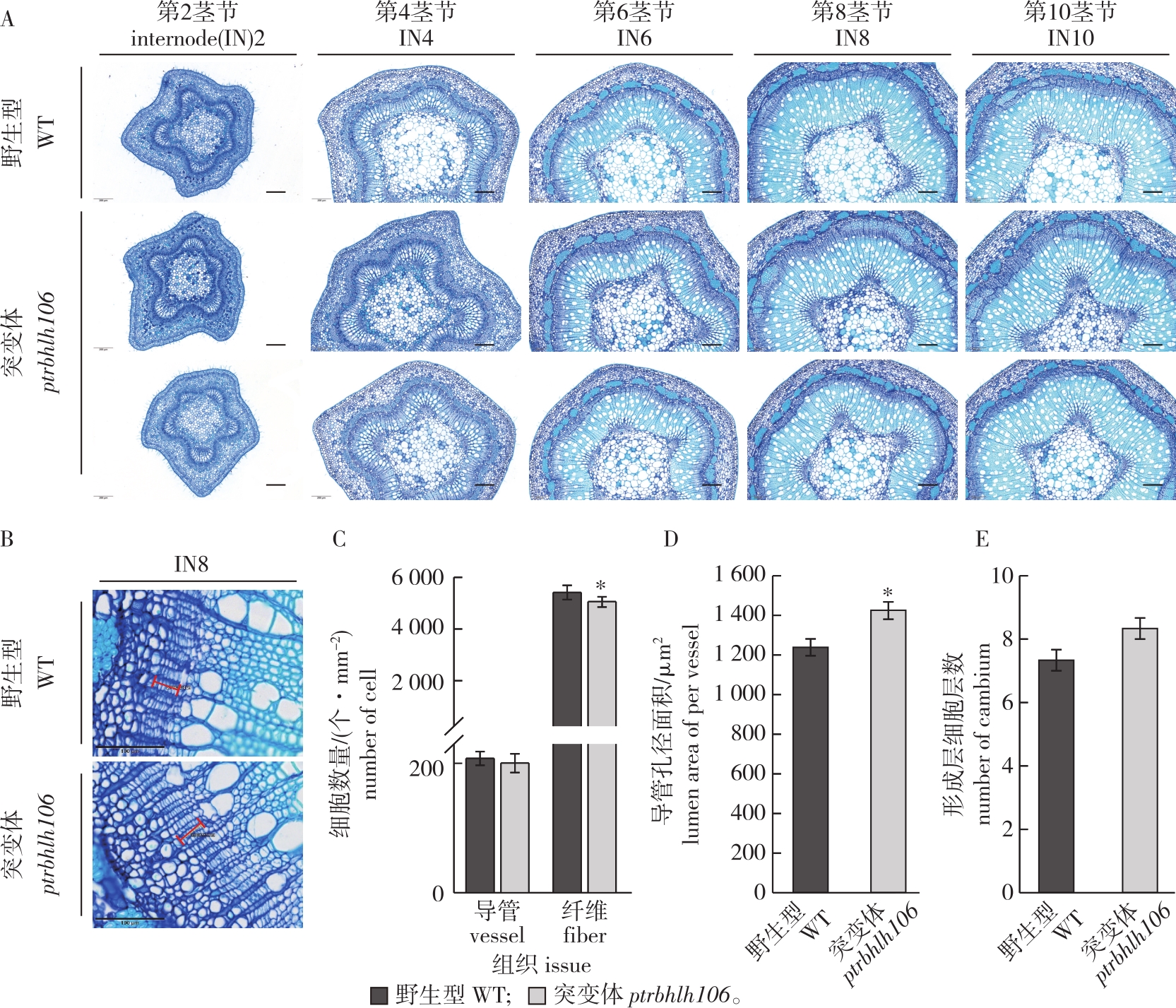
图6
毛果杨ptrbhh106突变体石蜡切片观察及细胞统计 A. 野生型(WT)和突变体(ptrbhlh106)毛果杨各茎节细胞形态观察(比例尺为200 μm)morphologic observation of stem internodes of WT and ptrbhlh106 (Bars=200 μm);B. 形成层细胞形态观察(红色线表示形成层区域,比例尺为100 μm)morphologic observation of cambium cells (Red line showed cambium areas, Bars=100 μm);C. 单位面积细胞数目统计statistics analysis of number of fiber and vessel cells in per unit cells;D. 导管孔径面积统计statistics analysis of lumen area of per vessel;E. 形成层细胞层数统计statistics analysis of number of cambium cell layer。"
| [1] |
NULL. Esau’s plant anatomy:meristems,cells,and tissues of the plant body: their structure,function,and development[J]. Choice Rev Online, 2007, 44(7):44-3861.DOI: 10.5860/choice.44-3861.
doi: 10.5860/choice.44-3861 |
| [2] | 李慧, 郭晓蕊, 刘雅琳, 等. 木材形成过程中次生壁沉积和细胞程序性死亡的分子调控机制[J]. 中国科学(生命科学), 2020, 50(2):123-135. |
|
LI H, GUO X R, LIU Y L, et al. The molecular mechanism in secondary wall deposition and programmed cell death of wood formation[J]. Sci Sin (Vitae), 2020, 50(2):123-135.DOI: 10.1360/SSv-2019-0133.
doi: 10.1360/SSv-2019-0133 |
|
| [3] | EASU K. Plant anatomy[M]. New York: John Wiley & Sons, 1964. |
| [42] |
ZOBEL B J, JETT J B. Genetics of wood production[M]. Berlin,Heidelberg:Springer, 1995.DOI: 10.1007/978-3-642-79514-5.
doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-79514-5 |
| [43] | 康向阳. 林木遗传育种研究进展[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 44(3):1-10. |
| [4] |
MCCARTHY R L, ZHONG R, YE Z H. Secondary wall NAC binding element (SNBE),a key Cis-acting element required for target gene activation by secondary wall NAC master switches[J]. Plant Signal Behav, 2011, 6(9):1282-1285.DOI: 10.4161/psb.6.9.16402.
doi: 10.4161/psb.6.9.16402 |
| [5] |
LIN Y C, LI W, SUN Y H, et al. SND1 transcription factor-directed quantitative functional hierarchical genetic regulatory network in wood formation in Populus trichocarpa[J]. Plant Cell, 2013, 25(11):4324-4341.DOI: 10.1105/tpc.113.117697.
doi: 10.1105/tpc.113.117697 |
| [6] |
CHEN H, WANG J P, LIU H Z, et al. Hierarchical transcription factor and chromatin binding network for wood formation in Populus trichocarpa[J]. Plant Cell, 2019, 31(3):602-626.DOI: 10.1105/tpc.18.00620.
doi: 10.1105/tpc.18.00620 |
| [7] | 文静, 王春涛, 杨永平. 植物木质部次生细胞壁加厚调控的研究进展[J]. 西南林业大学学报(自然科学), 2021, 41(2):182-188. |
|
WEN J, WANG C T, YANG Y P. Advances in regulation of xylem secondary cell wall thickening in plants[J]. J Southwest For Univ (Nat Sci), 2021, 41(2):182-188.DOI: 10.11929/j.swfu.201909077.
doi: 10.11929/j.swfu.201909077 |
|
| [8] |
HEIM M A, JAKOBY M, WERBER M, et al. The basic helix-loop-helix transcription factor family in plants: a genome-wide study of protein structure and functional diversity[J]. Mol Biol Evol, 2003, 20(5):735-747.DOI: 10.1093/molbev/msg088.
doi: 10.1093/molbev/msg088 |
| [9] |
NAKATA M, MITSUDA N, HERDE M, et al. A bHLH-type transcription factor,aba-inducible BHLH-type Transcription Factor/JA-Associated MYC2-Like1,Acts as a repressor to negatively regulate jasmonate signaling in Arabidopsis[J]. Plant Cell, 2013, 25(5):1641-1656.DOI: 10.1105/tpc.113.111112.
doi: 10.1105/tpc.113.111112 |
| [10] |
QI T, HUANG H, WU D, et al. Arabidopsis DELLA and JAZ proteins bind the WD-repeat/bHLH/MYB complex to modulate gibberellin and jasmonate signaling synergy[J]. Plant Cell, 2014, 26(3):1118-1133.DOI: 10.1105/tpc.113.121731.
doi: 10.1105/tpc.113.121731 |
| [11] |
NI M, TEPPERMAN J M, QUAIL P H. PIF3,a phytochrome-interacting factor necessary for normal photoinduced signal transduction,is a novel basic helix-loop-helix protein[J]. Cell, 1998, 95(5):657-667.DOI: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81636-0.
doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81636-0 |
| [12] |
HUQ E, QUAIL P H. PIF4,a phytochrome-interacting bHLH factor,functions as a negative regulator of phytochrome B signaling in Arabidopsis[J]. EMBO J, 2002, 21(10):2441-2450.DOI: 10.1093/emboj/21.10.2441.
doi: 10.1093/emboj/21.10.2441 |
| [13] |
ABE H, URAO T, ITO T, et al. Arabidopsis AtMYC2 (bHLH) and AtMYB2 (MYB) function as transcriptional activators in abscisic acid signaling[J]. Plant Cell, 2003, 15(1):63-78.DOI: 10.1105/tpc.006130.
doi: 10.1105/tpc.006130 |
| [14] |
WANG Y, JIANG C J, LI Y Y, et al. CsICE1 and CsCBF1:two transcription factors involved in cold responses in Camellia sinensis[J]. Plant Cell Rep, 2012, 31(1):27-34.DOI: 10.1007/s00299-011-1136-5.
doi: 10.1007/s00299-011-1136-5 |
| [15] |
AHMAD A, NIWA Y, GOTO S, et al. bHLH106 integrates functions of multiple genes through their G-box to confer salt tolerance on Arabidopsis[J]. PLoS One, 2015, 10(5):e0126872.DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0126872.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0126872 |
| [16] |
OHASHI-ITO K, MATSUKAWA M, FUKUDA H. An atypical bHLH transcription factor regulates early xylem development downstream of auxin[J]. Plant Cell Physiol, 2013, 54(3):398-405.DOI: 10.1093/pcp/pct013.
doi: 10.1093/pcp/pct013 |
| [17] |
LIU Z H, CHEN Y, WANG N N, et al. A basic helix-loop-helix protein (GhFP1) promotes fibre elongation of cotton (Gossypium hirsutum) by modulating brassinosteroid biosynjournal and signalling[J]. New Phytol, 2020, 225(6):2439-2452.DOI: 10.1111/nph.16301.
doi: 10.1111/nph.16301 |
| [18] |
CASSAN-WANG H, GOUÉ N, SAIDI M N, et al. Identification of novel transcription factors regulating secondary cell wall formation in Arabidopsis[J]. Front Plant Sci, 2013, 4:189.DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2013.00189.
doi: 10.3389/fpls.2013.00189 |
| [19] |
DE RYBEL B, MÖLLER B, YOSHIDA S, et al. A bHLH complex controls embryonic vascular tissue establishment and indeterminate growth in Arabidopsis[J]. Dev Cell, 2013, 24(4):426-437.DOI: 10.1016/j.devcel.2012.12.013.
doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2012.12.013 |
| [20] |
OHASHI-ITO K, SAEGUSA M, IWAMOTO K, et al. A bHLH complex activates vascular cell division via cytokinin action in root apical meristem[J]. Curr Biol, 2014, 24(17):2053-2058.DOI: 10.1016/j.cub.2014.07.050.
doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2014.07.050 |
| [21] |
KNOTT G J, DOUDNA J A. CRISPR-Cas guides the future of genetic engineering[J]. Science, 2018, 361(6405):866-869.DOI: 10.1126/science.aat5011.
doi: 10.1126/science.aat5011 |
| [22] | 林萌萌, 李春娟, 闫彩霞, 等. CRISPR/Cas9基因编辑技术在作物中的应用[J]. 核农学报, 2021, 35(6):1329-1339. |
|
LIN M M, LI C J, YAN C X, et al. Application of CRISPR/Cas9 gene editing technology in crops[J]. J Nucl Agric Sci, 2021, 35(6):1329-1339.DOI: 10.11869/j.issn.100-8551.2021.06.1329.
doi: 10.11869/j.issn.100-8551.2021.06.1329 |
|
| [23] |
JINEK M, CHYLINSKI K, FONFARA I, et al. A programmable dual-RNA-guided DNA endonuclease in adaptive bacterial immunity[J]. Science, 2012, 337(6096):816-821.DOI: 10.1126/science.1225829.
doi: 10.1126/science.1225829 |
| [24] |
BORTESI L, FISCHER R. The CRISPR/Cas9 system for plant genome editing and beyond[J]. Biotechnol Adv, 2015, 33(1):41-52.DOI: 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2014.12.006.
doi: 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2014.12.006 |
| [25] |
ZAFAR S A, ZAIDI S S, GABA Y, et al. Engineering abiotic stress tolerance via CRISPR/ Cas-mediated genome editing[J]. J Exp Bot, 2020, 71(2):470-479.DOI: 10.1093/jxb/erz476.
doi: 10.1093/jxb/erz476 |
| [26] |
KIEU N P, LENMAN M, WANG E S, et al. Mutations introduced in susceptibility genes through CRISPR/Cas9 genome editing confer increased late blight resistance in potatoes[J]. Sci Rep, 2021, 11(1):4487.DOI: 10.1038/s41598-021-83972-w.
doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-83972-w |
| [27] |
DE MEESTER B, MADARIAGA CALDERÓN B, DE VRIES L, et al. Tailoring poplar lignin without yield penalty by combining a null and haploinsufficient CINNAMOYL-CoA REDUCTASE2 allele[J]. Nat Commun, 2020, 11(1):5020.DOI: 10.1038/s41467-020-18822-w.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-18822-w |
| [28] |
FAN D, LIU T, LI C, et al. Efficient CRISPR/Cas9-mediated targeted mutagenesis in Populus in the first generation[J]. Sci Rep, 2015, 5:12217.DOI: 10.1038/srep12217.
doi: 10.1038/srep12217 |
| [29] | 林娇娇. 毛果杨PtrVCS2基因在木材形成中的功能研究[D]. 哈尔滨:东北林业大学, 2020. |
| LIN J J. Function analysis of PtrVCS2 gene in wood formation in Populus trichocarpa[D]. Harbin:Northeast Forestry University, 2020. | |
| [30] | 毛昱力. 毛果杨PtrDLT和PtrWOX4基因在维管形成层发育中的功能解析[D]. 哈尔滨:东北林业大学, 2020. |
| MAO Y L. Functional analysis of PtrDLT and PtrWOX4 genes in the development of vascular cambium in Populus trichocarpa[D]. Harbin:Northeast Forestry University, 2020. | |
| [31] |
LI S, ZHEN C, XU W, et al. Simple,rapid and efficient transformation of genotype Nisqually-1:a basic tool for the first sequenced model tree[J]. Sci Rep, 2017, 7(1):2638.DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-02651-x.
doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-02651-x |
| [32] |
WANG Z F, MAO Y L, GUO Y J, et al. MYB transcription Factor161 mediates feedback regulation of secondary wall-associated NAC: domain1 family genes for wood formation[J]. Plant Physiol, 2020, 184(3):1389-1406.DOI: 10.1104/pp.20.01033.
doi: 10.1104/pp.20.01033 |
| [33] |
OSAKABE Y, LIANG Z, REN C, et al. CRISPR-Cas9-mediated genome editing in apple and grapevine[J]. Nat Protoc, 2018, 13(12):2844-2863.DOI: 10.1038/s41596-018-0067-9.
doi: 10.1038/s41596-018-0067-9 |
| [34] |
NISHITANI C, HIRAI N, KOMORI S, et al. Efficient genome editing in apple using a CRISPR/Cas9 system[J]. Sci Rep, 2016, 6:31481.DOI: 10.1038/srep31481.
doi: 10.1038/srep31481 |
| [35] |
LI S, LIN Y J, WANG P, et al. The AREB1 transcription factor influences histone acetylation to regulate drought responses and tolerance in Populus trichocarpa[J]. Plant Cell, 2019, 31(3):663-686.DOI: 10.1105/tpc.18.00437.
doi: 10.1105/tpc.18.00437 |
| [36] |
ZHU H, LI C, GAO C. Applications of CRISPR-Cas in agriculture and plant biotechnology[J]. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol, 2020, 21(11):661-677.DOI: 10.1038/s41580-020-00288-9.
doi: 10.1038/s41580-020-00288-9 |
| [37] |
LI G, SRETENOVIC S, EISENSTEIN E, et al. Highly efficient C-to-T and A-to-G base editing in a Populus hybrid[J]. Plant Biotechnol J, 2021, 19(6):1086-1088.DOI: 10.1111/pbi.13581.
doi: 10.1111/pbi.13581 |
| [38] |
KUBO M, UDAGAWA M, NISHIKUBO N, et al. Transcription switches for protoxylem and metaxylem vessel formation[J]. Genes Dev, 2005, 19(16):1855-1860.DOI: 10.1101/gad.1331305.
doi: 10.1101/gad.1331305 |
| [39] | 沈方圆, 王岚春, 李校. 欧洲山杨bHLH转录因子家族全基因组分析[J]. 四川大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 58(3):179-187. |
|
SHEN F Y, WANG L C, LI X. Genome-wide analysis of the bHLH transcription factor family in Populus tremula[J]. J Sichuan Univ (Nat Sci Ed), 2021, 58(3):179-187.DOI: 10.19907/j.0490-6756.2021.036003.
doi: 10.19907/j.0490-6756.2021.036003 |
|
| [40] |
ZHANG J, XIE M, TUSKAN G A, et al. Recent advances in the transcriptional regulation of secondary cell wall biosynjournal in the woody plants[J]. Front Plant Sci, 2018, 9:1535.DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2018.01535.
doi: 10.3389/fpls.2018.01535 |
| [41] | 李少锋. 林木木材形成机制及材性改良研究进展[J]. 温带林业研究, 2019, 2(2):40-47. |
|
LI S F. Wood formation mechanism and properties improvement in forest trees[J]. J Temp For Res, 2019, 2(2):40-47.DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.2096-4900.2019.02.007.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2096-4900.2019.02.007 |
|
| [43] |
KANG X Y. Research progress of forest genetics and tree breeding[J]. J Nanjing For Univ (Nat Sci Ed), 2020, 44(3):1-10.DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2006.202002033.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2006.202002033 |
| [1] | 高源, 孙佳彤, 周晨光, 姜立泉, 李伟, 李爽. LBD12转录因子调控毛果杨木材形成研究[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2024, 48(1): 29-38. |
| [2] | 王竹雯, 国艳娇, 李爽, 周晨光, 姜立泉, 李伟. 基于CRISPR/Cas9的毛果杨PtrHBI1基因功能解析[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 45(6): 31-39. |
| [3] | 张晨, 臧颖, 许倩, 郑兆娟, 欧阳嘉. 毛果杨苯丙氨酸解氨酶活性比较及肉桂酸制备[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 44(1): 97-104. |
| [4] | 李丹蕾,王峰,陈俏丽,张瑞芝,王佳楠. 美洲黑杨×毛果杨NDR1基因表达对E4锈菌侵染的响应[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 42(01): 21-26. |
| [5] | 王浩然,李爽爽,乐丽娜,匡华琳,黄敏仁,陈英. miR164a及其靶基因PeNAC1相互作用研究[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2016, 40(05): 29-33. |
| [6] | 朱煜,谭梦月,邹爱兰,张文举,戚金亮,杨永华. 拟南芥、水稻和毛果杨中CesA基因的进化和表达分析[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2013, 37(03): 11-16. |
| [7] | 陈英,王浩然,许庆,黄敏仁*. ptr-MIR156a启动子克隆及特征分析[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2011, 35(06): 1-5. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||