 PDF(1115 KB)
PDF(1115 KB)


多情景模拟下县域生境质量时空演变预测——以桃源县为例
杨宇萍, 陈彩虹, 佘济云, 林楚璇, 肖芬, 陈楚琳
南京林业大学学报(自然科学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 48 ›› Issue (6) : 201-209.
 PDF(1115 KB)
PDF(1115 KB)
 PDF(1115 KB)
PDF(1115 KB)
多情景模拟下县域生境质量时空演变预测——以桃源县为例
Prediction of the spatiotemporal evolution of county habitat quality under multi-scenario simulation: a case of Taoyuan County
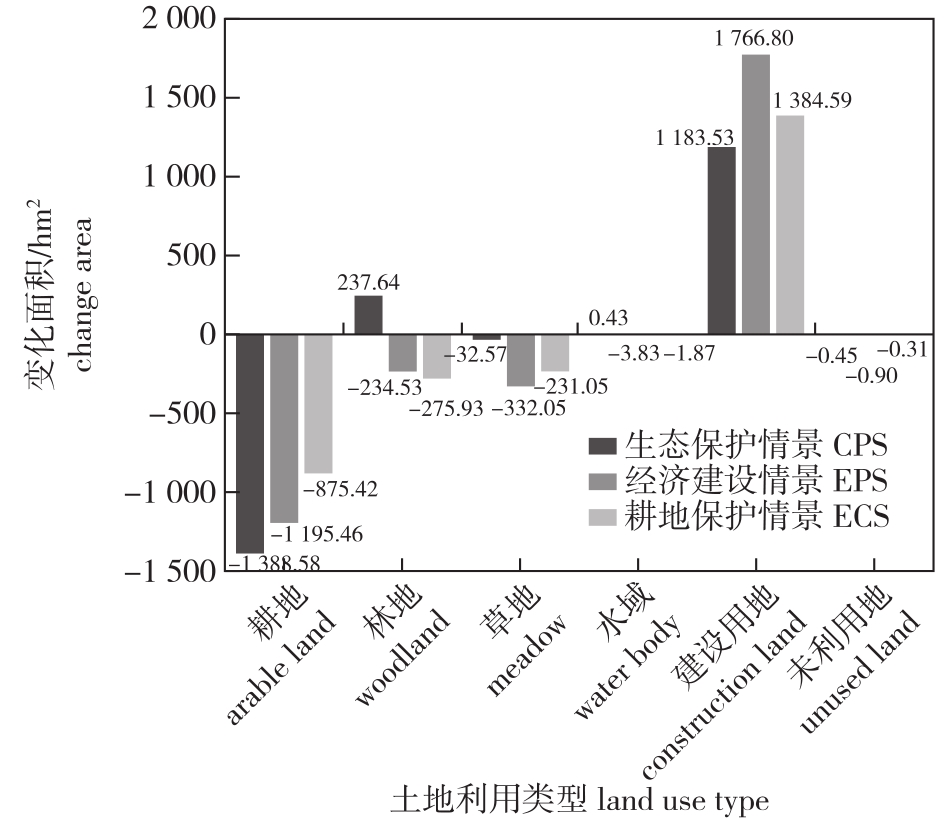
【目的】探究不同发展情景下的县域生境质量分布格局,为区域生态保护和社会经济可持续发展提供保障。【方法】以湖南省常德市桃源县为例,结合GeoSOS-FLUS模型与InVEST模型预测耕地保护情景(CPS)、生态保护情景(EPS)和经济建设情景(ECS)下的土地利用和生境质量时空演变格局,并借助地理探测器探测生境质量空间差异的影响因素。【结果】①2000—2020年,桃源县土地利用变化总体表现为草地、耕地、林地规模逐渐减少,建设用地持续扩张;生境质量呈下降趋势,低生境质量面积占比逐年升高。②2035年桃源县在3种情景下的生境质量均值从大到小为EPS(0.818 7)>CPS(0.817 9)>ECS(0.817 3);在ECS下,林地面积实现正增长,高生境质量区域减少幅度放缓,建设用地扩张对生态的破坏得到最大程度遏制;在CPS下,较低生境质量面积占比达到28.07%;在ECS下,低生境质量区域面积占比2.07%,呈持续增长趋势。③地形因子是影响桃源县生境质量空间分布的主要因素,其次为GDP与人口密度。【结论】在县域未来发展中,可考虑优化生态用地空间布局,鼓励发展生态农业,合理控制建设用地增量,提高生态稳定性,促进国土空间高质量发展。
【Objective】This study aims to explore the distribution patterns of habitat quality in county-level areas under different development scenarios to support regional ecological protection and socio-economic sustainable development.【Method】Using Taoyuan County as a case study, we applied the GeoSOS-FLUS model and the InVEST model to simulate the spatial-temporal evolution of land use and habitat quality under three scenarios: cultivated land protection scenario (CPS), ecological protection scenario (EPS), and economic construction scenario (ECS). We also analyzed the factors influencing spatial variations in habitat quality using Geographic Detectors.【Result】From 2000 to 2020, land use changes in Taoyuan County included a gradual decrease in grassland, cultivated land, and woodland, while construction land expanded continuously. Habitat quality declined, with a yearly increase in the proportion of low habitat quality areas. By 2035, the average habitat quality values under the three scenarios were ranked as follows: EPS (0.818 7)>CPS (0.817 9)>ECS (0.817 3). Under EPS, woodland area increased positively, the reduction in high habitat quality areas slowed, and ecological damage from construction land expansion was minimized. Under CPS, 28.07% of the area had low habitat quality. Under ECS, 2.07% of the area had low habitat quality, which showed a continuous increase. Topographic factors were the primary determinants of habitat quality distribution in Taoyuan County, followed by GDP and population density.【Conclusion】Future county development should consider optimizing the spatial layout of ecological land, promoting ecological agriculture, controlling construction land expansion, improving ecological stability, and advancing high-quality land space development.
多情景模拟 / 生境质量 / 碳储量 / 土地利用 / GeoSOS-FLUS模型 / InVEST模型 / 湖南桃源县
multi-scenario simulation / habitat quality / carbon storage / land use / GeoSOS-FLUS model / InVEST model / Taoyuan County of Hunan Province
| [1] |
邱国玉, 张晓楠. 21世纪中国的城市化特点及其生态环境挑战[J]. 地球科学进展, 2019, 34(6):640-649.
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
刘春芳, 王川. 基于土地利用变化的黄土丘陵区生境质量时空演变特征——以榆中县为例[J]. 生态学报, 2018, 38(20):7300-7311.
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
李营, 张峰, 杨海军, 等. 生物多样性生态功能区生境质量变化遥感监测研究[J]. 环境与可持续发展, 2016, 41(2):46-48.
|
| [6] |
邱炳文, 陈崇成. 基于多目标决策和CA模型的土地利用变化预测模型及其应用[J]. 地理学报, 2008, 63(2):165-174.
|
| [7] |
严栋飞, 姜仁贵, 解建仓, 等. 基于Markov模型的渭河干流陕西段土地利用动态变化研究[J]. 西安理工大学学报, 2019, 35(1):34-39.
|
| [8] |
王蒙. 基于FLUS模型的土地利用变化模拟与预测方法研究[J]. 测绘与空间地理信息, 2022, 45(1):161-166.
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
侯建坤, 陈建军, 张凯琪, 等. 基于InVEST和GeoSoS-FLUS模型的黄河源区碳储量时空变化特征及其对未来不同情景模式的响应[J]. 环境科学, 2022, 43(11):5253-5262.
|
| [11] |
刘小平, 黎夏, 叶嘉安, 等. 利用蚁群智能挖掘地理元胞自动机的转换规则[J]. 中国科学(D辑:地球科学), 2007, 37(6):824-834.
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
马良, 金陶陶, 文一惠, 等. InVEST模型研究进展[J]. 生态经济, 2015, 31(10):126-131,179.
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
黄木易, 岳文泽, 冯少茹, 等. 基于InVEST模型的皖西大别山区生境质量时空演化及景观格局分析[J]. 生态学报, 2020, 40(9):2895-2906.
|
| [20] |
刘孟竹, 张红娟, 王彦芳, 等. 基于土地利用的北方农牧交错带生境质量研究[J]. 水土保持研究, 2021, 28(3):156-162.
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
尚俊, 蔡海生, 龙月, 等. 基于InVEST模型的鄱阳湖区生境质量时空演化及其变迁特征分析[J]. 长江流域资源与环境, 2021, 30(8):1901-1915.
|
| [23] |
许文宁, 王鹏新, 韩萍, 等. Kappa系数在干旱预测模型精度评价中的应用:以关中平原的干旱预测为例[J]. 自然灾害学报, 2011, 20(6):81-86.
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
戴云哲, 李江风, 杨建新. 长沙都市区生境质量对城市扩张的时空响应[J]. 地理科学进展, 2018, 37(10):1340-1351.
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
谢怡凡, 姚顺波, 邓元杰, 等. 延安市退耕还林(草)工程对生境质量时空格局的影响[J]. 中国生态农业学报(中英文), 2020, 28(4):575-586.
|
| [28] |
刘园, 周勇, 杜越天. 基于InVEST模型的长江中游经济带生境质量的时空分异特征及其地形梯度效应[J]. 长江流域资源与环境, 2019, 28(10):2429-2440.
|
| [29] |
邓楚雄, 郭方圆, 黄栋良, 等. 基于INVEST模型的洞庭湖区土地利用景观格局对生境质量的影响研究[J]. 生态科学, 2021, 40(2):99-109.
|
| [30] |
朱增云, 阿里木江·卡斯木. 基于地理探测器的伊犁谷地生境质量时空演变及其影响因素[J]. 生态学杂志, 2020, 39(10): 3408-3420.
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
李骞国, 王录仓, 石培基, 等. 基于生境质量的绿洲城镇增长边界划定——以黑河中游地区为例[J]. 经济地理, 2020, 40(3):92-101.
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
周德志, 关颖慧, 张冰彬, 等. 基于土地利用变化的陕北地区生境质量时空演变及其驱动因素[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2022, 44(6):85-95.
|
| [35] |
欧维新, 张伦嘉, 陶宇, 等. 基于土地利用变化的长三角生态系统健康时空动态研究[J]. 中国人口·资源与环境, 2018, 28(5):84-92.
|
| [36] |
马克明, 傅伯杰, 黎晓亚, 等. 区域生态安全格局:概念与理论基础[J]. 生态学报, 2004, 24(4):761-768.
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |