 PDF(2052 KB)
PDF(2052 KB)


引种美国红枫在两种紫色土区的生长和光合特性比较
魏静, 谭星, 王昌盛, 闫瑞, 李林珂, 宁月, 刘芸
南京林业大学学报(自然科学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 48 ›› Issue (1) : 97-105.
 PDF(2052 KB)
PDF(2052 KB)
 PDF(2052 KB)
PDF(2052 KB)
引种美国红枫在两种紫色土区的生长和光合特性比较
Comparison of growth and photosynthetic characteristics of introduced Acer rubrum on two purple soils
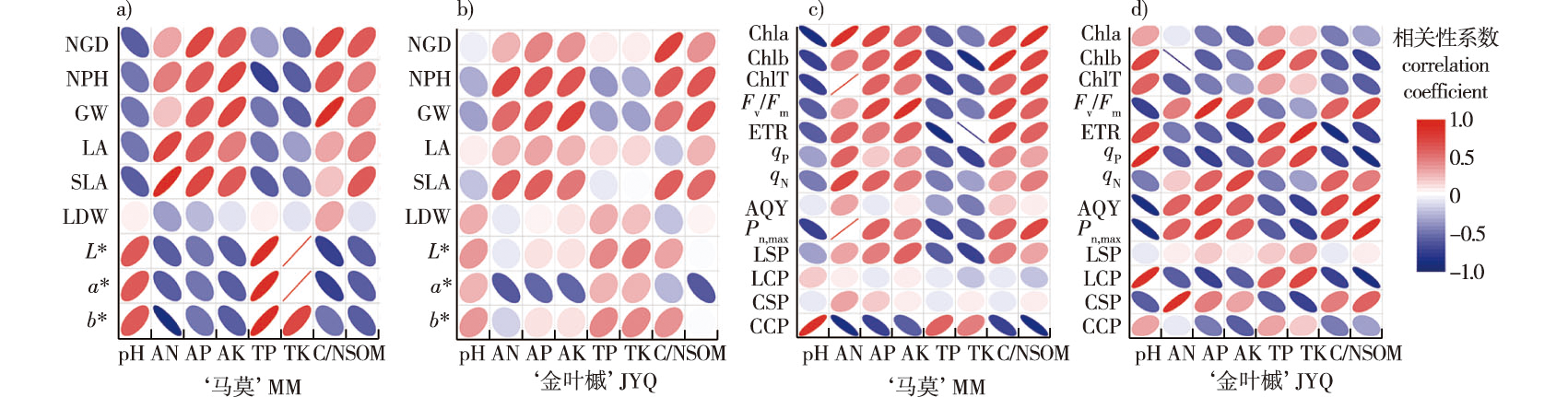
【目的】研究引种美国红枫(Acer rubrum)在两种紫色土区的生长和光合特性,为美国红枫在重庆地区的发展和适地适品种提供参考。【方法】以生长在重庆地区中性紫色土区(NS1)和石灰性紫色土区(AS2)的引种美国红枫‘马莫’(A. rubrum × freemanii ‘Marmo’)和‘金叶美国槭’(文中为‘金叶槭’A. rubrum‘Aurea’)为研究对象,在生长旺盛的夏季,对美国红枫在两种紫色土区生长、叶色和光合特性进行测定。【结果】①‘马莫’的净株高、冠幅、叶面积与土壤碱解氮(AN)、速效钾(AK)和有机质(SOM)含量、碳氮比(C/N)呈极显著正相关(P<0.05),与土壤pH呈极显著负相关(P<0.05)。中性和石灰性紫色土区‘马莫’株高较引种初期分别增加3.44、1.18 m,地径分别增加5.14、2.22 cm,引种前后叶面积、比叶面积差异显著(P<0.05);‘金叶槭’净株高、净地径、比叶面积无显著性差异。②中性紫色土区‘马莫’叶绿素a(Chla)、叶绿素b(Chlb)、总叶绿素(ChlT)、类胡萝卜素(Car)含量及色彩亮度(L*)、红绿色度(a*)、黄蓝色度(b*)、最大光化学效率(Fv/Fm)、电子传递效率(ETR)、实际光能捕获效率Y(Ⅱ)、光化学猝灭系数(qP)、最大净光合速率(Pn,max)、光饱和点(LSP)、表观量子效率(AQY)、叶片羧化速率(α)和光呼吸速率(Rp)显著高于石灰性紫色土区(P<0.05);与石灰性紫色土区相比,中性紫色土区‘金叶槭’Pn,max和胞间CO2浓度(CSP)显著增加、光补偿点(LCP)、CO2补偿点(CCP)显著降低(P<0.05),而两种紫色土‘金叶槭’Chla、ChlT含量及Chl a/b、L*、a*、b*、Fv/Fm、ETR、Y(Ⅱ)、qPLSP、AQY、暗呼吸速率(Rd)、CCP和Rp差异均不显著(P>0.05)。【结论】‘马莫’在中性紫色土区通过增加光能捕获面积提高PSⅡ光合电子传递速率和光合速率,降低有机物质的消耗,从而增强光合能力,表现出较强的生长适应性,而在石灰性紫色土区的表现较差,说明该品种对碱性紫色土壤的适应性一般;两种紫色土区‘金叶槭’的光合特性和生长均表现出较强的适应性。
【Objective】 The growth and photosynthetic characteristics responses of Acer rubrum following introduction to two kinds of purple soil were studied, to provide reference data for the development and use of a suitable variety of A. rubrum in the Chongqing area of China. 【Method】 A. rubrum ‘Marmo’ and ‘Aurea’ introduced into neutral purple soil (NS1) and callitic purple soil (AS2) were analyzed. Growth, leaf color, and photosynthetic characteristics of A. rubrum were compared in the two kinds of purple soil in summer, when their growth was vigorous. 【Result】 The net plant height, crown width, leaf area of ‘Marmo’ were positively correlated with alkali-hydrolyzed nitrogen, available potassium, carbon/nitrogen ratio, and organic matter, and negatively correlated with soil pH. Compared with the initial introduction, the plant height of ‘Marmo’ in the neutral and calcareous zones increased by 3.44 m and 1.18 m, respectively, ground diameter increased by 5.14 cm and 2.22 cm, respectively, and the leaf area and specific leaf area were significantly different. However, there were no significant differences of ‘Aurea’ in net plant height, net ground diameter, or specific leaf area. The chlorophyll a (ChlT), chlorophyll b (Chlb), total chlorophyll (ChlT), carotenoid (Car), L*, a* and b* values, maximum photochemical efficiency (Fv/Fm), electron transfer efficiency (ETR), light energy capture efficiency Y(Ⅱ), photochemical quenching coefficients (qP), leaf maximum net photosynthetic rate, light saturation point (LSP), apparent quantum yield (AQY), leaf carboxylation rate, leaf carboxylation rate (α), and photorespiration rate (Rp) of ‘Marmo’ in neutral zone were significantly higher than that of in calcareous zone (P<0.05). Compared with purple soil alkaline zone, Pn,max and intercellular CO2 concentration of (Cs) ‘Aurea, in the neutral zone were significantly increased, LCP, CO2 compensation point (CCP) were significantly decreased (P<0.05). Chla, ChlT, Chl a/b, L*, a*, b* Fv/Fm, ETR, Y(Ⅱ), qP, LSP, AQY, CCP, Rd and Rp of ‘Aurea’ in the neutral zone were not significantly different from those in the calcareous zone (P>0.05). 【Conclusion】 Among the two types of purple soil, ‘Marmo’ increased the photosynthetic electron transfer rate and photosynthetic rate of photosystem Ⅱ and reduced the consumption of organic matter by increasing the light energy capture area. The photosynthetic capacity was enhanced and growth was strong in the neutral region, while the performance of ‘Marmo’ was poor in the calcareous zone, indicating that this variety is not suitable for alkaline purple soil. The photosynthetic characteristics and growth of ‘Aurea’ showed strong adaptability to the two types of purple soil.
引种 / 美国红枫 / 生长适应性 / 光合特性 / 叶绿素荧光参数 / 叶色参数
introduction / Acer rubrum / growth adaptability / photosynthetic characteristics / chlorophyll fluorescence parameter / leaf color parameter
| [1] |
颜廷武. 不同种源美国红枫苗期光合特性研究[J]. 辽宁林业科技, 2014(6): 24-26.
|
| [2] |
何素芬, 钟栎, 何剑平. 美国红枫引种繁育与规模化栽培技术初报[J]. 农业科技与信息, 2016, 13(22):111,113.
|
| [3] |
吴雅琼, 刘婧, 汪贵斌, 等. 美国红枫的组织培养与快繁技术[J]. 北方园艺, 2016(20): 97-102.
|
| [4] |
何素芬, 吴戎, 顾大勤. 美国红枫硬枝扦插育苗试验研究[J]. 四川林业科技, 2014, 35(1): 61-62,88.
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
李力. 北美红枫呈色生理机制及叶色调控[D]. 重庆: 西南大学, 2016.
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
熊淑萍, 张娟娟, 杨阳, 等. 不同冬小麦品种在3种质地土壤中氮代谢特征及利用效率分析[J]. 植物生态学报, 2013, 37(7): 601-610.
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
丁武泉, 包兵, 李航, 等. 三峡库区消落区紫色土对重金属的吸附特征[J]. 生态与农村环境学报, 2007, 23(1):40-42,62.
|
| [11] |
袁贵琼, 刘芸, 邬静淳, 等. 模拟三峡库区消落带水淹对3类土壤中桑树和水桦生长的影响[J]. 西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 46(6): 65-74.
|
| [12] |
黄小辉, 刘芸, 李佳杏, 等. 模拟三峡库区消落带土壤干旱对桑树生理特性的影响[J]. 西南大学学报(自然科学版), 2013, 35(9): 127-132.
|
| [13] |
王峰, 陈玉真, 尤志明, 等. 不同类型茶园土壤团聚体组成特征及稳定性研究[J]. 茶叶科学, 2014, 34(2): 129-136.
|
| [14] |
张淑勇, 周泽福, 夏江宝, 等. 不同土壤水分条件下小叶扶芳藤叶片光合作用对光的响应[J]. 西北植物学报, 2007, 27(12): 2514-2521.
|
| [15] |
夏贵菊, 何彤慧, 赵永全, 等. 不同土壤类型对芦苇生长及光合特征的影响[J]. 西北植物学报, 2014, 34(6): 1252-1258.
|
| [16] |
闫小莉, 王德炉. 不同类型土壤栽培对苦丁茶树叶片生长和光合特性的影响[J]. 生态学报, 2019, 39(19): 7208-7217.
|
| [17] |
杨剑虹, 王成林, 代亨林. 土壤农化分析与环境监测[M]. 北京: 中国大地出版社, 2008.
|
| [18] |
苍晶, 赵会杰. 植物生理学实验教程[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2013: 57-59.
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
陈芳清, 郭成圆, 王传华, 等. 水淹对秋华柳幼苗生理生态特征的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 2008, 19(6): 1229-1233.
|
| [22] |
谢春, 周长芳, 龙水云, 等. 挺水植物与浮叶植物光合荧光特性的差异[J]. 生态学报, 2018, 38(7): 2493-2502.
|
| [23] |
白宇清, 谢利娟, 王定跃. 不同遮荫、土壤排水处理对毛棉杜鹃幼苗生长及光合特性的影响[J]. 林业科学, 2017, 53(2): 44-53.
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
陆燕元, 马焕成, 李昊民, 等. 土壤干旱对转基因甘薯光合曲线的响应[J]. 生态学报, 2015, 35(7): 2155-2160.
|
| [27] |
叶子飘, 赵则海. 遮光对三叶鬼针草光合作用和叶绿素含量的影响[J]. 生态学杂志, 2009, 28(1): 19-22.
|
| [28] |
王荣荣, 夏江宝, 杨吉华, 等. 贝壳砂生境干旱胁迫下杠柳叶片光合光响应模型比较[J]. 植物生态学报, 2013, 37(2): 111-121.
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
李威, 杨德光, 牟尧, 等. 去遮荫后东北红豆杉幼苗和幼树光合特性对比[J]. 林业科学, 2018, 54(2): 179-185.
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
王振夏, 魏虹, 吕茜, 等. 枫杨幼苗对土壤水分“湿-干”交替变化光合及叶绿素荧光的响应[J]. 生态学报, 2013, 33(3): 888-897.
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
饶立华, 蒋德安, 薛建明, 等. 钾营养对水稻光合器功能的效应与谷粒产量的影响[J]. 植物生理学报, 1989, 15(2): 191-197.
|
| [38] |
韩辉, 宫伟. 不同土壤酸碱度对紫花槭秋季叶色变化的影响[J]. 吉林农业, 2010(6): 76-80.
|
| [39] |
苏娓娓. 不同K+和pH水平对红叶石楠叶色和生理的影响[D]. 南京: 南京林业大学, 2011.
|
| [40] |
邓雪花, 喻阳华, 熊康宁, 等. 不同林龄花椒光合特性及对土壤养分的响应[J]. 森林与环境学报, 2022, 42(2): 149-157.
|
| [41] |
张黛静, 陈倩青, 宗洁静, 等. 增施有机肥对冬小麦同化物积累与分配的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 2019, 30(6): 1869-1876.
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |