 PDF(3468 KB)
PDF(3468 KB)


Prediction of potential distribution areas of the endangered Cathaya argyrophylla based on shared socio-economic pathways (SSPs) climate scenarios
LUO Chuying, SHE Jiyun, TANG Zichao
Journal of Nanjing Forestry University (Natural Sciences Edition) ›› 2024, Vol. 48 ›› Issue (1) : 161-168.
 PDF(3468 KB)
PDF(3468 KB)
 PDF(3468 KB)
PDF(3468 KB)
Prediction of potential distribution areas of the endangered Cathaya argyrophylla based on shared socio-economic pathways (SSPs) climate scenarios
【Objective】This study explored key factors affecting the occurrence of endangered Cathaya argyrophylla populations and predicted their potential distribution areas in the present and future, providing a theoretical basis for the conservation and introduction of C. argyrophylla natural resources. 【Method】Based on 41 sample sites of C. argyrophylla, the MaxEnt model was used to predict the potential distribution areas of C. argyrophylla under the current scenario by combining climate, topography, soil and radiation factor data, and to assess the effects of different environmental factors on the geographical distribution of C. argyrophylla. Also, future shared socio-economic pathways (SSPs) were used as climate data to predict future changes in the growth distribution areas of C. argyrophylla. 【Result】Under the current climate conditions, the core suitable area for C. argyrophylla is approximately 1.325 × 105 km2, accounting for approximately 1.38% of China’s land area. It has a cumulative contribution rate of 91.9% to the distribution of C. argyrophylla due to precipitation in the driest month, downward ultraviolet radiation, altitude, and the lowest temperature in the coldest month. They are the dominant factor affecting the geographical distribution of C. argyrophylla. If the survival probability is greater than 0.5 as the adaptation range, the main environmental conditions suitable for the survival of C. argyrophylla are: precipitation in the driest month is 18.03~215.63 mm, downward ultraviolet radiation is 1 070 728~1 437 806 W/m2, altitude is 493.68~1 731.10 m, and the lowest temperature in the coldest month is -1.01~4.05 ℃. In the future, under SSP1-2.6, SSP2-4.5, and SSP5-8.5, the core suitable areas for C. argyrophylla will increase. However, they will still be centered in Guizhou, Hunan, Guangxi, and Chongqing.【Conclusion】Precipitation during the driest month and downward ultraviolet radiation were the main factors influencing the potential distribution of C. argyrophylla. Under the three future climate scenarios, the core area suitable for C. argyrophylla showed an expanding trend. The expansion areas were mainly distributed in Yunnan, Zhejiang, Fujian and Guizhou. The intermediate development scenario (SSP2-4.5) was more suitable for the growth and reproduction of C. argyrophylla. This study provides an important theoretical basis for the conservation of C. argyrophylla planting resources.
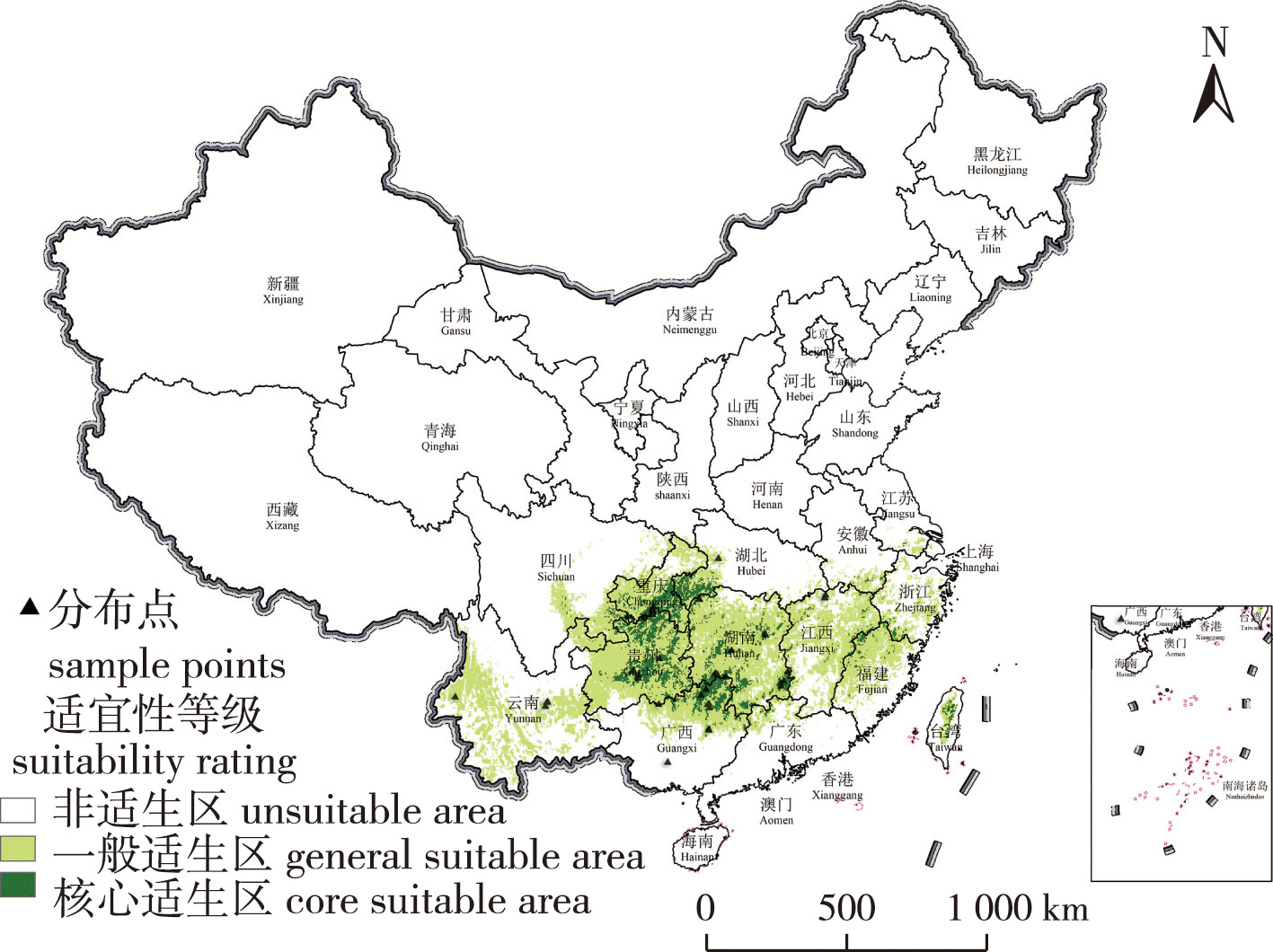
Cathaya argyrophylla / shared socio-economic pathways(SSPs) / potential distribution area / climatic factor / endangered plant
| [1] |
张明珠, 叶兴状, 刘益鹏, 等. 基于SSPs预测格木在中国的潜在地理分布[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2022, 44(4):54-65.
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
叶兴状, 张明珠, 赖文峰, 等. 基于MaxEnt优化模型的闽楠潜在适宜分布预测[J]. 生态学报, 2021, 41(20):8135-8144.
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
陈春谛. 被遗忘的城市“生境”:重庆市墙体自生植物调查分析[J]. 生态学报, 2020, 40(2):473-483.
|
| [6] |
刘鹏, 何万存, 黄小春, 等. 花榈木研究现状及保护对策[J]. 南方林业科学, 2017, 45(3):45-48.
|
| [7] |
刘冬, 刘顶鼎, 马丽, 等. 花榈木提取物对慢性不可预知应激小鼠认知损害的影响[J]. 生物化学与生物物理进展, 2020, 47(8):768-779.
|
| [8] |
杨军, 王婷, 许仕, 等. 珍稀濒危树种银杉的研究进展[J]. 中国园艺文摘, 2014, 30(12):53-55.
|
| [9] |
李乔明, 张耀尹, 冯育才, 等. 银杉播种苗木不同年份生长量研究[J]. 种子, 2019, 38(1):90-93.
|
| [10] |
谢宗强, 陈伟烈. 中国特有植物银杉的濒危原因及保护对策[J]. 植物生态学报, 1999, 23(1):1.
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
宋红敏, 张清芬, 韩雪梅, 等. CLIMEX:预测物种分布区的软件[J]. 昆虫知识, 2004, 41(4):379-387.
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
吕彤, 郭倩, 丁永霞, 等. 基于MaxEnt模型预测未来气候变化情景下中国区域水稻潜在适生区的变化[J]. 中国农业气象, 2022, 43(4):262-275.
|
| [15] |
邢丁亮, 郝占庆. 最大熵原理及其在生态学研究中的应用[J]. 生物多样性, 2011, 19(3):295-302.
|
| [16] |
陈禹衡, 吕一维, 殷晓洁. 气候变化下西南地区12种常见针叶树种适宜分布区预测[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 43(6): 113-120.
|
| [17] |
杨楠, 马东源, 钟雪, 等. 基于MaxEnt模型的四川王朗国家级自然保护区蓝马鸡栖息地适宜性评价[J]. 生态学报, 2020, 40(19):7064-7072.
|
| [18] |
韩淑敏, 闫伟, 杨雪栋, 等. 白榆在我国的潜在分布格局及未来变化[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2023, 47(3):103-110.
|
| [19] |
周炳江, 王玉洁, 马长乐, 等. 基于MaxEnt与ArcGIS的云南榧树潜在生境分析[J]. 生态学报, 2022, 42(11):4485-4493.
|
| [20] |
王茹琳, 李庆, 封传红, 等. 基于MaxEnt的西藏飞蝗在中国的适生区预测[J]. 生态学报, 2017, 37(24):8556-8566.
|
| [21] |
刘倩, 齐增湘, 周永, 等. 我国银杉潜在分布区预测及适宜性评价[J]. 安徽农学通报, 2019, 25(18):53-57.
|
| [22] |
冉巧, 卫海燕, 赵泽芳, 等. 气候变化对孑遗植物银杉的潜在分布及生境破碎度的影响[J]. 生态学报, 2019, 39(7):2481-2493.
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
侯沁文, 白海艳, 李云玲, 等. 马铃薯甲虫在中国的适生区[J]. 生态学杂志, 2020, 39(10):3311-3319.
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
刘维, 赵儒楠, 圣倩倩, 等. 矮牡丹在中国的地理分布及潜在分布区预测[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2021, 43(12):83-92.
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
赵儒楠, 何倩倩, 褚晓洁, 等. 气候变化下千金榆在我国潜在分布区预测[J]. 应用生态学报, 2019, 30(11):3833-3843.
|
| [29] |
龙莉, 高超, 杨瑞, 等. 贵州大沙河濒危植物银杉资源现状及保护策略[J]. 广东蚕业, 2022, 56(3):55-57.
|
| [30] |
李雪, 潘学军, 张文娥. UV辐射对植物多酚代谢的影响[J]. 山地农业生物学报, 2016, 35(6):54-60.
|
| [31] |
张旺锋, 樊大勇, 谢宗强, 等. 濒危植物银杉幼树对生长光强的季节性光合响应[J]. 生物多样性, 2005, 13(5):387-397.
|
| [32] |
陈凯军. 国宝“银杉”[J]. 林业与生态, 2020(7):F0004.
|
| [33] |
周满, 张昌文. 践行初心使命谱写绿色赞歌:记“银杉之父”罗仲春[J]. 林业与生态, 2020(12):22-23.
|
| [34] |
魏书精, 罗斯生, 罗碧珍, 等. 气候变化背景下森林火灾发生规律研究[J]. 林业与环境科学, 2020, 36(2):133-143.
|
| [35] |
姜大膀, 富元海.2 ℃全球变暖背景下中国未来气候变化预估[J]. 大气科学, 2012, 36(2):234-246.
|
| [36] |
张杰, 曹丽格, 李修仓, 等. IPCC AR5中社会经济新情景(SSPs)研究的最新进展[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2013, 9(3):225-228.
|
| [37] |
郑芊卉, 周春国, 韦海航, 等. 各国应对气候变化自主贡献目标及林业对策[J]. 世界林业研究, 2019, 32(2):1-6.
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |