 PDF(4527 KB)
PDF(4527 KB)


Prediction of potential suitable regions of Prunus pseudocerasus based on MaxEnt model under climate change
FU Chenlong, LI Meng, TIAN Changfen, SONG Yanfeng, YI Xiangui, WANG Xianrong
Journal of Nanjing Forestry University (Natural Sciences Edition) ›› 2024, Vol. 48 ›› Issue (4) : 235-242.
 PDF(4527 KB)
PDF(4527 KB)
 PDF(4527 KB)
PDF(4527 KB)
Prediction of potential suitable regions of Prunus pseudocerasus based on MaxEnt model under climate change
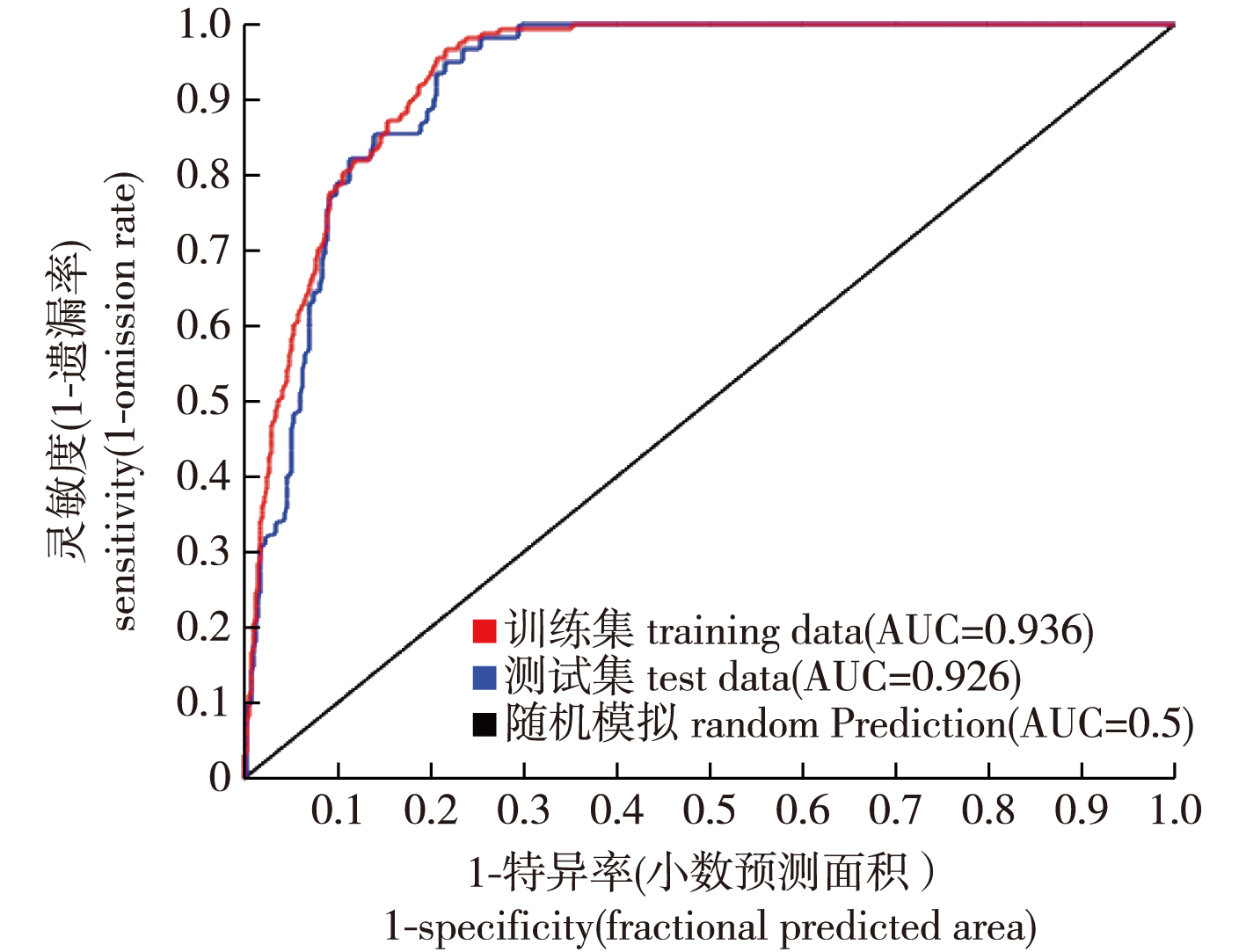
【Objective】Prunus pseudocerasus, one of the oldest cultivated species in China, is the focus of this study which predicts its suitable growth regions currently and in the future. This serves as a reference for understanding its growth habits and enhancing its cultivation.【Method】The MaxEnt model simulated the distribution of potential suitable areas for P. pseudocerasus under four climate scenarios (SSP126,SSP245,SSP370 and SSP585) at different times. This was based on geographic and environmental climate data. Important climatic variables influencing these areas were identified, and changes in potential suitable regions were analyzed.【Result】The accuracy of the predictions was validated using ROC analysis, achieving a high score of 0.936. Key climatic factors included annual precipitation, minimum temperature of the coldest month, and mean temperature of the warmest quarter. Soil factors did not significantly limit the distribution of P. pseudocerasus. Currently, suitable areas are primarily in the eastern, central and southwest China, with highly suitable regions in central and eastern Shandong, and southern Shaanxi. Climate change is expected to reduce these areas while creating new suitable regions in central Xizang and eastern Jilin.【Conclusion】Under future climate change scenarios, the potential suitable areas for P. pseudocerasus will become fragmented and shift towards higher latitudes and altitudes. These findings provide a theoretical basis for the conservation and industrial development of P. pseudocerasus in China.
Prunus pseudocerasus / potential suitable regions / protection of germplasm resources / MaxEnt model
| [1] |
World Meteorological Organization. State of the global climate 2020, provisional report[R]. Geneva: World Meteorological Organization, 2020.
|
| [2] |
中国科学院中国植物志编辑委员会. 中国植物志:第38卷[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1986:52.
Editorial Committee of Chinese Flora, Chinese Academy of Sciences. Flora of China: Volume 38[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1986:52.
|
| [3] |
刘长江, 刘美州. 山西侯马铸铜遗址种子类遗物的鉴定[M]. 北京: 文物出版社, 1993:65-71.
|
| [4] |
董渭雪. 樱桃黄酮组分及降尿酸作用研究[D]. 汉中: 陕西理工大学, 2020.
|
| [5] |
王月华. 江苏省栽培果树品种资源特征与生态适应性分析[D]. 南京: 南京农业大学, 2009.
|
| [6] |
陈涛, 李良, 张静, 等. 中国樱桃种质资源的考察、收集和评价[J]. 果树学报, 2016, 33(8):917-933.
|
| [7] |
刘针杉, 何文, 王燕, 等. 中国樱桃‘黑珍珠’离体的培养技术[J]. 分子植物育种, 2019, 17(24):8215-8220.
|
| [8] |
沈均波. 浙江省中国樱桃控根栽培技术[J]. 现代农业科技, 2021(22):55-56,64.
|
| [9] |
王建华. 中国樱桃‘黑珍珠’大棚矮冠栽培表现及技术[J]. 中国果树, 2020(4):85-87,142.
|
| [10] |
徐养诚, 刘孝贤, 王婷, 等. 基于MaxEnt模型的菜豆象全球潜在适生区预测[J]. 生物安全学报, 2021, 30(3):213-219.
|
| [11] |
王文婷, 杨婷婷, 金磊, 等. 未来气候变化下两种红景天植物的脆弱性[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(12):1620-1628.
|
| [12] |
高健, 赵辉. 基于MaxEnt模型评估槭属鸡爪槭组物种的空间分布[J]. 西北林学院学报, 2021, 36(1):163-167,265.
|
| [13] |
林丽, 晋玲, 王振恒, 等. 气候变化背景下藏药黑果枸杞的潜在适生区分布预测[J]. 中国中药杂志, 2017, 42(14):2659-2669.
|
| [14] |
杨宏, 董京京, 吴桐, 等. 基于MaxEnt模型的迎春樱桃潜在适生区预测[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2023, 47(4):131-138.
|
| [15] |
周佩, 钱增强, 陈克克, 等. 气候变化背景下费菜在中国适生区分布预测[J]. 中药材, 2015, 38(7):1379-1383.
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
张丽霞, 陈晓龙, 辛晓歌. CMIP6情景模式比较计划(ScenarioMIP)概况与评述[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2019, 15(5):519-525.
|
| [18] |
姜彤, 吕嫣冉, 黄金龙, 等. CMIP6模式新情景(SSP-RCP)概述及其在淮河流域的应用[J]. 气象科技进展, 2020, 10(5):102-109.
|
| [19] |
王运生, 谢丙炎, 万方浩, 等. ROC曲线分析在评价入侵物种分布模型中的应用[J]. 生物多样性, 2007, 15(4):365-372.
|
| [20] |
吴晓萌, 叶冬梅, 白玉娥, 等. 基于MaxEnt模型的中国白杄分布格局及未来变化[J]. 西北植物学报, 2022, 42(1):162-172.
|
| [21] |
麻亚鸿. 基于最大熵模型(MaxEnt)和地理信息系统(ArcGIS)预测藓类植物的地理分布范围:以广西花坪自然保护区为例[D]. 上海: 上海师范大学, 2013.
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
孔维尧, 李欣海, 邹红菲. 最大熵模型在物种分布预测中的优化[J]. 应用生态学报, 2019, 30(6):2116-2128.
|
| [25] |
朱耿平, 乔慧捷. MaxEnt模型复杂度对物种潜在分布区预测的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2016, 24(10):1189-1196.
|
| [26] |
童晓利, 韩金龙, 唐冬兰, 等. 南京地区中国樱桃发展现状与栽培建议[J]. 江苏农业科学, 2019, 47(8):165-167.
|
| [27] |
曹福祥, 徐庆军, 曹受金, 等. 全球变暖对物种分布的影响研究进展[J]. 中南林业科技大学学报, 2008, 28(6):86-89.
|
| [28] |
吴建国, 吕佳佳. 气候变化对我国干旱区分布及其范围的潜在影响[J]. 环境科学研究, 2009, 22(2):199-206.
|
| [29] |
张兴旺, 李垚, 方炎明. 麻栎在中国的地理分布及潜在分布区预测[J]. 西北植物学报, 2014, 34(8):1685-1692.
|
| [30] |
袁峰. 冬虫夏草居群谱系地理与适生区分布研究[D]. 昆明: 云南大学, 2015.
|
| [31] |
李垚, 张兴旺, 方炎明. 小叶栎分布格局对末次盛冰期以来气候变化的响应[J]. 植物生态学报, 2016, 40(11):1164-1178.
|
| [32] |
韩金龙, 童晓利, 曹荣祥, 等. 中国樱桃品种在南京地区的引种试验[J]. 安徽农业科学, 2022, 50(3):53-55.
|
| [33] |
吴延军, 陈锦宇, 赵新军, 等. 中国樱桃新品种‘紫晶’[J]. 园艺学报, 2020, 47(S2):2894-2895.
|
| [34] |
刘珠琴, 汪国云, 汪国武, 等. 中国樱桃新品种梁弄红的选育[J]. 果树学报, 2022, 39(11):2201-2204.
|
| [35] |
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |